给定完整的二叉树,任务是按顺时针遍历顺序打印元素。
树的顺时针遍历定义为:
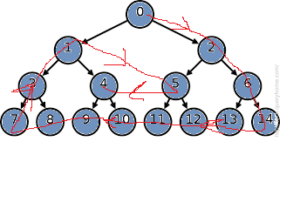
For the above binary tree, the Clockwise Traingular traversal will be
0, 2, 6, 14, 13, 12, 11, 10, 9, 8, 7, 3, 1, 5, 4
例子:
Input:
1
/ \
2 3
/ \ / \
4 5 6 7
/ \ /\
8 9 10 11
Output: 1, 3, 7, 11, 10, 9, 8, 4, 2, 6, 5
Input:
1
/ \
2 3
Output: 1, 3, 2
方法:
创建一个向量tree [] ,其中tree [i]将在i级别存储树的所有节点。取一个整数k ,它跟踪我们正在遍历哪个级别的其他整数和周期,在其中跟踪已经完成了多少个周期。现在,开始打印尚未遍历的最右边剩余节点的节点,并继续向下移动直到您到达尚未遍历的最后一层,现在从右向左打印此级别,然后将打印的最左边剩余的最左边的元素打印每个级别都从最后一个级别开始,直到移动到尚未遍历所有元素的最高级别,现在再次执行相同的操作,直到尚未遍历所有元素。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program for the
// above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Function to create an
// edge between two vertices
void addEdge(int a, int b, vector tree[])
{
// Add a to b's list
tree[a].push_back(b);
// Add b to a's list
tree[b].push_back(a);
}
// Function to create
// complete binary tree
void createTree(int n, vector tree[])
{
for (int i = 1;; i++) {
// Adding edge to
// a binary tree
int c = 0;
if (2 * i <= n) {
addEdge(i, 2 * i, tree);
c++;
}
if (2 * i + 1 <= n) {
addEdge(i, 2 * i + 1, tree);
c++;
}
if (c == 0)
break;
}
}
// Modified Breadth-First Function
void bfs(int node, vector tree[], bool vis[],
int level[], vector nodes[], int& maxLevel)
{
// Create a queue of
// {child, parent}
queue > qu;
// Push root node in the front of
// the queue and mark as visited
qu.push({ node, 0 });
nodes[0].push_back(node);
vis[node] = true;
level[1] = 0;
while (!qu.empty()) {
pair p = qu.front();
// Dequeue a vertex
// from queue
qu.pop();
vis[p.first] = true;
// Get all adjacent vertices of the dequeued
// vertex s. If any adjacent has not
// been visited then enqueue it
for (int child : tree[p.first]) {
if (!vis[child]) {
qu.push({ child, p.first });
level[child] = level[p.first] + 1;
maxLevel = max(maxLevel, level[child]);
nodes[level[child]].push_back(child);
}
}
}
}
// Function to display the pattern
void display(vector nodes[], int maxLevel)
{
// k represents the level no.
// cycle represents how many
// cycles has been completed
int k = 0, cycle = 0;
// While there are nodes
// left to traverse
while (cycle - 1 <= maxLevel / 2) {
// Traversing rightmost element
// in each cycle as we move down
while (k < maxLevel - cycle) {
int j = nodes[k].size() - 1;
cout << nodes[k][j - cycle] << " ";
k++;
}
// Traversing each element of remaing
// last level from right to left
if (k == maxLevel - cycle) {
int j = nodes[k].size() - 1;
for (j -= cycle; j >= cycle; j--)
cout << nodes[k][j] << " ";
}
k--;
// Traversing leftmost remaing element
// in each cycle as we move up
while (k > cycle) {
cout << nodes[k][cycle] << " ";
k--;
}
// No of cycles
// completed
cycle++;
// updating from which level to
// start new cycle
k = cycle + 1;
}
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
// Number of vertices
int n = 12;
const int sz = 1e5;
int maxLevel = 0;
vector tree[sz + 1];
bool vis[sz + 1];
int level[sz + 1];
vector nodes[sz + 1];
createTree(n, tree);
bfs(1, tree, vis, level, nodes, maxLevel);
display(nodes, maxLevel);
return 0;
} Python3
# Python3 program for the
# above approach
# Function to create an
# edge between two vertices
def addEdge(a, b):
# Add a to b's list
tree[a].append(b);
# Add b to a's list
tree[b].append(a);
# Function to create
# complete binary tree
def createTree(n):
i = 1
while True:
# Adding edge to
# a binary tree
c = 0;
if (2 * i <= n):
addEdge(i, 2 * i);
c += 1;
if (2 * i + 1 <= n):
addEdge(i, 2 * i + 1);
c += 1
if (c == 0):
break;
i += 1
# Modified Breadth-First
# Function
def bfs(node, maxLevel):
# Create a queue of
# {child, parent}
qu = []
# Push root node in the
# front of the queue and
# mark as visited
qu.append([node, 0]);
nodes[0].append(node);
vis[node] = True;
level[1] = 0;
while (len(qu) != 0):
p = qu[0];
# Dequeue a vertex
# from queue
qu.pop(0);
vis[p[0]] = True;
# Get all adjacent vertices
# of the dequeued vertex s.
# If any adjacent has not
# been visited then enqueue it
for child in tree[p[0]]:
if (not vis[child]):
qu.append([child, p[0]]);
level[child] = level[p[0]] + 1;
maxLevel = max(maxLevel,
level[child]);
nodes[level[child]].append(child);
return maxLevel
# Function to display
# the pattern
def display(maxLevel):
# k represents the level no.
# cycle represents how many
# cycles has been completed
k = 0
cycle = 0;
# While there are nodes
# left to traverse
while (cycle - 1 <= maxLevel // 2):
# Traversing rightmost element
# in each cycle as we move down
while(k < maxLevel - cycle):
j = len(nodes[k]) - 1;
print(nodes[k][j - cycle],
end = ' ')
k += 1
# Traversing each element of
# remaining last level from right
# to left
if (k == maxLevel - cycle):
j = len(nodes[k]) - 1 - cycle;
while(j >= cycle):
print(nodes[k][j],
end = ' ')
j -= 1
k -= 1
# Traversing leftmost remaining
# element in each cycle as we
# move up
while (k > cycle):
print(nodes[k][cycle],
end = ' ')
k -= 1
# No of cycles
# completed
cycle += 1
# updating from which
# level to start new cycle
k = cycle + 1;
# Driver code
if __name__=="__main__":
# Number of vertices
n = 12;
sz = 100005;
maxLevel = 0;
tree = [[] for i in range(sz + 1)]
vis = [False for i in range(sz + 1)]
level = [0 for i in range(sz + 1)]
nodes = [[] for i in range(sz + 1)]
createTree(n);
maxLevel = bfs(1, maxLevel);
display(maxLevel);
# This code is contributed by Rutvik_56输出:
1 3 7 12 11 10 9 8 4 2 6 5
时间复杂度: O(n)
如果您希望与行业专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅《 Geeks现场课程》和《 Geeks现场课程美国》。