给定一个 NxM 整数的二维向量。任务是按照从左上角到右下角的降序对向量的元素进行对角排序。
例子:
Input: arr[][] = { { 10, 2, 3 }, { 4, 5, 6 }, {7, 8, 9 } }
Output:
10 2 0
4 9 0
0 0 5
Input: arr[][] = { { 10, 2, 43 }, { 40, 5, 16 }, { 71, 8, 29 }, {1, 100, 5} }
Output:
29 2 0
8 10 0
71 5 5
0 0 0
方法:
观察:
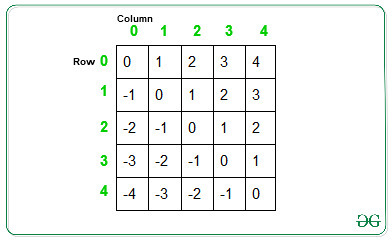
上图显示了每个单元格的列索引和行索引之间的差异。从左上到下的单元格具有相同差异的单元格形成对角线。
以下是按降序对对角线进行排序的步骤:
- 将具有正差值的对角线元素存储在一个向量数组(例如Pos[] )中,以便将单元格中具有差异(例如a )的元素存储在 Pos[]数组的索引 an 处。
- 将具有负差的对角线元素存储在另一个向量数组(例如Neg[] )中,以便将单元格中具有差异(例如-b )的元素存储在 Neg[]数组的索引 abs(-b) = b处。
- 按升序对向量数组进行排序。
- 遍历给定的二维向量并使用存储在 Pos[] 和 Neg[] 数组中的值更新当前单元格处的值。
- 如果列和行索引之间的差异(例如d )为正,则更新 Pos[d] 数组中的值并将最后一个元素删除为:
d = i - j
arr[i][j] = Pos[d][Pos.size()-1]
Pos[d].pop_back()- 如果列和行索引之间的差异(比如d )为负,则更新 Neg[d] 数组中的值并将最后一个元素删除为:
d = j - i
arr[i][j] = Neg[d][Neg.size()-1]
Neg[d].pop_back()下面是上述方法的实现:
CPP
// C++ program to sort the 2D vector
// diagonally in decreasing order
#include "bits/stdc++.h"
using namespace std;
// Function that sort the elements
// of 2D vector
void diagonalSort(vector >& mat)
{
// Calculate the rows and column
int row = mat.size();
int col = mat[0].size();
// Array of vectors to store the
// diagonal elements
vector Neg[row];
vector Pos[col];
// Traverse the 2D vector and put
// element in Array of vectors at
// index difference between indexes
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < col; j++) {
// If diff is negative, then
// push element to Neg[]
if (j < i) {
Neg[i - j].push_back(mat[i][j]);
}
// If diff is positive, then
// push element to Pos[]
else if (j > i) {
Pos[j - i].push_back(mat[i][j]);
}
// If diff is 0, then push
// element to Pos[0]
else {
Pos[0].push_back(mat[i][j]);
}
}
}
// Sort the Array of vectors
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++) {
sort(Neg[i].begin(), Neg[i].end());
}
for (int i = 0; i < col; i++) {
sort(Pos[i].begin(), Pos[i].end());
}
// Update the value to arr[][]
// from the sorted Array of vectors
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < col; j++) {
// If diff is positive
if (j < i) {
int d = i - j;
int l = Neg[d].size() - 1;
mat[i][j] = Neg[d][l - 1];
Neg[d].pop_back();
}
// If diff is negative
else if (j > i) {
int d = j - i;
int l = Pos[d].size() - 1;
mat[i][j] = Pos[d][l - 1];
Pos[d].pop_back();
}
// If diff is 0
else {
int l = Pos[0].size();
mat[i][j] = Pos[0][l - 1];
Pos[0].pop_back();
}
}
}
}
// Function to print element
void printElement(vector >& arr)
{
// Traverse the 2D vector
for (int i = 0; i < arr.size(); i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < arr[0].size(); j++) {
cout << arr[i][j] << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
vector > arr
= { { 10, 2, 3 }, { 4, 5, 6 }, { 7, 8, 9 } };
diagonalSort(arr);
// Function call to print elements
printElement(arr);
} Python3
# Python program for the above approach
from collections import defaultdict
def diagonalSort(matrix, n, m):
# make a dict of list, where we
# wil store the diagonal elements
to = defaultdict(list)
# store the diagonal elements with
# respect to their row-col value
# remember every row-col value for
# each diagonal will be different
for row in range(n):
for col in range(m):
to[row-col].append(matrix[row][col])
# sort the elements of each
# diagonal as required
for i in to:
# upper triangle diagonals
if i < 0:
to[i].sort(reverse=True)
# median
elif i == 0:
pass
# lower triangle diagonals
else:
to[i].sort()
# store the new diagonal elements to
# their respective position in the matrix
for row in range(n):
for col in range(m):
matrix[row][col] = to[row-col].pop(0)
return matrix
# Driver Code
if __name__ == "__main__":
matrix = [[10, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6],
[7, 8, 9]]
n = len(matrix)
m = len(matrix[0])
matrix = diagonalSort(matrix, n, m)
for row in range(n):
for col in range(m):
print(matrix[row][col], end=' ')
print()输出:
10 2 0
4 9 0
0 0 5时间复杂度: O(N*M*log(min(N,M)))
空间复杂度:O(N*M)
如果您想与行业专家一起参加直播课程,请参阅Geeks Classes Live