给定一个大小为n的数组,任务是找到使该数组的所有元素可被4整除的最小步骤数。一个步骤定义为从数组中删除任何两个元素,然后将这些元素的总和相加到阵列。
例子:
Input: array = {1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3, 8}
Output: 3
Explanation:
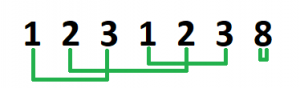
As we can see in the image,
combining array[0] and array[2] makes it 4. Similarly for array[1] and array[4] as well as array[3] and array[5]. array[6] is already divisible by 4. So by doing 3 steps, all the elements in the array become divisible by 4.
Input: array = {12, 31, 47, 32, 93, 24, 61, 29, 21, 34}
Output: 4
方法:这里的想法是将数组中的所有元素转换为模数4。首先,数组中所有元素的总和应被4整除。如果不能,则无法完成此任务。
- 初始化大小为4到0的数组模数。
- 将计数器计数初始化为0,以跟踪完成的步骤数。
- 遍历输入数组并获取每个元素的模数4。
- 将模数数组中mod 4值的值增加1。
- 模数[0]是已经被4整除的元素的计数。因此,无需将它们与任何其他元素配对。
- 可以将模数[1]和模数[3]元素组合在一起,得到一个可被4整除的数字。因此,将计数递增至两者的最小值。
- 可以将模数[2]的每2个元素进行组合,以得到可除以4的元素。
- 对于其余元素,将值模数[2]递增模数[1]和模数[3]的一半。
- 现在,以一半模数[2]递增计数。之所以取一半,是因为每两个元素都合并为一个。
- count的最终值是转换输入数组可被4整除的所有元素所需的步骤数。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
#include
using namespace std;
int getSteps(int arr[], int n)
{
// Count to keep track of the
// number of steps done.
int count = 0;
// Modulus array to store all elements mod 4
int modulus[4] = { 0 };
// sum to check if given task is possible
int sum = 0;
// Loop to store all elements mod 4
// and calculate sum;
int i;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
int mod = arr[i] % 4;
sum += mod;
modulus[mod]++;
}
// If sum is not divisible by 4,
// not possible
if (sum % 4 != 0)
{
return -1;
}
else
{
// Find minimum of modulus[1] and modulus[3]
// and increment the count by the minimum
if (modulus[1] > modulus[3])
{
count += modulus[3];
}
else
{
count += modulus[1];
}
// Update the values in modulus array.
modulus[1] -= count;
modulus[3] -= count;
// Use modulus[2] to pair remaining elements.
modulus[2] += modulus[1] / 2;
modulus[2] += modulus[3] / 2;
// incrememnt count to half of remaining
// modulus[1] or modulus of [3] elements.
count += modulus[1] / 2;
count += modulus[3] / 2;
// increment count by half of modulus[2]
count += modulus[2] / 2;
return count;
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// size of array
int n = 7;
// input array
int arr[] = { 1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3, 8 };
int count = getSteps(arr, n);
cout << count;
}
// This code is contributed
// by Akanksha Rai C
#include
#include
int getSteps(int arr[], int n)
{
// Count to keep track of the number of steps done.
int count = 0;
// Modulus array to store all elements mod 4
int modulus[4] = { 0 };
// sum to check if given task is possible
int sum = 0;
// Loop to store all elements mod 4 and calculate sum;
int i;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int mod = arr[i] % 4;
sum += mod;
modulus[mod]++;
}
// If sum is not divisible by 4, not possible
if (sum % 4 != 0) {
return -1;
}
else {
// Find minimum of modulus[1] and modulus[3]
// and increment the count by the minimum
if (modulus[1] > modulus[3]) {
count += modulus[3];
}
else {
count += modulus[1];
}
// Update the values in modulus array.
modulus[1] -= count;
modulus[3] -= count;
// Use modulus[2] to pair remaining elements.
modulus[2] += modulus[1] / 2;
modulus[2] += modulus[3] / 2;
// incrememnt count to half of remaining
// modulus[1] or modulus of [3] elements.
count += modulus[1] / 2;
count += modulus[3] / 2;
// increment count by half of modulus[2]
count += modulus[2] / 2;
return count;
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// size of array
int n = 7;
// input array
int arr[] = { 1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3, 8 };
int count = getSteps(arr, n);
printf("%d", count);
} Java
// Java program for the above approach
class GFG
{
static int getSteps(int arr[], int n)
{
// Count to keep track of the number of steps done.
int count = 0;
// Modulus array to store all elements mod 4
int modulus[] = new int[4];
// sum to check if given task is possible
int sum = 0;
// Loop to store all elements
// mod 4 and calculate sum;
int i;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
int mod = arr[i] % 4;
sum += mod;
modulus[mod]++;
}
// If sum is not divisible by 4, not possible
if (sum % 4 != 0)
{
return -1;
}
else {
// Find minimum of modulus[1] and modulus[3]
// and increment the count by the minimum
if (modulus[1] > modulus[3])
{
count += modulus[3];
}
else
{
count += modulus[1];
}
// Update the values in modulus array.
modulus[1] -= count;
modulus[3] -= count;
// Use modulus[2] to pair remaining elements.
modulus[2] += modulus[1] / 2;
modulus[2] += modulus[3] / 2;
// incrememnt count to half of remaining
// modulus[1] or modulus of [3] elements.
count += modulus[1] / 2;
count += modulus[3] / 2;
// increment count by half of modulus[2]
count += modulus[2] / 2;
return count;
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// size of array
int n = 7;
// input array
int arr[] = { 1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3, 8 };
int count = getSteps(arr, n);
System.out.printf("%d", count);
}
}
// This code has been contributed by 29AjayKumarPython3
# Python 3 program for the above approach
def getSteps(arr, n):
# Count to keep track of the
# number of steps done.
count = 0
# Modulus array to store all elements mod 4
modulus = [0 for i in range(4)]
# Sum to check if given task is possible
Sum = 0
# Loop to store all elements mod 4
# and calculate Sum
i = 0
for i in range(n):
mod = arr[i] % 4
Sum += mod
modulus[mod] += 1
# If Sum is not divisible by 4,
# not possible
if (Sum % 4 != 0):
return -1
else:
# Find minimum of modulus[1] and modulus[3]
# and increment the count by the minimum
if (modulus[1] > modulus[3]):
count += modulus[3]
else:
count += modulus[1]
# Update the values in modulus array.
modulus[1] -= count
modulus[3] -= count
# Use modulus[2] to pair remaining elements.
modulus[2] += modulus[1] // 2
modulus[2] += modulus[3] // 2
# incrememnt count to half of remaining
# modulus[1] or modulus of [3] elements.
count += modulus[1] // 2
count += modulus[3] // 2
# increment count by half of modulus[2]
count += modulus[2] // 2
return count
# Driver Code
# size of array
n = 7
# input array
arr = [1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3, 8]
count = getSteps(arr, n)
print(count)
# This code is contributed by mohit kumarC#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
class GFG
{
static int getSteps(int []arr, int n)
{
// Count to keep track of the number of steps done.
int count = 0;
// Modulus array to store all elements mod 4
int []modulus = new int[4];
// sum to check if given task is possible
int sum = 0;
// Loop to store all elements
// mod 4 and calculate sum;
int i;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
int mod = arr[i] % 4;
sum += mod;
modulus[mod]++;
}
// If sum is not divisible by 4, not possible
if (sum % 4 != 0)
{
return -1;
}
else
{
// Find minimum of modulus[1] and modulus[3]
// and increment the count by the minimum
if (modulus[1] > modulus[3])
{
count += modulus[3];
}
else
{
count += modulus[1];
}
// Update the values in modulus array.
modulus[1] -= count;
modulus[3] -= count;
// Use modulus[2] to pair remaining elements.
modulus[2] += modulus[1] / 2;
modulus[2] += modulus[3] / 2;
// incrememnt count to half of remaining
// modulus[1] or modulus of [3] elements.
count += modulus[1] / 2;
count += modulus[3] / 2;
// increment count by half of modulus[2]
count += modulus[2] / 2;
return count;
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// size of array
int n = 7;
// input array
int []arr = { 1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3, 8 };
int count = getSteps(arr, n);
Console.Write("{0}", count);
}
}
// This code contributed by Rajput-JiPHP
$modulus[3])
{
$count += $modulus[3];
}
else
{
$count += $modulus[1];
}
// Update the values in modulus array.
$modulus[1] -= $count;
$modulus[3] -= $count;
// Use modulus[2] to pair remaining elements.
$modulus[2] += (int)($modulus[1] / 2);
$modulus[2] += (int)($modulus[3] / 2);
// incrememnt count to half of remaining
// modulus[1] or modulus of [3] elements.
$count += (int)($modulus[1] / 2);
$count += (int)($modulus[3] / 2);
// increment count by half of modulus[2]
$count += (int)($modulus[2] / 2);
return $count;
}
}
// Driver Code
// size of array
$n = 7;
// input array
$arr = array( 1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3, 8 );
$count = getSteps($arr, $n);
print($count);
// This code contributed by mits
?>Javascript
输出:
3如果您希望与行业专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅《 Geeks现场课程》和《 Geeks现场课程美国》。