本文重点计算一维、二维、三维数组中行主序和列主序任意元素的地址。
计算一维数组中任何元素的地址:一维数组(或一维数组)是一种线性数组。访问其元素涉及可以表示行或列索引的单个下标。
例子:
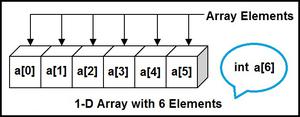
要查找数组中元素的地址,请执行以下操作 使用公式——
Address of A[I] = B + W * (I – LB)
I = Subset of element whose address to be found,
B = Base address,
W = Storage size of one element store in any array(in byte),
LB = Lower Limit/Lower Bound of subscript(If not specified assume zero).
例子:给定数组A[1300…………1900]的基地址为1020 ,每个元素在内存中的大小为 2 个字节,求A[1700]的地址?
解决方案:
Given:
Base address B = 1020
Lower Limit/Lower Bound of subscript LB = 1300
Storage size of one element store in any array W = 2 Byte
Subset of element whose address to be found I = 1700
Formula:
Address of A[I] = B + W * (I – LB)
Solution:
Address of A[1700] = 1020 + 2 * (1700 – 1300)
= 1020 + 2 * (400)
= 1020 + 800
Address of A[1700] = 1820
计算二维数组中任意元素的地址:二维数组可以定义为数组的数组。二维数组被组织为矩阵,可以将行和列的集合表示为 array[M][N],其中 M 是行数,N 是列数。
例子:

要查找二维数组中任何元素的地址,有以下两种方法-
- 行主要订单
- 列主要订单
行主要顺序:行主要顺序将连续元素分配到连续的内存位置,这些元素在行之间移动,然后向下移动到下一行。在简单的语言中,数组的元素以 Row-Wise 方式存储。
要使用行优先顺序查找元素的地址,请使用以下公式:
Address of A[I][J] = B + W * ((I – LR) * N + (J – LC))
I = Row Subset of an element whose address to be found,
J = Column Subset of an element whose address to be found,
B = Base address,
W = Storage size of one element store in an array(in byte),
LR = Lower Limit of row/start row index of the matrix(If not given assume it as zero),
LC = Lower Limit of column/start column index of the matrix(If not given assume it as zero),
N = Number of column given in the matrix.
示例:给定一个数组, arr[1………10][1………15] ,基值为100 ,每个元素的大小在内存中为 1 Byte。借助行主序找到arr[8][6]的地址?
解决方案:
Given:
Base address B = 100
Storage size of one element store in any array W = 1 Bytes
Row Subset of an element whose address to be found I = 8
Column Subset of an element whose address to be found J = 6
Lower Limit of row/start row index of matrix LR = 1
Lower Limit of column/start column index of matrix = 1
Number of column given in the matrix N = Upper Bound – Lower Bound + 1
= 15 – 1 + 1
= 15
Formula:
Address of A[I][J] = B + W * ((I – LR) * N + (J – LC))
Solution:
Address of A[8][6] = 100 + 1 * ((8 – 1) * 15 + (6 – 1))
= 100 + 1 * ((7) * 15 + (5))
= 100 + 1 * (110)
Address of A[I][J] = 210
列主要顺序:如果数组的元素以列主要方式存储意味着跨列移动,然后移动到下一列,则它按列主要顺序。要使用列主序查找元素的地址,请使用以下公式:
Address of A[I][J] = B + W * ((J – LC) * M + (I – LR))
I = Row Subset of an element whose address to be found,
J = Column Subset of an element whose address to be found,
B = Base address,
W = Storage size of one element store in any array(in byte),
LR = Lower Limit of row/start row index of matrix(If not given assume it as zero),
LC = Lower Limit of column/start column index of matrix(If not given assume it as zero),
M = Number of rows given in the matrix.
示例:给定一个数组arr[1………10][1………15] ,基值为100 ,每个元素的大小为内存中的 1 字节,借助以下命令找到 arr[8][6] 的地址列主序。
解决方案:
Given:
Base address B = 100
Storage size of one element store in any array W = 1 Bytes
Row Subset of an element whose address to be found I = 8
Column Subset of an element whose address to be found J = 6
Lower Limit of row/start row index of matrix LR = 1
Lower Limit of column/start column index of matrix = 1
Number of column given in the matrix M = Upper Bound – Lower Bound + 1
= 10 – 1 + 1
= 10
Formula:
Address of A[I][J] = B + W * ((J – LC) * M + (I – LR))
Address of A[8][6] = 100 + 1 * ((6 – 1) * 10 + (8 – 1))
= 100 + 1 * ((5) * 10 + (7))
= 100 + 1 * (57)
Address of A[I][J] = 157
从上面的例子可以看出,对于同一个位置,得到了两个不同的地址位置,这是因为以行为主的顺序移动是跨行然后向下移动到下一行,而在列优先的顺序中,首先移动向下到第一列,然后是下一列。所以两个答案都是对的。
因此,这完全基于要找到其地址的元素的位置,在某些情况下,同样的答案也会以行优先顺序和列优先顺序获得,而在某些情况下,会得到不同的答案。
计算 3 维数组中任意元素的地址: 3 维数组是 2 维数组的集合。它通过使用三个下标来指定:
- 块大小
- 行大小
- 列大小
数组中的更多维度意味着可以在该数组中存储更多数据。
例子:
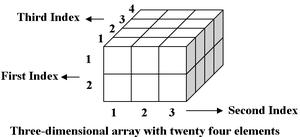
要查找 3 维数组中任何元素的地址,有以下两种方法-
- 行主要订单
- 列主要订单
行主序:要使用行主序查找元素的地址,请使用以下公式:
Address of[i][j][k] = B + W * {[(I – LR) * N] +
[(J – LC)]} * R + [K + LB]
I = Row Subset of an element whose address to be found,
J = Column Subset of an element whose address to be found,
K = Block Subset of an element whose address to be found,
B = Base address,
W = Storage size of one element store in any array(in byte),
LR = Lower Limit of row/start row index of matrix(If not given assume it as zero),
LC = Lower Limit of column/start column index of matrix(If not given assume it as zero),
LB = Lower Limit of blocks in matrix,
N = Number of column given in the matrix
R = Number of blocks given in the matrix.
示例:给定一个数组arr[1:9, -4:1, 5:10] ,基值为400 ,每个元素的大小为2 字节在内存中找到元素arr[5][-1][8] 的地址在行优先顺序的帮助下?
解决方案:
Given:
Row Subset of an element whose address to be found I = 5
Column Subset of an element whose address to be found J = -1
Block Subset of an element whose address to be found K = 8
Base address B = 400
Storage size of one element store in any array(in Byte) = 2
Lower Limit of row/start row index of matrix LR = 1
Lower Limit of column/start column index of matrix LC = -4
Lower Limit of blocks in matrix LB = 5
Number of column given in the matrix N = Upper Bound – Lower Bound + 1
= 1 – (-4) + 1
= 6
Number of blocks given in the matrix R = Upper Bound – Lower Bound + 1
= 10 – 5 + 1
= 6
Formula:
Address of[i][j][k] = B + W * {[(I – LR) * N] + [(J – LC)]} * R + [K – LB]
Solution:
Address of[][][] = 400 + 2 * {[(5 – 1) * 6] + [(-1 + 4)]} * 6 + [8 – 5]
= 400 + 2 * ((4 * 6 + 3) * 6 + 3)
= 400 + 2 * (165)
= 730
列主序:要使用列主序查找元素的地址,请使用以下公式-
Address of[i][j][k] = B + W * {[(I – LR)] + [(J – LC) * M]} * R + [K – LB]
I = Row Subset of an element whose address to be found,
J = Column Subset of an element whose address to be found,
K = Block Subset of an element whose address to be found
B = Base address,
W = Storage size of one element store in any array(in byte),
LR = Lower Limit of row/start row index of matrix(If not given assume it as zero),
LC = Lower Limit of column/start column index of matrix(If not given assume it as zero),
LB = Lower Limit of blocks in matrix,
M = Number of rows given in the matrix,
R = Number of blocks given in the matrix.
示例:给定一个数组arr[1:8, -5:5, -10:5]基值为400 ,每个元素的大小为4 字节在内存中找到元素arr[3][3][3] 的地址在列主序的帮助下?
解决方案:
Given:
Row Subset of an element whose address to be found I = 3
Column Subset of an element whose address to be found J = 3
Block Subset of an element whose address to be found K = 3
Base address B = 400
Storage size of one element store in any array(in Byte) = 4
Lower Limit of row/start row index of matrix LR = 1
Lower Limit of column/start column index of matrix LC = -5
Lower Limit of blocks in matrix LB = -10
Number of rows given in the matrix M = Upper Bound – Lower Bound + 1
= 8 – 1 + 1
= 8
Number of blocks given in the matrix R = Upper Bound – Lower Bound + 1
= 5 + 10 + 1
= 16
Formula:
Address of[i][j][k] = B + W * {[(I – LR)] + [(J – LC) * M]} * R + [K – LB]
Solution:
Address of[3][3][3] = 400 + 4 * {[(3 – 1)] + [3 + 5] * 8]} * 16 + [3 + 10]
= 400 + 4 * ((2 + 64) * 16 + 13)
= 400 + 4 * (1069)
= 400 + 4276
= 4676
如果您想与行业专家一起参加直播课程,请参阅Geeks Classes Live