流可以定义为数据的序列或连续的数据流。流是处理输入/输出的一种清晰方式。流有两种类型,如下所示:
在上图中,我们的 InputStream 和 OutputStream 将驻留在 Byte Stream 中。那么让我们来讨论字节流。
1. Byte Stream: Byte Stream 提供了一种方便的方式来处理字节的输入和输出。字节流被进一步划分为各种类,但最顶层的类如下所示:
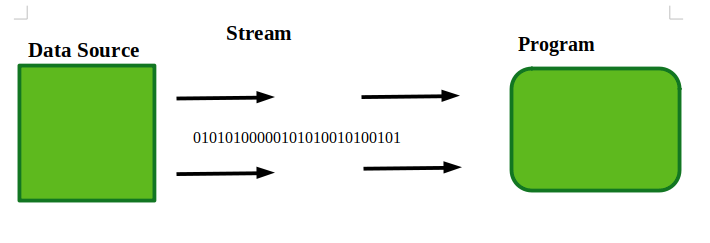
1.1 InputStream: InputStream是Byte Stream的抽象类,描述流输入,用于读取,可以是文件、图片、音频、视频、网页等,无所谓。因此, InputStream 一次从源读取一项数据。
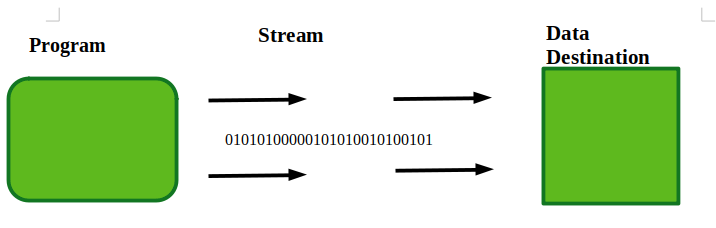
1.2 OutputStream: OutputStream是Byte Stream的抽象类,描述流输出,用于向文件、图像、音频等写入数据,因此OutputStream一次向目的地写入数据。
InputStream 和 OutputStream 的区别
| InputStream | OutputStream |
|---|---|
| 1. It is an abstract class that describes Stream Input. | 1. It is an abstract class that describes Stream Output. |
| 2. InputStream Read data from the source once at a time. | 2. OutputStream Write Data to the destination once at a time. |
|
3. InputStream consist of method which performs:
|
3. Output Stream consists of methods which perform:
|
|
4. Types of InputStream are:
In these types the most important and mostly used type is FileInputStream. |
4. Types of OutputStream are:
In these types the most important and mostly used type is FileOutput Stream. |
InputStream 的程序:
在本程序中,文件 gfg.txt 由“GEEKSFORGEEKS”组成。
注意:在文件保存在Java程序保存的同一位置然后按照下面的程序。如果文件保存在某个特定位置,则写入详细信息,例如。
FileInputStream fileIn=new FileInputStream("C:\\gfg.txt"); Java
// Imported to use methods
import java.io.FileInputStream;
// Main Class
public class InputStreamExample {
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Reading from Source file
try {
FileInputStream fileIn
= new FileInputStream("gfg.txt");
int i = 0;
while ((i = fileIn.read()) != -1) {
System.out.print((char)i);
}
fileIn.close();
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}Java
// Imported to use inbuilt methods
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
// Main class
public class OutputStreamExample {
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Writing in file gfg.txt
try {
FileOutputStream fileOut
= new FileOutputStream("gfg.txt");
String s = "GeeksforGeeks";
// converting string into byte array
byte b[] = s.getBytes();
fileOut.write(b);
fileOut.close();
System.out.println(
"file is successfully updated!!");
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}输出:
GEEKSFORGEEKS 输出流程序
这里 gfg.txt 文件是空的,并且保存在Java Program 的保存位置。该程序将 GeeksforGeeks 写入空文件,如果文本成功写入文件,则显示消息“文件已成功更新”。
Java
// Imported to use inbuilt methods
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
// Main class
public class OutputStreamExample {
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Writing in file gfg.txt
try {
FileOutputStream fileOut
= new FileOutputStream("gfg.txt");
String s = "GeeksforGeeks";
// converting string into byte array
byte b[] = s.getBytes();
fileOut.write(b);
fileOut.close();
System.out.println(
"file is successfully updated!!");
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}
输出:
file is successfully updated!!当我们再次使用第一个程序读取文件时,输出如下所示:
GeeksforGeeks