1.远程方法调用(RMI):
RMI 应用程序提供两个独立的程序,服务器和客户端。有一些任务是由服务器程序执行的,即创建一些远程对象,引用这个对象,并等待客户端,以便他们调用这些对象上的方法。客户端程序获取对服务器上一个或多个远程对象的远程引用,并调用它们的方法。基本上,RMI 提供了服务器和客户端可以通过它来回通信和传递信息的机制。 RMI 由三层组成:
- 存根/骨架层
- 远程参考层
- 传输层
这些层之间的关系如下图所示:
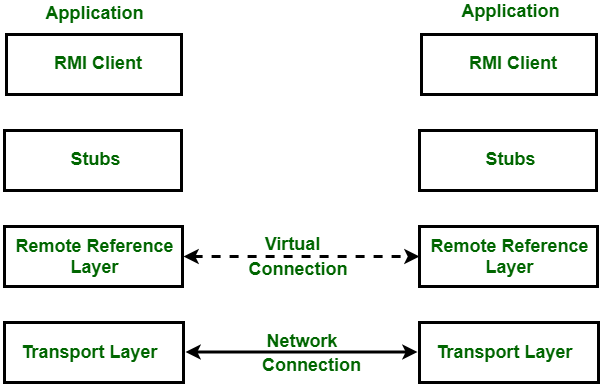
图 – RMI 架构
2. 通用对象请求代理架构(CORBA):
它是对象管理组开发的标准,用于提供分布式对象之间的互操作性。它是世界领先的中间件解决方案。它支持信息、独立硬件平台、编程语言和操作系统的交换。它通常被定义为“软件总线”,因为它是一种基于软件的通信接口,通过它可以定位和访问对象。

图 – CORBA 体系结构
RMI 和 CORBA 的区别:
| RMI | CORBA |
|---|---|
| RMI is a Java-specific technology. | CORBA has implementation for many languages. |
| It uses Java interface for implementation. | It uses Interface Definition Language (IDL) to separate interface from implementation. |
| RMI objects are garbage collected automatically. | CORBA objects are not garbage collected because it is language independent and some languages like C++ does not support garbage collection. |
| RMI programs can download new classes from remote JVM’s. | CORBA does not this code sharing mechanism. |
| RMI passes objects by remote reference or by value. | CORBA passes objects by reference. |
| Java RMI is a server-centric model. | CORBA is a peer-to-peer system. |
| RMI uses the Java Remote Method Protocol as its underlying remoting protocol. | CORBA use Internet Inter- ORB Protocol as its underlying remoting protocol. |
| The responsibility of locating an object implementation falls on JVM. | The responsibility of locating an object implementation falls on Object Adapter either Basic Object Adapter or Portable Object Adapter. |