📌 相关文章
- RichFaces Rich:Tree
- RichFaces Rich:Tree(1)
- RichFaces Rich:List(1)
- RichFaces Rich:List
- RichFaces Rich:Select(1)
- RichFaces Rich:Select
- RichFaces Rich:日历(1)
- RichFaces Rich:日历
- RichFaces Rich:工具栏
- RichFaces Rich:工具栏(1)
- RichFaces Rich:Message
- RichFaces Rich:Message(1)
- RichFaces Rich:Datatable
- RichFaces Rich:Datatable(1)
- RichFaces Rich:Panel(1)
- RichFaces Rich:Editor
- RichFaces Rich:Panel
- RichFaces Rich:Editor(1)
- RichFaces Rich:工具提示
- RichFaces Rich:工具提示(1)
- RichFaces Rich:DataGrid(1)
- RichFaces Rich:DataGrid
- RichFaces Rich:Progressbar(1)
- RichFaces Rich:Progressbar
- RichFaces Rich:AutoComplete(1)
- RichFaces Rich:AutoComplete
- RichFaces Rich:Messages
- RichFaces Rich:Messages(1)
- RichFaces Rich:FileUpload
📜 RichFaces-Rich Tree
📅 最后修改于: 2020-10-20 05:09:33 🧑 作者: Mango
在本章中,我们将学习RichFaces中的树处理。 RichFaces提供了创建和操作树的所有必需组件。
该标签用于创建分层树。
在以下示例中,我们将使用后端的
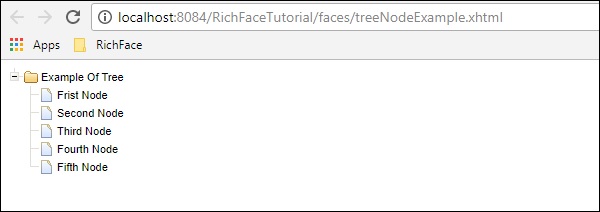
TreeNode Example
以下是实现“ TreeNodeImpl”接口的相关Java类。
import javax.faces.bean.ManagedBean;
import javax.faces.bean.RequestScoped;
import org.richfaces.model.TreeNodeImpl;
@ManagedBean
@RequestScoped
public class Tree extends TreeNodeImpl {
private Tree stationRoot;
private Tree populateNode;
private Object data;
public Tree() {
super();
}
public Tree(boolean leaf, Object data) {
super(leaf);
this.data = data;
}
public Object getData() {
return data;
}
public Tree getPopulateNode() {
if (populateNode == null) {
String[] List_OF_Node = {
"Frist Node", "Second Node", "Third Node", "Fourth Node", "Fifth Node"};
stationRoot = new Tree(false, "Example Of Tree");
for (int i = 0; i < List_OF_Node.length; i++) {
Tree child = new Tree(true, List_OF_Node[i]);
stationRoot.addChild(i, child);
}
populateNode = new Tree();
populateNode.addChild(0, stationRoot);
}
return populateNode;
}
}
上面的代码将在浏览器中产生以下输出。
该组件将Map作为输入,对其进行迭代,并在浏览器中生成所需的输出。每当需要填充递归地图时,我们都可以使用另一个名为
以下示例显示了如何在浏览器中呈现项目结构。在RichFaces 3中,使用这两个标签
Tree Model and Recursive Model Example
在此示例中,我们需要创建两个新的Java Bean。以下是Bean类“ FileSystemBean.java”的代码片段,其中包含所需的文件夹名称。
import java.util.List;
import javax.faces.bean.ManagedBean;
import javax.faces.bean.RequestScoped;
@ManagedBean
@RequestScoped
public class FileSystemBean {
private static final String SRC_PATH = "/WEB-INF";
private List srcRoots;
public synchronized List getSourceRoots() {
if (srcRoots == null) {
srcRoots = new FileSystemNode(SRC_PATH).getDirectories();
}
return srcRoots;
}
}
以下是Bean类“ FileSystemNode.java”的代码片段,其中包含项目所需的叶节点。
import static com.google.common.base.Predicates.containsPattern;
import static com.google.common.base.Predicates.not;
import static com.google.common.collect.Iterables.filter;
import static com.google.common.collect.Iterables.transform;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Set;
import javax.faces.context.ExternalContext;
import javax.faces.context.FacesContext;
import com.google.common.base.Function;
import com.google.common.collect.Iterables;
import com.google.common.collect.Lists;
public class FileSystemNode {
private static final Function
FACTORY = new Function() {
public FileSystemNode apply(String from) {
return new FileSystemNode(from.substring(0, from.length() - 1));
};
};
private static final Function
TO_SHORT_PATH = new Function() {
public String apply(String from) {
int idx = from.lastIndexOf('/');
if (idx < 0) {
return from;
}
return from.substring(idx + 1);
};
};
private String path;
private List directories;
private List files;
private String shortPath;
public FileSystemNode(String path) {
this.path = path;
int idx = path.lastIndexOf('/');
if (idx != -1) {
shortPath = path.substring(idx + 1);
} else {
shortPath = path;
}
}
public synchronized List getDirectories() {
if (directories == null) {
directories = Lists.newArrayList();
Iterables.addAll(directories, transform(filter(
getResourcePaths(), containsPattern("/$")), FACTORY));
}
return directories;
}
public synchronized List getFiles() {
if (files == null) {
files = new ArrayList();
Iterables.addAll(files, transform(filter(
getResourcePaths(), not(containsPattern("/$"))), TO_SHORT_PATH));
}
return files;
}
private Iterable getResourcePaths() {
FacesContext facesContext = FacesContext.getCurrentInstance();
ExternalContext externalContext = facesContext.getExternalContext();
Set resourcePaths = externalContext.getResourcePaths(this.path);
if (resourcePaths == null) {
resourcePaths = Collections.emptySet();
}
return resourcePaths;
}
public String getShortPath() {
return shortPath;
}
}
上面的示例将在浏览器中产生以下输出。