给定一个整数N和一个如下形式的 N 元树:
- 每个节点都按顺序编号,从1开始,直到包含节点N的最后一层。
- 每个奇数级别的节点包含2个子节点,每个偶数级别的节点包含4个子节点。
任务是打印从根节点到节点N的路径。
例子:
Input: N = 14
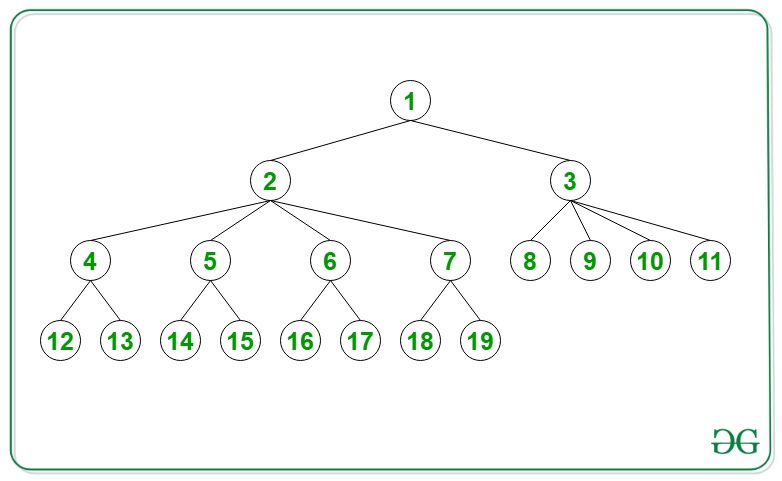
Output: 1 2 5 14
Explanation: The path from node 1 to node 14 is 1 – > 2 – > 5 – > 14.
Input: N = 11
Output: 1 3 11
Explanation: The path from node 1 to node 11 is 1 – > 3 – > 11.
处理方法:按照以下步骤解决问题:
- 初始化一个数组来存储树的每一层中存在的节点数,即 {1, 2, 8, 16, 64, 128 ….} 并存储它。
- 计算数组的前缀和,即 {1 3 11 27 91 219 …….}
- 使用lower_bound() 在前缀和数组中找到超过或等于N的索引ind。因此, ind表示到达节点 N需要遍历的层数。
- 初始化一个变量,比如temp = N和一个数组path[]来存储从 root 到N的节点。
- 递减ind直到它小于或等于1并不断更新val = temp – prefix[ind – 1] 。
- 如果ind是奇数,则更新temp = prefix[ind – 2] + (val + 1) / 2。
- 否则,如果ind是偶数,则更新temp = prefix[ind – 2] + (val + 3) / 4。
- 将temp附加到path[]数组中。
- 最后,打印数组path[] 。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
// Function to find the path
// from root to N
void PrintPathNodes(ll N)
{
// Stores the number of
// nodes at (i + 1)-th level
vector arr;
arr.push_back(1);
// Stores the number of nodes
ll k = 1;
// Stores if the current
// level is even or odd
bool flag = true;
while (k < N) {
// If level is odd
if (flag == true) {
k *= 2;
flag = false;
}
// If level is even
else {
k *= 4;
flag = true;
}
// If level with
// node N is reached
if (k > N) {
break;
}
// Push into vector
arr.push_back(k);
}
ll len = arr.size();
vector prefix(len);
prefix[0] = 1;
// Compute prefix sums of count
// of nodes in each level
for (ll i = 1; i < len; ++i) {
prefix[i] = arr[i] + prefix[i - 1];
}
vector::iterator it
= lower_bound(prefix.begin(),
prefix.end(), N);
// Stores the level in which
// node N s present
ll ind = it - prefix.begin();
ll temp = N;
// Store path
vector path;
path.push_back(N);
while (ind > 1) {
ll val = temp - prefix[ind - 1];
if (ind % 2 != 0) {
temp = prefix[ind - 2]
+ (val + 1) / 2;
}
else {
temp = prefix[ind - 2]
+ (val + 3) / 4;
}
--ind;
// Insert temp into path
path.push_back(temp);
}
if (N != 1)
path.push_back(1);
// Print path
for (int i = path.size() - 1;
i >= 0; i--) {
cout << path[i] << " ";
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
ll N = 14;
// Function Call
PrintPathNodes(N);
return 0;
} Python3
# Python3 program for the above approach
from bisect import bisect_left
# Function to find the path
# from root to N
def PrintPathNodes(N):
# Stores the number of
# nodes at (i + 1)-th level
arr = []
arr.append(1)
# Stores the number of nodes
k = 1
# Stores if the current
# level is even or odd
flag = True
while (k < N):
# If level is odd
if (flag == True):
k *= 2
flag = False
# If level is even
else:
k *= 4
flag = True
# If level with
# node N is reached
if (k > N):
break
# Push into vector
arr.append(k)
lenn = len(arr)
prefix = [0]*(lenn)
prefix[0] = 1
# Compute prefix sums of count
# of nodes in each level
for i in range(1,lenn):
prefix[i] = arr[i] + prefix[i - 1]
it = bisect_left(prefix, N)
# Stores the level in which
# node N s present
ind = it
temp = N
# Store path
path = []
path.append(N)
while (ind > 1):
val = temp - prefix[ind - 1]
if (ind % 2 != 0):
temp = prefix[ind - 2] + (val + 1) // 2
else:
temp = prefix[ind - 2] + (val + 3) // 4
ind -= 1
# Insert temp into path
path.append(temp)
if (N != 1):
path.append(1)
# Print path
for i in range(len(path)-1, -1, -1):
print(path[i], end=" ")
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
N = 14
# Function Call
PrintPathNodes(N)
# This code is contributed by mohit kumar 29输出:
1 2 5 14时间复杂度: O(log(N))
辅助空间: O(log(N))
如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。