Pascal三角形的一个有用的应用是组合的计算。寻找n C r的公式是n! / r! *(n – r)!这也是Pascal三角形单元格的公式。
帕斯卡的三角形:
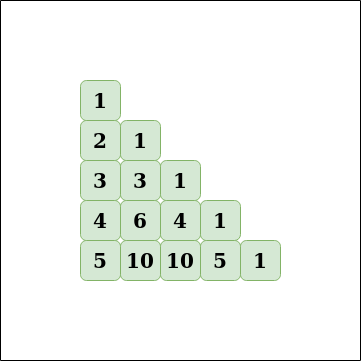
Input: n = 5, r = 3
Output: 10
Explanation:
n! / r! * (n - r)! = 5! / 3! * (2!) = 120 / 12 = 10
Input: n = 7, r = 2
Output: 21
Explanation:
n! / r! * (n - r)! = 7! / 5! * (2!) = 42 / 2 = 21的方法:我们的想法是帕斯卡三角存储在随后的矩阵的值n C R将是单元格的值在第n行和r列。
要创建帕斯卡三角形,请使用以下两个公式:
- n C 0 = 1 ,从一组n个元素中选择0个元素的方式为0
- n C r = n-1 C r-1 + n-1 C r ,从一组n个元素中选择r个元素的方法数量是从n-1个元素中选择r-1个元素的方法和选择方法的总和n-1个元素中的r个元素。
想法是使用子问题的值来计算较大值的答案。例如,要计算n C r ,请使用n-1 C r-1和n-1 C r的值。因此,DP可用于预处理范围内的所有值。
算法:
- 创建一个大小为1000 * 1000的矩阵,分配基本案例的值,即运行一个从0到1000的循环,并分配matrix [i] [0] = 1, n C 0 = 1
- 从i = 1到1000运行一个嵌套循环(外循环),从j = 1到i + 1运行内部循环。
- 使用公式n C r = n为每个元素(i,j)分配矩阵[i] [j] =矩阵[i-1] [j-1] +矩阵[i-1] [j]的值-1 C r-1 + n-1 C r
- 填充矩阵后,将n C r的值作为矩阵[n] [r]
执行:
C++
// C++ implementation of the approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Initialize the matrix with 0
int l[1001][1001] = { 0 };
void initialize()
{
// 0C0 = 1
l[0][0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < 1001; i++) {
// Set every nCr = 1 where r = 0
l[i][0] = 1;
for (int j = 1; j < i + 1; j++) {
// Value for the current cell of Pascal's triangle
l[i][j] = (l[i - 1][j - 1] + l[i - 1][j]);
}
}
}
// Function to return the value of nCr
int nCr(int n, int r)
{
// Return nCr
return l[n][r];
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
// Build the Pascal's triangle
initialize();
int n = 8;
int r = 3;
cout << nCr(n, r);
}
// This code is contributed by ihritik Java
// Java implementation of the approach
class GFG {
// Initialize the matrix with 0
static int l[][] = new int[1001][1001];
static void initialize()
{
// 0C0 = 1
l[0][0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < 1001; i++) {
// Set every nCr = 1 where r = 0
l[i][0] = 1;
for (int j = 1; j < i + 1; j++) {
// Value for the current cell of Pascal's triangle
l[i][j] = (l[i - 1][j - 1] + l[i - 1][j]);
}
}
}
// Function to return the value of nCr
static int nCr(int n, int r)
{
// Return nCr
return l[n][r];
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Build the Pascal's triangle
initialize();
int n = 8;
int r = 3;
System.out.println(nCr(n, r));
}
}
// This code is contributed by ihritikPython3
# Python3 implementation of the approach
# Initialize the matrix with 0
l = [[0 for i in range(1001)] for j in range(1001)]
def initialize():
# 0C0 = 1
l[0][0] = 1
for i in range(1, 1001):
# Set every nCr = 1 where r = 0
l[i][0] = 1
for j in range(1, i + 1):
# Value for the current cell of Pascal's triangle
l[i][j] = (l[i - 1][j - 1] + l[i - 1][j])
# Function to return the value of nCr
def nCr(n, r):
# Return nCr
return l[n][r]
# Driver code
# Build the Pascal's triangle
initialize()
n = 8
r = 3
print(nCr(n, r))C#
// C# implementation of the approach
using System;
class GFG {
// Initialize the matrix with 0
static int[, ] l = new int[1001, 1001];
static void initialize()
{
// 0C0 = 1
l[0, 0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < 1001; i++) {
// Set every nCr = 1 where r = 0
l[i, 0] = 1;
for (int j = 1; j < i + 1; j++) {
// Value for the current cell of Pascal's triangle
l[i, j] = (l[i - 1, j - 1] + l[i - 1, j]);
}
}
}
// Function to return the value of nCr
static int nCr(int n, int r)
{
// Return nCr
return l[n, r];
}
// Driver code
public static void Main()
{
// Build the Pascal's triangle
initialize();
int n = 8;
int r = 3;
Console.WriteLine(nCr(n, r));
}
}
// This code is contributed by ihritik输出:
56复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度: O(1)。
所有对的值都是预先计算的,因此回答查询的时间为O(1),尽管预计算会花费一些时间,但理论上预计算会花费固定的时间。 - 空间复杂度: O(1)。
需要恒定的空间。
如果您希望与行业专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅《 Geeks现场课程》和《 Geeks现场课程美国》。