给定一个正整数N ,任务是找到用尺寸为2 × 1 , 1 × 2的瓷砖(也称为多米诺骨牌)和一个“ L ”形瓷砖填充尺寸为2*N的板的方法数(也称为tromino )如下所示,可以旋转90度。
The L shape tile:
XX
X
After rotating L shape tile by 90:
XX
X
or
X
XX例子:
Input: N = 3
Output: 5
Explanation:
Below is the image to illustrate all the combinations:
Input: N = 1
Output: 1
方法:可以根据以下观察结果解决给定的问题:
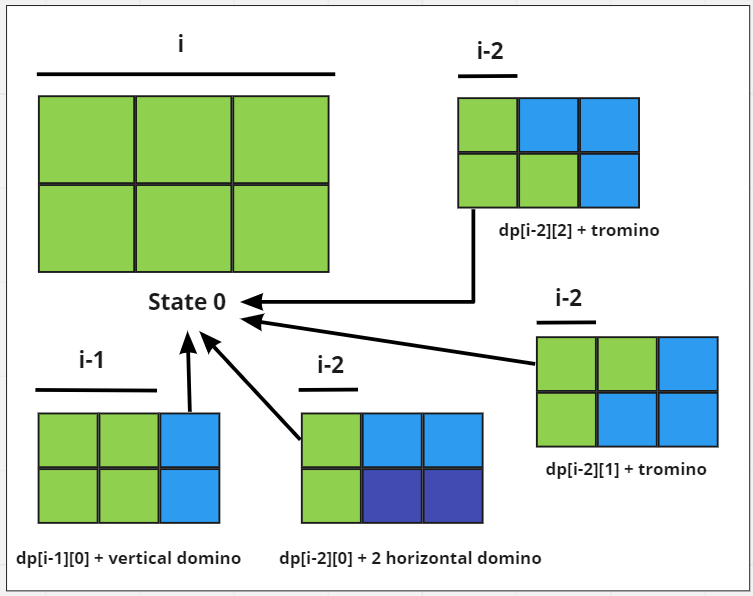
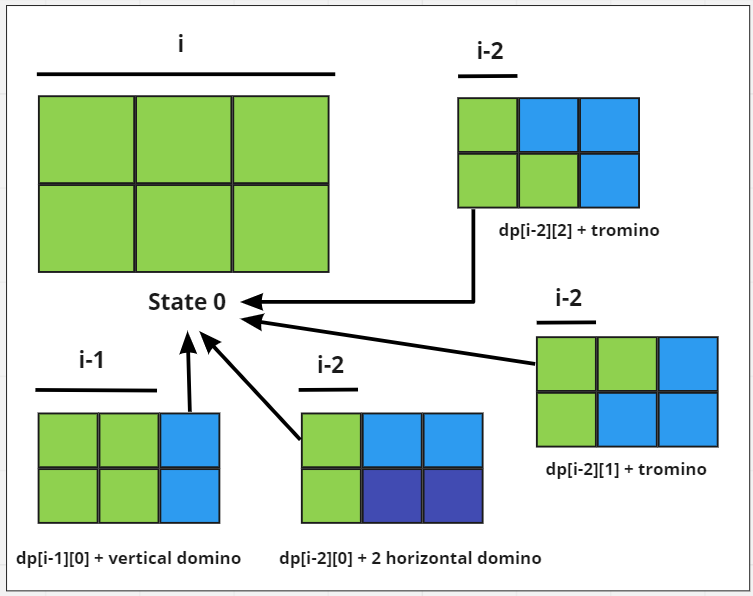
让我们定义一个2状态,动态规划说dp[i, j]表示列索引i中的以下安排之一。
- 当前列可以在状态0下被填充1,2×1张多米诺骨牌,如果前一列有状态0。
- 当前列可以填充有2,1×2在状态0水平骨牌中,如果i – 2列具有状态0。
- 如果前一列的状态为0 ,则当前列可以用状态1和状态2的“ L ”形多米诺骨牌填充。
- 如果前一列具有状态2或在状态2 中(如果前一列具有状态1 ) ,则当前列可以在状态1 中填充1 × 2形状的多米诺骨牌。
- 因此,状态的转移可以定义如下:
- dp[i][0] = (dp[i – 1][0] + dp[i – 2][0]+ dp[i – 2][1] + dp[i – 2][2]) 。
- dp[i][1] = dp[i – 1][0] + dp[i – 1][2] 。
- dp[i][2] = dp[i – 1][0] + dp[i – 1][1] 。
根据以上观察,请按照以下步骤解决问题:
- 如果N的值小于3 ,则打印N作为总路数。
- 初始化一个二维数组,比如说dp[][3] ,它存储了 dp 的所有状态。
- 考虑基本情况: dp[0][0] = dp[1][0] = dp[1][1] = dp[1][2] = 1 。
- 迭代给定范围[2, N]并使用变量i并在 dp 中执行以下转换:
- dp[i][0]等于(dp[i – 1][0] + dp[i – 2][0]+ dp[i – 2][1] + dp[i – 2][2]) 。
- dp[i][1]等于dp[i – 1][0] + dp[i – 1][2] 。
- dp[i][2]等于dp[i – 1][0] + dp[i – 1][1] 。
- 完成上述步骤后,打印dp[N][0] 中存储的总路数。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
const long long MOD = 1e9 + 7;
// Function to find the total number
// of ways to tile a 2*N board using
// the given types of tile
int numTilings(int N)
{
// If N is less than 3
if (N < 3) {
return N;
}
// Store all dp-states
vector > dp(
N + 1, vector(3, 0));
// Base Case
dp[0][0] = dp[1][0] = 1;
dp[1][1] = dp[1][2] = 1;
// Traverse the range [2, N]
for (int i = 2; i <= N; i++) {
// Update the value of dp[i][0]
dp[i][0] = (dp[i - 1][0]
+ dp[i - 2][0]
+ dp[i - 2][1]
+ dp[i - 2][2])
% MOD;
// Update the value of dp[i][1]
dp[i][1] = (dp[i - 1][0]
+ dp[i - 1][2])
% MOD;
// Update the value of dp[i][2]
dp[i][2] = (dp[i - 1][0]
+ dp[i - 1][1])
% MOD;
}
// Return the number of ways as
// the value of dp[N][0]
return dp[N][0];
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int N = 3;
cout << numTilings(N);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.util.Arrays;
class GFG{
public static long MOD = 1000000007l;
// Function to find the total number
// of ways to tile a 2*N board using
// the given types of tile
public static long numTilings(int N)
{
// If N is less than 3
if (N < 3)
{
return N;
}
// Store all dp-states
long[][] dp = new long[N + 1][3];
for(long[] row : dp)
{
Arrays.fill(row, 0);
}
// Base Case
dp[0][0] = dp[1][0] = 1;
dp[1][1] = dp[1][2] = 1;
// Traverse the range [2, N]
for(int i = 2; i <= N; i++)
{
// Update the value of dp[i][0]
dp[i][0] = (dp[i - 1][0] + dp[i - 2][0] +
dp[i - 2][1] + dp[i - 2][2]) % MOD;
// Update the value of dp[i][1]
dp[i][1] = (dp[i - 1][0] + dp[i - 1][2]) % MOD;
// Update the value of dp[i][2]
dp[i][2] = (dp[i - 1][0] + dp[i - 1][1]) % MOD;
}
// Return the number of ways as
// the value of dp[N][0]
return dp[N][0];
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String args[])
{
int N = 3;
System.out.println(numTilings(N));
}
}
// This code is contributed by gfgkingPython3
# Python3 program for the above approache9 + 7;
# Function to find the total number
# of ways to tile a 2*N board using
# the given types of tile
MOD = 1e9 + 7
def numTilings(N):
# If N is less than 3
if (N < 3):
return N
# Store all dp-states
dp = [[0] * 3 for i in range(N + 1)]
# Base Case
dp[0][0] = dp[1][0] = 1
dp[1][1] = dp[1][2] = 1
# Traverse the range [2, N]
for i in range(2, N + 1):
# Update the value of dp[i][0]
dp[i][0] = (dp[i - 1][0] +
dp[i - 2][0] +
dp[i - 2][1] +
dp[i - 2][2]) % MOD
# Update the value of dp[i][1]
dp[i][1] = (dp[i - 1][0] +
dp[i - 1][2]) % MOD
# Update the value of dp[i][2]
dp[i][2] = (dp[i - 1][0] +
dp[i - 1][1]) % MOD
# Return the number of ways as
# the value of dp[N][0]
return int(dp[N][0])
# Driver Code
N = 3
print(numTilings(N))
# This code is contributed by gfgkingC#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG{
static int MOD = 1000000007;
// Function to find the total number
// of ways to tile a 2*N board using
// the given types of tile
static int numTilings(int N)
{
// If N is less than 3
if (N < 3) {
return N;
}
// Store all dp-states
int [,]dp = new int[N+1,3];
// Base Case
dp[0,0] = dp[1,0] = 1;
dp[1,1] = dp[1,2] = 1;
// Traverse the range [2, N]
for (int i = 2; i <= N; i++) {
// Update the value of dp[i,0]
dp[i,0] = (dp[i - 1,0]
+ dp[i - 2,0]
+ dp[i - 2,1]
+ dp[i - 2,2])
% MOD;
// Update the value of dp[i,1]
dp[i,1] = (dp[i - 1,0]
+ dp[i - 1,2])
% MOD;
// Update the value of dp[i,2]
dp[i,2] = (dp[i - 1,0]
+ dp[i - 1,1])
% MOD;
}
// Return the number of ways as
// the value of dp[N,0]
return dp[N,0];
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main()
{
int N = 3;
Console.Write(numTilings(N));
}
}
// This code is contributed by SURENDRA_GANGWAR.Javascript
输出:
5时间复杂度: O(N)
辅助空间: O(N)
如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。