Python SQLite – CRUD 操作
在本文中,我们将使用Python的 SQLite 模块完成 CRUD 操作。
CRUD 操作
缩写 CRUD 扩展为创建、读取、更新和删除。这四个是数据库中的基本操作。在示例数据库中,我们将创建它,并进行一些操作。让我们借助示例一一讨论这些操作。
创建
create 命令用于在数据库中创建表。首先我们将通过它的语法然后通过一个例子来理解。
Syntax: CREATE TABLE table_name ( Attr1 Type1, Attr2 Type2, … , Attrn Typen ) ;
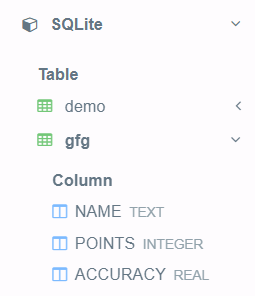
在这个例子中,我们将创建一个名为“gfg”的表,具有三个属性:
- 姓名
- 积分
- 准确性
Python
# Python code to create a relation
# using SQLite3
# import the sqlite3 package
import sqlite3
# create a database named backup
cnt = sqlite3.connect("backup.dp")
# create a table named gfg
cnt.execute('''CREATE TABLE gfg(
NAME TEXT,
POINTS INTEGER,
ACCURACY REAL);''')Python3
# Python3 Code to insert data into
# the database
# Insert three tuples into the gfg table
# insert in default order
cnt.execute('''INSERT INTO gfg VALUES(
'Count Inversion',20,80.5);''')
# insert in different order
cnt.execute('''INSERT INTO gfg(ACCURACY, POINTS, NAME) VALUES(
90.5, 15, 'Kadanes Algo');''')
cnt.execute('''INSERT INTO gfg(NAME, ACCURACY, POINTS) VALUES(
'REVERSE STR', 100, 5);''')
# commit changes to the database
cnt.commit()Python3
# Python3 code to read data from a table
print('Name, Points and Accuracy from '
'records with accuracy greater than 85')
cursor = cnt.execute('''SELECT * FROM gfg WHERE ACCURACY>85;''')
# print data using the cursor object
for i in cursor:
print(i[0]+" "+str(i[1])+" "+str(i[2]))
print('') # Print new line
print('Name, Accuracy from '
'records with accuracy greater than 85')
cursor = cnt.execute('''SELECT NAME, ACCURACY FROM
gfg WHERE ACCURACY>85;''')
# print data using the cursor object
for i in cursor:
print(i[0]+" "+str(i[1]))Python3
# Python3 code to update records in a database
# Print records before updation
cursor = cnt.execute('''SELECT * FROM gfg''')
print('Before Updation')
for i in cursor:
print(i[0]+" "+str(i[1])+" "+str(i[2]))
print('') # print a newline
# Execute an Update statement
cnt.execute('''UPDATE gfg SET POINTS=POINTS+5 WHERE
POINTS<20;''')
cursor = cnt.execute('''SELECT * FROM gfg''')
print('After Updation')
for i in cursor:
print(i[0]+" "+str(i[1])+" "+str(i[2]))Python3
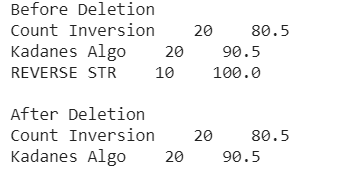
# Python3 code to delete records from database
# Print records before deletion
cursor = cnt.execute('''SELECT * FROM gfg''')
print('Before Deletion')
for i in cursor:
print(i[0]+" "+str(i[1])+" "+str(i[2]))
print('') # print a newline
# Execute a delete statement
cnt.execute('''DELETE FROM gfg WHERE ACCURACY>91;''')
cursor = cnt.execute('''SELECT * FROM gfg''')
print('After Deletion')
for i in cursor:
print(i[0]+" "+str(i[1])+" "+str(i[2]))输出:
插入
这是指将新数据插入表中。数据以元组的形式插入。元组中的属性数量必须等于创建表时在关系模式中定义的数量。
1. To insert attributes in the order specified in the relation schema:
Syntax: INSERT INTO tableName VALUES ( value1, value2, … valuen )
2.To insert attributes in the order specified in the relation schema or in a different order:
INSERT INTO tableName ( Attribute1, Attribute3, Attribute2 . . . ) VALUES ( value1, value3, value2 . . . )
下面的程序演示了向之前创建的 gfg 关系添加三个元组。
蟒蛇3
# Python3 Code to insert data into
# the database
# Insert three tuples into the gfg table
# insert in default order
cnt.execute('''INSERT INTO gfg VALUES(
'Count Inversion',20,80.5);''')
# insert in different order
cnt.execute('''INSERT INTO gfg(ACCURACY, POINTS, NAME) VALUES(
90.5, 15, 'Kadanes Algo');''')
cnt.execute('''INSERT INTO gfg(NAME, ACCURACY, POINTS) VALUES(
'REVERSE STR', 100, 5);''')
# commit changes to the database
cnt.commit()
输出:
读
这是指从数据库中读取数据。 read 语句包含三个子句:
- SELECT:以要查询的属性为谓词,所有属性都使用* 。
- FROM:将关系作为谓词。
- WHERE:将条件作为谓词,这不是强制性的。
在Python SQLite3中执行read语句后,返回一个可迭代的游标对象。这可用于打印数据。
Example: SELECT NAME, POINTS, ACCURACY FROM gfg WHERE ACCURACY>85;
下面的程序演示了 read 语句的用法。
蟒蛇3
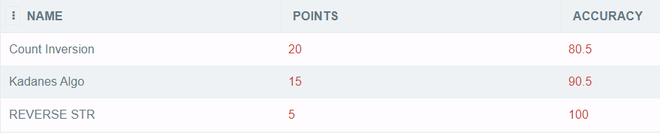
# Python3 code to read data from a table
print('Name, Points and Accuracy from '
'records with accuracy greater than 85')
cursor = cnt.execute('''SELECT * FROM gfg WHERE ACCURACY>85;''')
# print data using the cursor object
for i in cursor:
print(i[0]+" "+str(i[1])+" "+str(i[2]))
print('') # Print new line
print('Name, Accuracy from '
'records with accuracy greater than 85')
cursor = cnt.execute('''SELECT NAME, ACCURACY FROM
gfg WHERE ACCURACY>85;''')
# print data using the cursor object
for i in cursor:
print(i[0]+" "+str(i[1]))
输出:

更新
这是指更新表中已经存在的元组值。
Syntax: UPDATE tableName SET Attribute1 = Value1 , Attribute2 = Value2 , . . . WHERE condition;
The WHERE clause must be included, else all records in the table will be updated.
EXAMPLE: UPDATE gfg SET POINTS=POINTS+5 WHERE POINTS<20;
下面的程序演示了更新语句的用法。
蟒蛇3
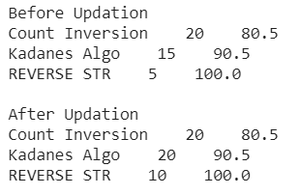
# Python3 code to update records in a database
# Print records before updation
cursor = cnt.execute('''SELECT * FROM gfg''')
print('Before Updation')
for i in cursor:
print(i[0]+" "+str(i[1])+" "+str(i[2]))
print('') # print a newline
# Execute an Update statement
cnt.execute('''UPDATE gfg SET POINTS=POINTS+5 WHERE
POINTS<20;''')
cursor = cnt.execute('''SELECT * FROM gfg''')
print('After Updation')
for i in cursor:
print(i[0]+" "+str(i[1])+" "+str(i[2]))
输出:
删除
这是指删除表中存在的元组。
SYNTAX: DELETE FROM tableName WHERE condition
If WHERE clause is not used then all the records will be deleted.
EXAMPLE: DELETE FROM gfg WHERE ACCURACY>91
下面的程序演示了删除语句的用法。
蟒蛇3
# Python3 code to delete records from database
# Print records before deletion
cursor = cnt.execute('''SELECT * FROM gfg''')
print('Before Deletion')
for i in cursor:
print(i[0]+" "+str(i[1])+" "+str(i[2]))
print('') # print a newline
# Execute a delete statement
cnt.execute('''DELETE FROM gfg WHERE ACCURACY>91;''')
cursor = cnt.execute('''SELECT * FROM gfg''')
print('After Deletion')
for i in cursor:
print(i[0]+" "+str(i[1])+" "+str(i[2]))
输出: