从Python执行 PostgreSQL CRUD 操作
DDL 由创建、读取、更新、删除( CRUD ) 操作组成,这些操作构成了任何SQL数据库系统的主干。让我们讨论如何使用Python在 PostgreSQL 数据库上执行 CRUD 操作。 Pyscopg2是最首选的模式,广泛用于使用Python连接 PostgreSQL 数据库。 Pyscopg2 是一个数据库 API,它是一个管理连接池的 PostgreSQL 兼容驱动程序。
在本文中,我们将介绍如何在Python中使用 SQLAlchemy 连接到 PostgreSQL 数据库,并了解如何对 PostgreSQL 数据库执行 CRUD 操作的过程。
与 PostgreSQL 数据库建立连接
作为第一步,使用Psycopg2的connect()函数与现有数据库建立连接。
Python3
from psycopg2 import connect
# declare the connection string specifying
# the host name database name
# use name and password
conn_string = "host='host_name' \
dbname='database_name' user='user_name'\
password='your_password'"
# use connect function to establish the connection
conn = connect(conn_string)Python3
import psycopg2
# Establishing the connection
conn = psycopg2.connect(
database="databasename",
user='username',
password='password',
host='hostname',
port='5432'
)
# Creating a cursor object using the
# cursor() method
cursor = conn.cursor()
# Doping EMPLOYEE table if already exists.
cursor.execute("DROP TABLE IF EXISTS publisher")
# Creating table as per requirement
sql = '''CREATE TABLE PUBLISHER(
publisher_id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
publisher_name VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
publisher_estd INT,
publsiher_location VARCHAR(255),
publsiher_type VARCHAR(255)
)'''
cursor.execute(sql)
print("Table created successfully........")
conn.commit()
# Closing the connection
conn.close()Python3
import psycopg2
try:
connection = psycopg2.connect(user="username",
password="password",
host="127.0.0.1",
port="5432",
database="databasename")
cursor = connection.cursor()
postgres_insert_query = """ INSERT INTO publisher(publisher_id,
publisher_name, publisher_estd, publsiher_location, publsiher_type)
VALUES (%s,%s,%s,%s,%s)"""
record_to_insert = [(1, 'Packt', 1950,
'chennai', 'books'),
(2, 'Springer', 1950,
'chennai', 'books'),
(3, 'Springer', 1950,
'chennai', 'articles'),
(4, 'Oxford', 1950,
'chennai', 'all'),
(5, 'MIT', 1950,
'chennai', 'books')]
for i in record_to_insert:
cursor.execute(postgres_insert_query, i)
connection.commit()
count = cursor.rowcount
print(count, "Record inserted successfully \
into publisher table")
except (Exception, psycopg2.Error) as error:
print("Failed to insert record into publisher table", error)
finally:
# closing database connection.
if connection:
cursor.close()
connection.close()
print("PostgreSQL connection is closed")Python3
import psycopg2
try:
connection = psycopg2.connect(user="username",
password="password",
host="hostname",
port="5432",
database="databasename")
cursor = connection.cursor()
postgreSQL_select_Query = "select * from publisher"
cursor.execute(postgreSQL_select_Query)
print("Selecting rows from publisher table using cursor.fetchall")
publisher_records = cursor.fetchall()
print("Print each row and it's columns values")
for row in publisher_records:
print("publisher_Id = ", row[0], )
print("publisher_name = ", row[1])
print("publisher_estd = ", row[2])
print("publisher_location = ", row[3])
print("publisher_type = ", row[4], "\n")
except (Exception, psycopg2.Error) as error:
print("Error while fetching data from PostgreSQL", error)
finally:
# closing database connection.
if connection:
cursor.close()
connection.close()
print("PostgreSQL connection is closed")Python3
import psycopg2
def updateTable(publisherId, establishedYear):
try:
connection = psycopg2.connect(user="username",
password="password",
host="hostname",
port="5432",
database="databasename")
cursor = connection.cursor()
# Update single record now
sql_update_query = """Update publisher set \
publisher_estd = %s where publisher_id = %s"""
cursor.execute(sql_update_query,
(establishedYear,
publisherId))
connection.commit()
count = cursor.rowcount
print(count, "Record Updated successfully ")
except (Exception, psycopg2.Error) as error:
print("Error in update operation", error)
finally:
# closing database connection.
if connection:
cursor.close()
connection.close()
print("PostgreSQL connection is closed")
# call the update function
publisherId = 3
establishedYear = 2000
updateTable(publisherId, establishedYear)Python3
import psycopg2
def deleteData(publisherId):
try:
connection = psycopg2.connect(user="username",
password="password",
host="hostname",
port="5432",
database="databasename")
cursor = connection.cursor()
# Update single record now
sql_delete_query = """Delete from publisher\
where publisher_id = %s"""
cursor.execute(sql_delete_query, (publisherId,))
connection.commit()
count = cursor.rowcount
print(count, "Record deleted successfully ")
except (Exception, psycopg2.Error) as error:
print("Error in Delete operation", error)
finally:
# closing database connection.
if connection:
cursor.close()
connection.close()
print("PostgreSQL connection is closed")
publisherId = 4
deleteData(publisherId)解释:
host – name of the host in which the database is hosted
Username – Name of the admin
Password – Password of the admin
dbname– database name
使用Python在 PostgreSQL 数据库中执行创建操作
- 创建表的语法类似于常规 SQL 语句中使用的语法。如图所示,创建具有所需列和列约束的不同表。如上所述,使用 connect() 与 PostgreSQL 建立连接
- 现在,实例化一个新的 cursor() 对象。游标是一个只读指针,它允许程序访问查询的结果集。
- 如果已存在,则删除任何同名的表。然后,将创建表的查询传递给 psycopg2 的 execute()函数。
- 最后调用commit()方法,表明创建的连接器对象是为了与数据库建立连接,将所有更改提交到数据库。这将确保创建表。
Python3
import psycopg2
# Establishing the connection
conn = psycopg2.connect(
database="databasename",
user='username',
password='password',
host='hostname',
port='5432'
)
# Creating a cursor object using the
# cursor() method
cursor = conn.cursor()
# Doping EMPLOYEE table if already exists.
cursor.execute("DROP TABLE IF EXISTS publisher")
# Creating table as per requirement
sql = '''CREATE TABLE PUBLISHER(
publisher_id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
publisher_name VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
publisher_estd INT,
publsiher_location VARCHAR(255),
publsiher_type VARCHAR(255)
)'''
cursor.execute(sql)
print("Table created successfully........")
conn.commit()
# Closing the connection
conn.close()
输出:
Table created successfully........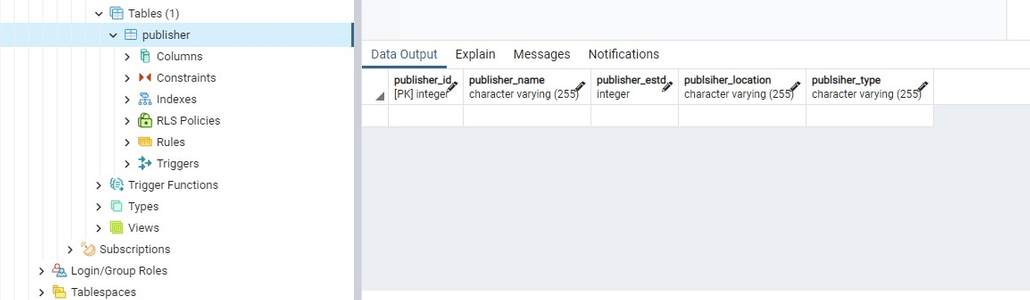
使用Python在 PostgreSQL 中创建表
使用Python在 PostgreSQL 数据库中执行插入操作
- 在表中插入记录的语法类似于常规 SQL 语句中使用的语法。如上所述建立与 PostgreSQL 数据库的连接。
- 现在,实例化一个新的 cursor() 对象。游标是一个只读指针,它允许程序访问查询的结果集。
- 然后,将插入表记录的查询传递给 psycopg2 的 execute()函数。
- 最后调用commit()方法,表明创建的连接器对象是为了与数据库建立连接,将所有更改提交到数据库。这将确保插入记录。
Python3
import psycopg2
try:
connection = psycopg2.connect(user="username",
password="password",
host="127.0.0.1",
port="5432",
database="databasename")
cursor = connection.cursor()
postgres_insert_query = """ INSERT INTO publisher(publisher_id,
publisher_name, publisher_estd, publsiher_location, publsiher_type)
VALUES (%s,%s,%s,%s,%s)"""
record_to_insert = [(1, 'Packt', 1950,
'chennai', 'books'),
(2, 'Springer', 1950,
'chennai', 'books'),
(3, 'Springer', 1950,
'chennai', 'articles'),
(4, 'Oxford', 1950,
'chennai', 'all'),
(5, 'MIT', 1950,
'chennai', 'books')]
for i in record_to_insert:
cursor.execute(postgres_insert_query, i)
connection.commit()
count = cursor.rowcount
print(count, "Record inserted successfully \
into publisher table")
except (Exception, psycopg2.Error) as error:
print("Failed to insert record into publisher table", error)
finally:
# closing database connection.
if connection:
cursor.close()
connection.close()
print("PostgreSQL connection is closed")
输出:
1 Record inserted successfully into publisher table
PostgreSQL connection is closed
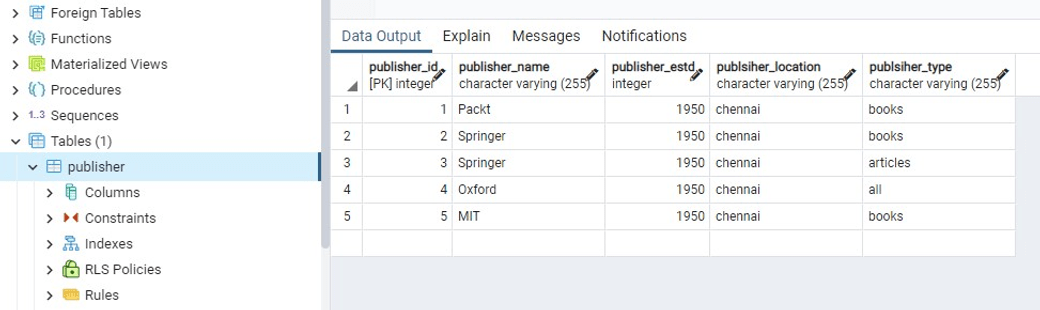
使用Python在 PostgreSQL 的表中插入记录
使用Python在 PostgreSQL 数据库中执行读取操作
- 如上所述建立与 PostgreSQL 数据库的连接。
- 现在,实例化一个新的 cursor() 对象。游标是一个只读指针,它允许程序访问查询的结果集。
- 然后,将创建表的查询传递给 psycopg2 的 execute()函数。
- 查询结果将存储在名为引擎的游标对象中。使用 fetchall() 方法获取结果查询的所有行。
- 现在,遍历每一行以查看查询结果,如图所示。为了在选择数据库中的记录时捕获任何错误并在提交所有更改后顺利关闭连接,请使用 try、expect 和 finally 块,如下面的代码所示。
Python3
import psycopg2
try:
connection = psycopg2.connect(user="username",
password="password",
host="hostname",
port="5432",
database="databasename")
cursor = connection.cursor()
postgreSQL_select_Query = "select * from publisher"
cursor.execute(postgreSQL_select_Query)
print("Selecting rows from publisher table using cursor.fetchall")
publisher_records = cursor.fetchall()
print("Print each row and it's columns values")
for row in publisher_records:
print("publisher_Id = ", row[0], )
print("publisher_name = ", row[1])
print("publisher_estd = ", row[2])
print("publisher_location = ", row[3])
print("publisher_type = ", row[4], "\n")
except (Exception, psycopg2.Error) as error:
print("Error while fetching data from PostgreSQL", error)
finally:
# closing database connection.
if connection:
cursor.close()
connection.close()
print("PostgreSQL connection is closed")
输出:
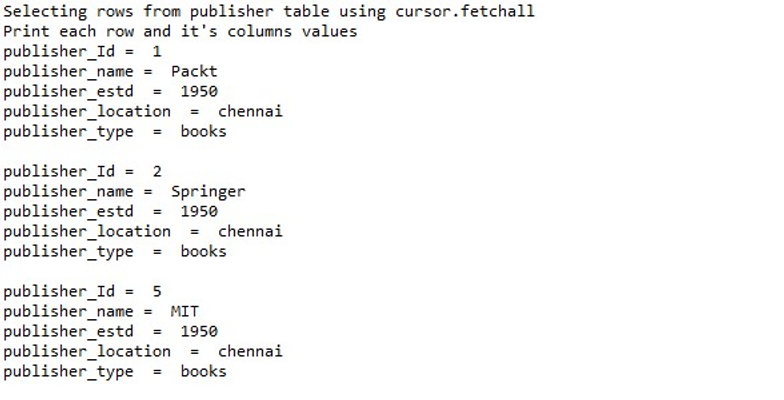
使用Python在 PostgreSQL 中读取表中的记录
使用Python在 PostgreSQL 数据库中执行更新操作
更新表的语法类似于传统 SQL 语句中使用的语法。在这里,我们编写了一个更新查询,通过发布者 ID 更新发布者名称,如图所示。
- 如上所述建立与 PostgreSQL 数据库的连接。
- 现在,实例化一个新的 cursor() 对象。游标是一个只读指针,它允许程序访问查询的结果集。
- 然后,将更新表的查询传递给 psycopg2 的 execute()函数。
- 使用rowcount函数计算更新的行数。
- 最后调用commit()方法,表明创建的连接器对象是为了与数据库建立连接,将所有更改提交到数据库。这将确保更新表。
- 为了在更新数据库中的表时捕获任何错误并在提交所有更改后顺利关闭连接,请使用 try、expect 和 finally 块,如下面的代码所示。
通过调用函数并检查更新来测试 update_publisher()函数。
Python3
import psycopg2
def updateTable(publisherId, establishedYear):
try:
connection = psycopg2.connect(user="username",
password="password",
host="hostname",
port="5432",
database="databasename")
cursor = connection.cursor()
# Update single record now
sql_update_query = """Update publisher set \
publisher_estd = %s where publisher_id = %s"""
cursor.execute(sql_update_query,
(establishedYear,
publisherId))
connection.commit()
count = cursor.rowcount
print(count, "Record Updated successfully ")
except (Exception, psycopg2.Error) as error:
print("Error in update operation", error)
finally:
# closing database connection.
if connection:
cursor.close()
connection.close()
print("PostgreSQL connection is closed")
# call the update function
publisherId = 3
establishedYear = 2000
updateTable(publisherId, establishedYear)
输出:
1 Record Updated successfully
PostgreSQL connection is closed这里,对应于 id = 3 的行被更新为 publsher_estd 的新值。
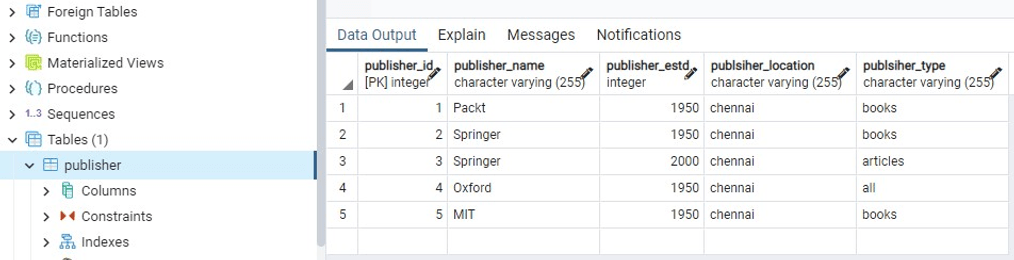
使用Python在 PostgreSQL 中更新表中的记录
使用Python在 PostgreSQL 数据库中执行删除操作
删除表的语法类似于常规 SQL 语句中使用的语法。在这里,我们将编写一个删除查询,按发布者 ID 删除记录,如图所示。
- 如上所述建立与 PostgreSQL 数据库的连接。
- 现在,实例化一个新的 cursor() 对象。游标是一个只读指针,它允许程序访问查询的结果集。
- 然后,将删除表中记录的查询传递给 psycopg2 的 execute()函数。
- 使用rowcount函数计算删除的行数。
- 最后调用commit()方法,表明创建的连接器对象是为了与数据库建立连接,将所有更改提交到数据库。这将确保删除记录。
- 为了在删除数据库中的记录时捕获任何错误并在提交所有更改后顺利关闭连接,请使用 try、expect 和 finally 阻塞,如下面的代码所示。
通过调用函数来测试 delete_publisher()函数并检查更新。
Python3
import psycopg2
def deleteData(publisherId):
try:
connection = psycopg2.connect(user="username",
password="password",
host="hostname",
port="5432",
database="databasename")
cursor = connection.cursor()
# Update single record now
sql_delete_query = """Delete from publisher\
where publisher_id = %s"""
cursor.execute(sql_delete_query, (publisherId,))
connection.commit()
count = cursor.rowcount
print(count, "Record deleted successfully ")
except (Exception, psycopg2.Error) as error:
print("Error in Delete operation", error)
finally:
# closing database connection.
if connection:
cursor.close()
connection.close()
print("PostgreSQL connection is closed")
publisherId = 4
deleteData(publisherId)
输出:
1 Record deleted successfully
PostgreSQL connection is closed此处, id = 4 的行已被删除
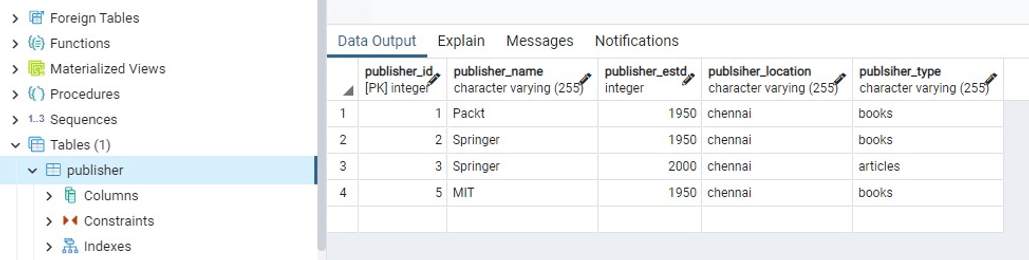
使用Python在 PostgreSQL 中删除表中的记录