给定一个由N 个节点和M 个边组成的加权无向图,任务是通过将一条边的权重减半来找到两个节点A和B之间的最短距离。
例子:
Input: A = 0, B = 2, Below is the graph
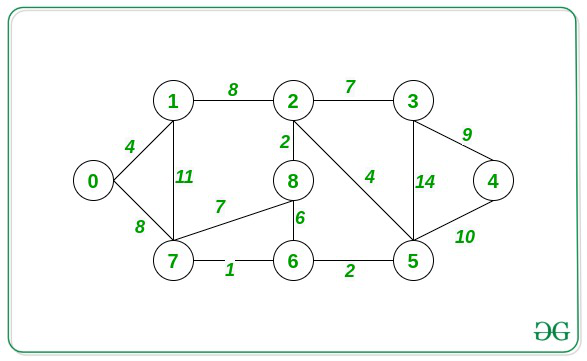
Output: 8
Explaination:
After reducing the weight of the edge connecting 1 and 2 by half modifies its new weight to 4. Now, the shortest distance to reach 2 from 0 through the path 0 -> 1 -> 2 is (4 + 4) = 8.
Therefore, print 8.
方法:给定的问题可以通过维护两个数组来解决,最短距离数组以源节点为 A 存储所有节点到A的最短距离,同样最短距离数组以源节点为B 。可以使用 Dijkstra 算法计算这些数组。请按照以下步骤解决上述问题:
- 使用 Dijkstra 算法将每个节点到A的最短距离存储到数组disA[] 中。
- 使用 Dijkstra 算法将每个节点到B的最短距离存储到数组disB[] 中。
- 假设边i = {u i , v i , wt i },即边i将节点u i连接到v i并且权重为wt i 。
- 现在,迭代所有边,并为每条边跟踪函数:
f(edgei) = min( disA[ui] + disB[vi], disA[vi] + disB[ui]) + (wti/2).
- 上述关系给出了f(edge)的最小值,即由此产生的最短距离。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++14
// C++ program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Stores the input Graph
vector > graph[100001];
// Stores edges of input Graph
vector > edges;
// Function to input Edges
void add_edge(int u, int v, int w)
{
graph[u].push_back({ v, w });
graph[v].push_back({ u, w });
edges.push_back({ u, v, w });
}
// Function to find the shortest distance
// to each node from the src node using
// Dijkstra’s Algorithm
vector dijsktras(int src, int N)
{
// Stores the shortest distance of
// each node form src node
vector dis(N, INT_MAX);
vector vis(N, false);
// Stores the node and currrent
// minimum distance in a heap
priority_queue,
vector >,
greater > >
pq;
pq.push({ 0, src });
dis[src] = 0;
// BFS for single source shortest
// path algorithm
while (!pq.empty()) {
// Top of the PQ
auto cur = pq.top();
pq.pop();
// Store the node and weight
int node = cur.second;
int weight = cur.first;
// If node is already visited
if (vis[node])
continue;
vis[node] = true;
// Traverse the adjacency list
// of the node
for (auto child : graph[node]) {
// If the distance obtained
// from parent is less than
// the current minimum
// distance stored for child
if (dis[child.first]
> child.second + weight) {
dis[child.first] = weight
+ child.second;
// Push the next pair
// in the PQ
pq.push({ dis[child.first],
child.first });
}
}
}
// Return the maximum distance
return dis;
}
// Function to find shortest distance
// between two nodes by reducing any
// one weight of an edge by half
int shortestDistance(int N, int M,
int A, int B)
{
// Stores the the shortest distance
// of each node from A
vector disA = dijsktras(A, N);
// Stores the the shortest distance
// of each node from B
vector disB = dijsktras(B, N);
int ans = disA[B];
for (auto edge : edges) {
int u = edge[0], v = edge[1];
int weight = edge[2];
// Calculate the value of f(edge)
// for the current edge
int cur = min(disA[u] + disB[v],
disA[v] + disB[u])
+ (weight / 2);
// Keep track of the mimimum of
// f(edge) for all edges
ans = min(ans, cur);
}
// Return Answer
return ans;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int N = 9, M = 14, A = 0, B = 2;
// Create a Graph
add_edge(0, 1, 4);
add_edge(1, 2, 8);
add_edge(2, 3, 7);
add_edge(3, 4, 9);
add_edge(4, 5, 10);
add_edge(5, 6, 2);
add_edge(6, 7, 1);
add_edge(7, 0, 8);
add_edge(1, 7, 11);
add_edge(7, 8, 7);
add_edge(2, 8, 2);
add_edge(6, 8, 6);
add_edge(2, 5, 4);
add_edge(3, 5, 14);
// Function Call
cout << shortestDistance(N, M, A, B);
return 0;
} 输出:
8
时间复杂度: O(M*log N)
辅助空间: O(N + M)
如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。