给定由N 个节点组成的有向树,任务是检查给定树中是否存在一个节点,以便通过从树中删除任何有向边并在树中的任何一对节点之间添加另一条有向边来检查所有其他节点是否可达树最多楼层(N/2)次。如果存在任何这样的节点,则打印“Yes” 。否则,打印“否” 。
例子:
Input: N = 3
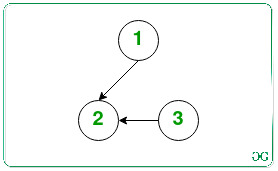
Output: Yes
Explanation:
Remove the edge 2 -> 3 and insert an edge 1 -> 3.
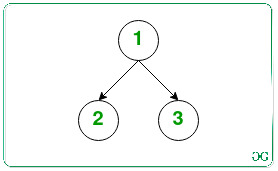
Therefore, both the remaining nodes (2, 3) are now accessible from the node 1.
Count of operations required is 1, which is <= floor(3/2) (= 1).
Input: N = 5
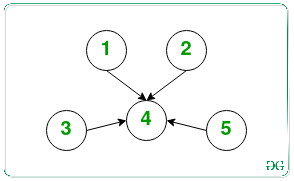
Output: No
方法:解决此问题的想法基于以下观察:
- 每个节点至少应该有一个父节点,即每个节点至少应该有1个入度,使树从所需要的节点访问。
- 可以得出结论,如果每个节点至少有 1 个入度,那么所有其他节点都可以访问。
- 因此,任务被简化为查找具有0 入度的节点数并检查它是否最多为N / 2 。
请按照以下步骤解决问题:
- 将树中每个节点的入度存储在大小为(N + 1)的辅助数组A[]中。
- 对于 Map 中的所有(键值)对,将此数组初始化为A[key] = pair 。
- 初始化一个变量,比如count为0,以存储入度等于0的节点数。
- 遍历数组A[]并计算值为0的数组元素的数量并将其存储在变量count 中。
- 完成上述步骤后,如果count的值最多为floor(N/2) ,则打印“Yes” 。否则,打印“否” 。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
void findNode(map mp, int n)
{
// Store the indegree
// of every node
int a[n];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
a[i] = mp[i + 1];
}
// Store the nodes having
// indegree equal to 0
int count0 = 0;
// Traverse the array
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
// If the indegree
// of i-th node is 0
if (a[i] == 0)
{
// Increment count0 by 1
count0++;
}
}
count0 -= 1;
// If the number of operations
// needed is at most floor(n/2)
if (count0 <= floor(((double)n) /
((double)2)))
{
cout << "Yes";
}
// Otherwise
else
cout << "No";
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Given number of nodes
int N = 3;
// Given Directed Tree
map mp;
mp[1] = 0;
mp[2] = 2;
mp[3] = 0;
findNode(mp, N);
}
// This code is contributed by SURENDRA_GANGWAR Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.io.*;
import java.util.HashMap;
class GFG {
// Function to check if there is a
// node in tree from where all other
// nodes are accessible or not
public static void
findNode(HashMap map,
int n)
{
// Store the indegree
// of every node
int[] a = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
a[i] = map.getOrDefault(i + 1, 0);
}
// Store the nodes having
// indegree equal to 0
int count0 = 0;
// Traverse the array
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// If the indegree
// of i-th node is 0
if (a[i] == 0) {
// Increment count0 by 1
count0++;
}
}
count0 -= 1;
// If the number of operations
// needed is at most floor(n/2)
if (count0
<= Math.floor(((double)n)
/ ((double)2))) {
System.out.println("Yes");
}
// Otherwise
else
System.out.println("No ");
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Given number of nodes
int N = 3;
// Given Directed Tree
HashMap map
= new HashMap<>();
map.put(1, 0);
map.put(2, 2);
map.put(3, 0);
findNode(map, N);
}
} Python3
# python 3 program for the above approach
def findNode(mp, n):
# Store the indegree
# of every node
a = [0]*n
for i in range(n):
a[i] = mp[i + 1]
# Store the nodes having
# indegree equal to 0
count0 = 0
# Traverse the array
for i in range(n):
# If the indegree
# of i-th node is 0
if (a[i] == 0):
# Increment count0 by 1
count0 += 1
count0 -= 1
# If the number of operations
# needed is at most floor(n/2)
if (count0 <= (n) /
(2)):
print("Yes")
# Otherwise
else:
print("No")
# Driver Code
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Given number of nodes
N = 3
# Given Directed Tree
mp = {}
mp[1] = 0
mp[2] = 2
mp[3] = 0
findNode(mp, N)C#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class GFG{
// Function to check if there is a
// node in tree from where all other
// nodes are accessible or not
public static void
findNode(Dictionary map,
int n)
{
// Store the indegree
// of every node
int[] a = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if(map.ContainsKey(i+1))
a[i] = map[i + 1];
else
a[i] = 0;
}
// Store the nodes having
// indegree equal to 0
int count0 = 0;
// Traverse the array
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// If the indegree
// of i-th node is 0
if (a[i] == 0) {
// Increment count0 by 1
count0++;
}
}
count0 -= 1;
// If the number of operations
// needed is at most floor(n/2)
if (count0
<= Math.Floor(((double)n)
/ ((double)2))) {
Console.WriteLine("Yes");
}
// Otherwise
else
Console.WriteLine("No ");
}
static public void Main ()
{
// Given number of nodes
int N = 3;
// Given Directed Tree
Dictionary map
= new Dictionary();
map[1]= 0;
map[2] = 2;
map[3] = 0;
findNode(map, N);
}
}
// This code is contributed by offbeat Javascript
输出:
Yes时间复杂度: O(N)
辅助空间: O(N)
如果您想与行业专家一起参加直播课程,请参阅Geeks Classes Live