给定一个由 n 组成的板,其中 n 的形式为 2 k ,其中 k >= 1(基本上 n 是 2 的幂,最小值为 2)。板上缺少一个单元格(大小为 1 x 1)。使用 L 形瓷砖填充板。 AL 形瓷砖是一个 2 x 2 的正方形,缺少一个大小为 1×1 的单元格。
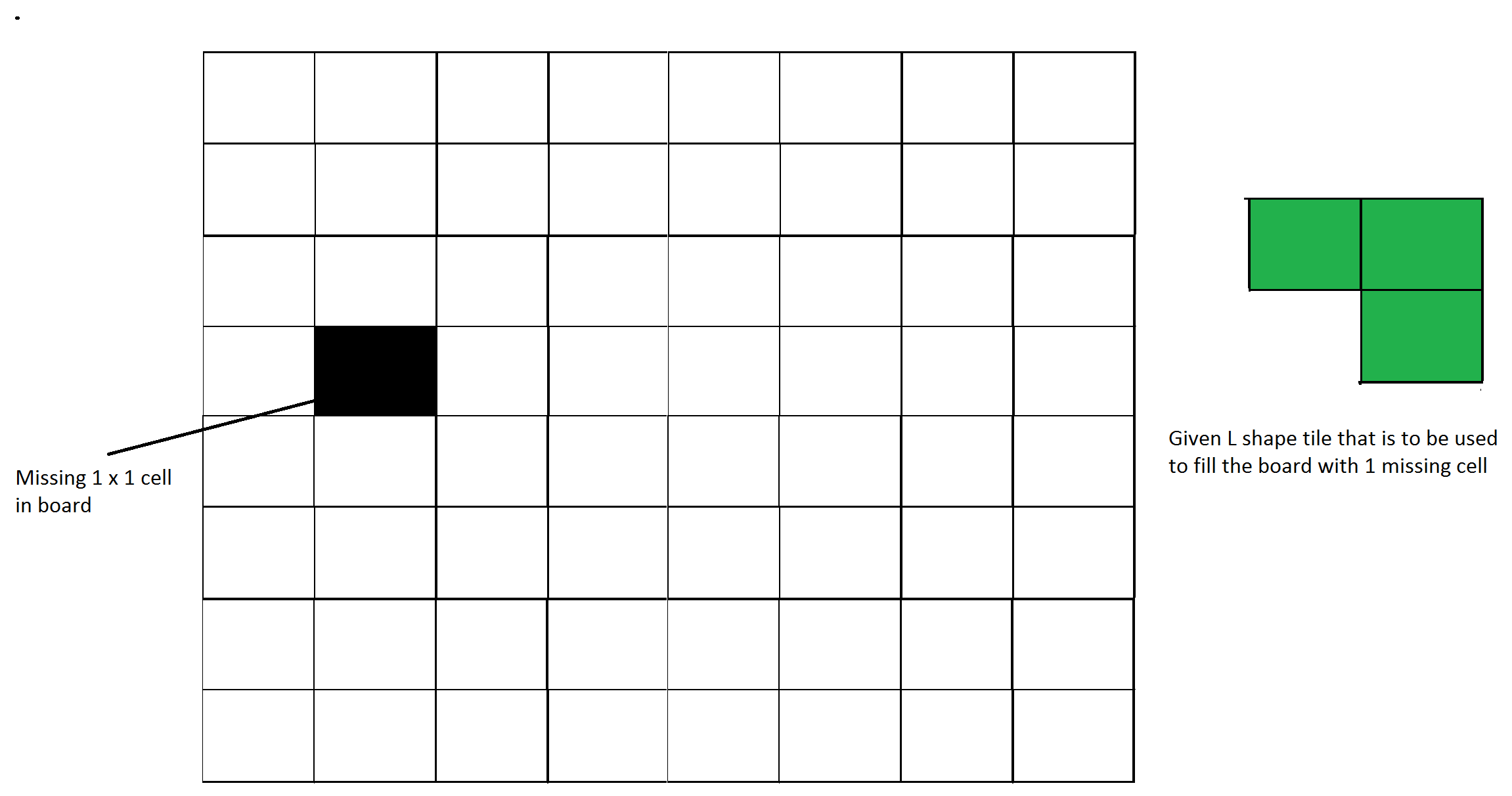
图 1:示例输入
这个问题可以用分而治之来解决。下面是递归算法。
// n is size of given square, p is location of missing cell
Tile(int n, Point p)
1) Base case: n = 2, A 2 x 2 square with one cell missing is nothing
but a tile and can be filled with a single tile.
2) Place a L shaped tile at the center such that it does not cover
the n/2 * n/2 subsquare that has a missing square. Now all four
subsquares of size n/2 x n/2 have a missing cell (a cell that doesn't
need to be filled). See figure 2 below.
3) Solve the problem recursively for following four. Let p1, p2, p3 and
p4 be positions of the 4 missing cells in 4 squares.
a) Tile(n/2, p1)
b) Tile(n/2, p2)
c) Tile(n/2, p3)
d) Tile(n/2, p3)下图显示了上述算法的工作
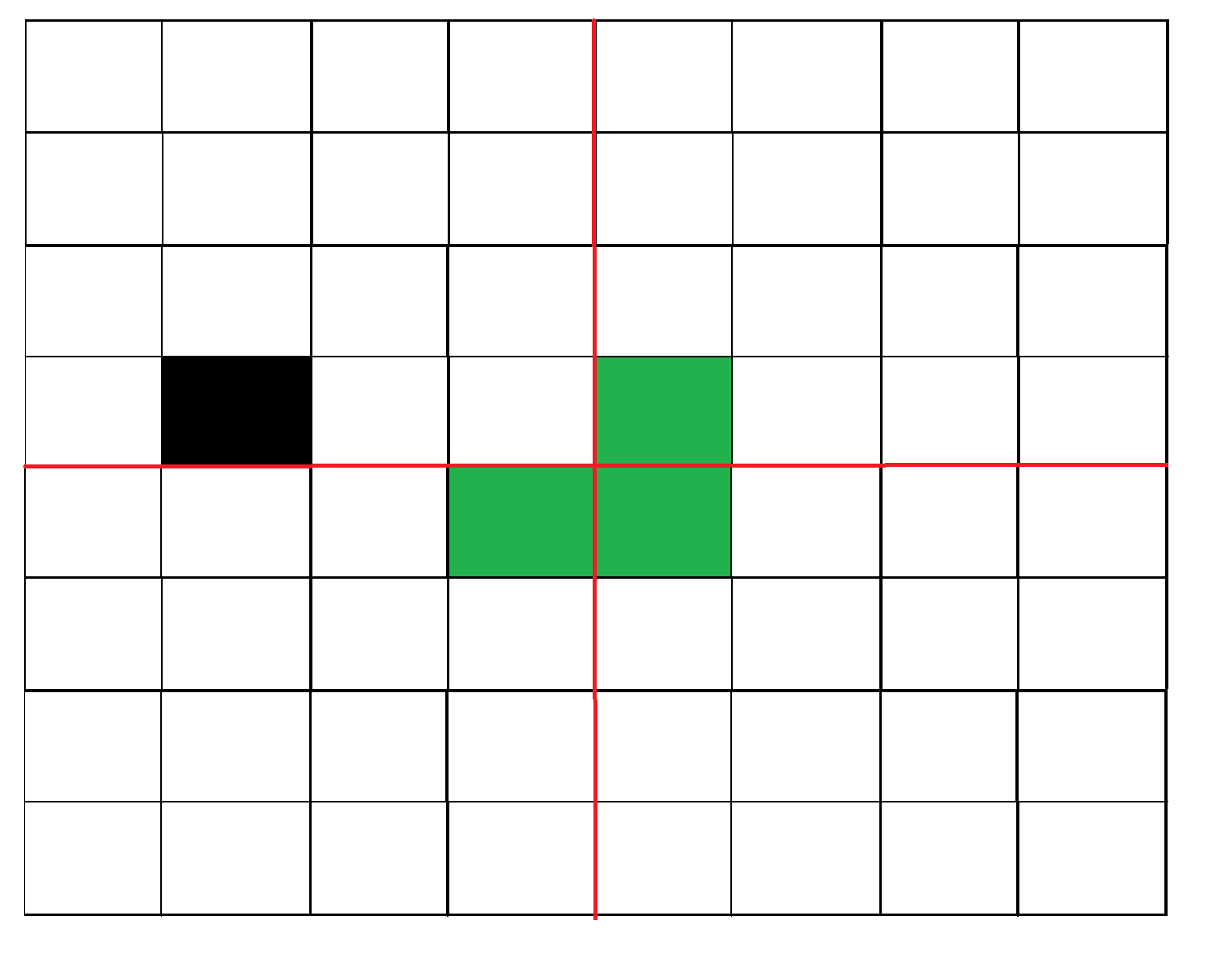
图 2:放置第一块瓷砖后
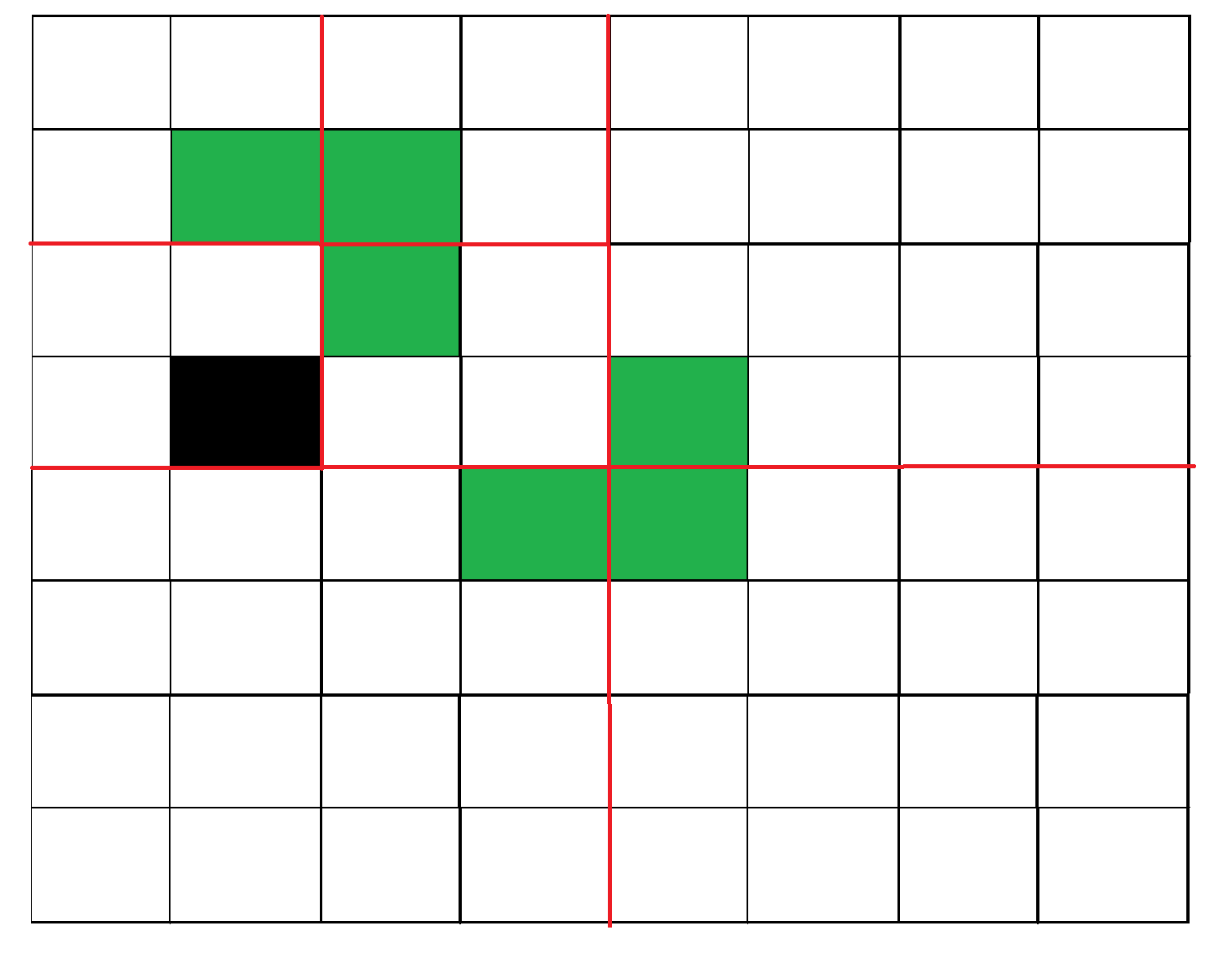
图 3:重复第一个子方格。
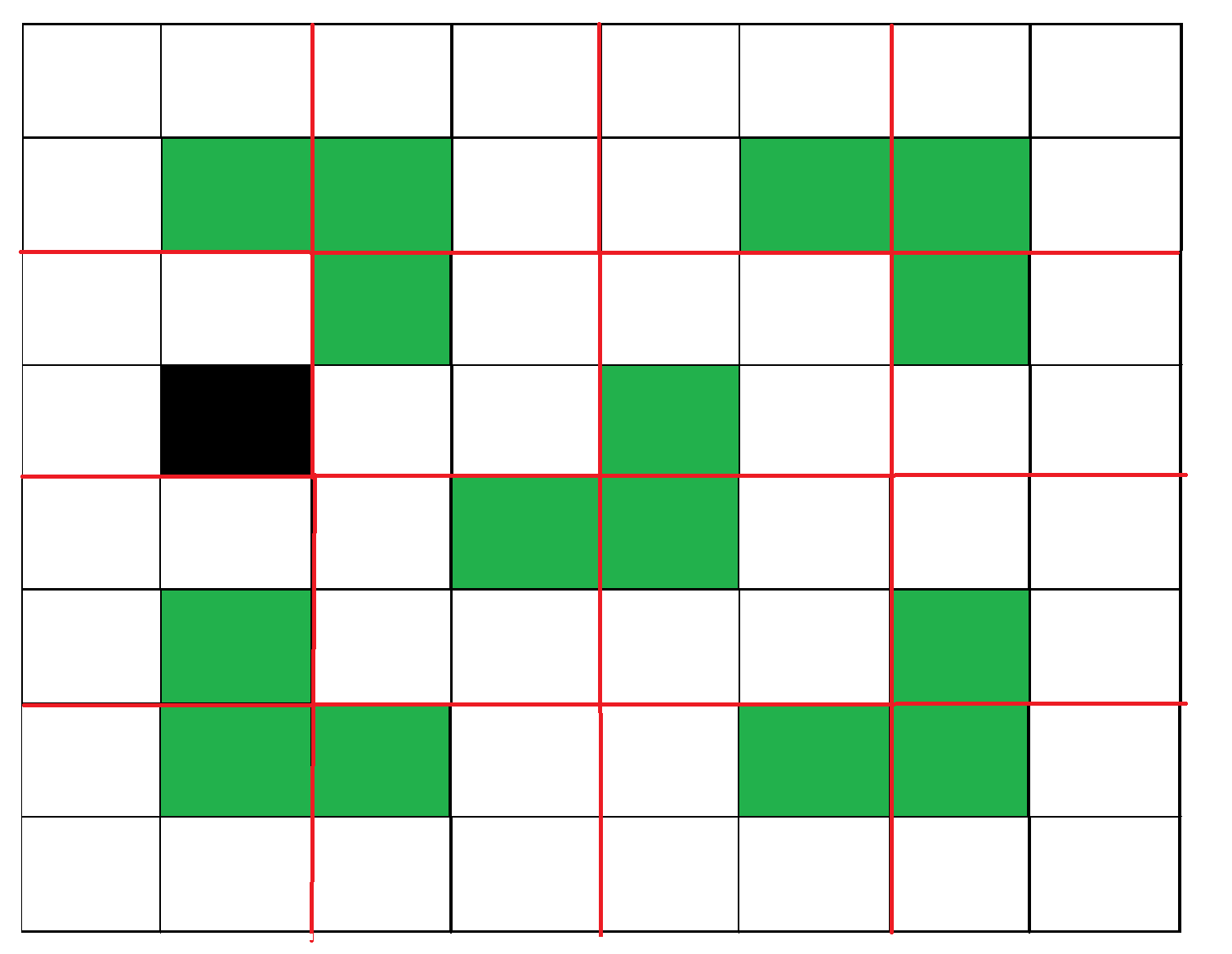
图 4:显示所有四个子方格中的第一步。例子:
Input : size = 2 and mark coordinates = (0, 0)
Output :
-1 1
1 1
Coordinate (0, 0) is marked. So, no tile is there. In the remaining three positions,
a tile is placed with its number as 1.
Input : size = 4 and mark coordinates = (0, 0)
Output :
-1 3 2 2
3 3 1 2
4 1 1 5
4 4 5 5以下是上述想法的 C++ 实现:
CPP
// C++ program to place tiles
#include
using namespace std;
int size_of_grid, b, a, cnt = 0;
int arr[128][128];
// Placing tile at the given coordinates
void place(int x1, int y1, int x2,
int y2, int x3, int y3)
{
cnt++;
arr[x1][y1] = cnt;
arr[x2][y2] = cnt;
arr[x3][y3] = cnt;
}
// Quadrant names
// 1 2
// 3 4
// Function based on divide and conquer
int tile(int n, int x, int y)
{
int r, c;
if (n == 2) {
cnt++;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (arr[x + i][y + j] == 0) {
arr[x + i][y + j] = cnt;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
// finding hole location
for (int i = x; i < x + n; i++) {
for (int j = y; j < y + n; j++) {
if (arr[i][j] != 0)
r = i, c = j;
}
}
// If missing tile is 1st quadrant
if (r < x + n / 2 && c < y + n / 2)
place(x + n / 2, y + (n / 2) - 1, x + n / 2,
y + n / 2, x + n / 2 - 1, y + n / 2);
// If missing Tile is in 3rd quadrant
else if (r >= x + n / 2 && c < y + n / 2)
place(x + (n / 2) - 1, y + (n / 2), x + (n / 2),
y + n / 2, x + (n / 2) - 1, y + (n / 2) - 1);
// If missing Tile is in 2nd quadrant
else if (r < x + n / 2 && c >= y + n / 2)
place(x + n / 2, y + (n / 2) - 1, x + n / 2,
y + n / 2, x + n / 2 - 1, y + n / 2 - 1);
// If missing Tile is in 4th quadrant
else if (r >= x + n / 2 && c >= y + n / 2)
place(x + (n / 2) - 1, y + (n / 2), x + (n / 2),
y + (n / 2) - 1, x + (n / 2) - 1,
y + (n / 2) - 1);
// diving it again in 4 quadrants
tile(n / 2, x, y + n / 2);
tile(n / 2, x, y);
tile(n / 2, x + n / 2, y);
tile(n / 2, x + n / 2, y + n / 2);
return 0;
}
// Driver program to test above function
int main()
{
// size of box
size_of_grid = 8;
memset(arr, 0, sizeof(arr));
// Coordinates which will be marked
a = 0, b = 0;
// Here tile can not be placed
arr[a][b] = -1;
tile(size_of_grid, 0, 0);
// The grid is
for (int i = 0; i < size_of_grid; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < size_of_grid; j++)
cout << arr[i][j] << " \t";
cout << "\n";
}
} Java
// Java program to place tiles
public class GFG
{
static int size_of_grid, b, a, cnt = 0;
static int[][] arr = new int[128][128];
// Placing tile at the given coordinates
static void place(int x1, int y1, int x2,
int y2, int x3, int y3)
{
cnt++;
arr[x1][y1] = cnt;
arr[x2][y2] = cnt;
arr[x3][y3] = cnt;
}
// Quadrant names
// 1 2
// 3 4
// Function based on divide and conquer
static int tile(int n, int x, int y)
{
int r = 0, c = 0;
if (n == 2)
{
cnt++;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
if (arr[x + i][y + j] == 0)
{
arr[x + i][y + j] = cnt;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
// finding hole location
for (int i = x; i < x + n; i++)
{
for (int j = y; j < y + n; j++)
{
if (arr[i][j] != 0)
{
r = i;
c = j;
}
}
}
// If missing tile is 1st quadrant
if (r < x + n / 2 && c < y + n / 2)
place(x + n / 2, y + (n / 2) - 1, x + n / 2,
y + n / 2, x + n / 2 - 1, y + n / 2);
// If missing Tile is in 3rd quadrant
else if (r >= x + n / 2 && c < y + n / 2)
place(x + (n / 2) - 1, y + (n / 2), x + (n / 2),
y + n / 2, x + (n / 2) - 1, y + (n / 2) - 1);
// If missing Tile is in 2nd quadrant
else if (r < x + n / 2 && c >= y + n / 2)
place(x + n / 2, y + (n / 2) - 1, x + n / 2,
y + n / 2, x + n / 2 - 1, y + n / 2 - 1);
// If missing Tile is in 4th quadrant
else if (r >= x + n / 2 && c >= y + n / 2)
place(x + (n / 2) - 1, y + (n / 2), x + (n / 2),
y + (n / 2) - 1, x + (n / 2) - 1,
y + (n / 2) - 1);
// diving it again in 4 quadrants
tile(n / 2, x, y + n / 2);
tile(n / 2, x, y);
tile(n / 2, x + n / 2, y);
tile(n / 2, x + n / 2, y + n / 2);
return 0;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// size of box
size_of_grid = 8;
// Coordinates which will be marked
a = 0; b = 0;
// Here tile can not be placed
arr[a][b] = -1;
tile(size_of_grid, 0, 0);
// The grid is
for (int i = 0; i < size_of_grid; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < size_of_grid; j++)
System.out.print(arr[i][j] + " ");
System.out.println();;
}
}
}
// This code is contributed by divyeshrabadiya07.C#
// C# program to place tiles
using System;
class GFG
{
static int size_of_grid, b, a, cnt = 0;
static int[,] arr = new int[128, 128];
// Placing tile at the given coordinates
static void place(int x1, int y1, int x2,
int y2, int x3, int y3)
{
cnt++;
arr[x1, y1] = cnt;
arr[x2, y2] = cnt;
arr[x3, y3] = cnt;
}
// Quadrant names
// 1 2
// 3 4
// Function based on divide and conquer
static int tile(int n, int x, int y)
{
int r = 0, c = 0;
if (n == 2)
{
cnt++;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
if (arr[x + i, y + j] == 0)
{
arr[x + i, y + j] = cnt;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
// finding hole location
for (int i = x; i < x + n; i++)
{
for (int j = y; j < y + n; j++)
{
if (arr[i, j] != 0)
{
r = i;
c = j;
}
}
}
// If missing tile is 1st quadrant
if (r < x + n / 2 && c < y + n / 2)
place(x + n / 2, y + (n / 2) - 1, x + n / 2,
y + n / 2, x + n / 2 - 1, y + n / 2);
// If missing Tile is in 3rd quadrant
else if (r >= x + n / 2 && c < y + n / 2)
place(x + (n / 2) - 1, y + (n / 2), x + (n / 2),
y + n / 2, x + (n / 2) - 1, y + (n / 2) - 1);
// If missing Tile is in 2nd quadrant
else if (r < x + n / 2 && c >= y + n / 2)
place(x + n / 2, y + (n / 2) - 1, x + n / 2,
y + n / 2, x + n / 2 - 1, y + n / 2 - 1);
// If missing Tile is in 4th quadrant
else if (r >= x + n / 2 && c >= y + n / 2)
place(x + (n / 2) - 1, y + (n / 2), x + (n / 2),
y + (n / 2) - 1, x + (n / 2) - 1,
y + (n / 2) - 1);
// diving it again in 4 quadrants
tile(n / 2, x, y + n / 2);
tile(n / 2, x, y);
tile(n / 2, x + n / 2, y);
tile(n / 2, x + n / 2, y + n / 2);
return 0;
}
// Driver code
static void Main()
{
// size of box
size_of_grid = 8;
// Coordinates which will be marked
a = 0; b = 0;
// Here tile can not be placed
arr[a, b] = -1;
tile(size_of_grid, 0, 0);
// The grid is
for (int i = 0; i < size_of_grid; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < size_of_grid; j++)
Console.Write(arr[i,j] + " ");
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
}
// This code is contributed by divyesh072019.Python3
# Python3 program to place tiles
size_of_grid = 0
b = 0
a = 0
cnt = 0
arr = [[0 for i in range(128)] for j in range(128)]
def place(x1, y1, x2, y2, x3, y3):
global cnt
cnt += 1
arr[x1][y1] = cnt;
arr[x2][y2] = cnt;
arr[x3][y3] = cnt;
def tile(n, x, y):
global cnt
r = 0
c = 0
if (n == 2):
cnt += 1
for i in range(n):
for j in range(n):
if(arr[x + i][y + j] == 0):
arr[x + i][y + j] = cnt
return 0;
for i in range(x, x + n):
for j in range(y, y + n):
if (arr[i][j] != 0):
r = i
c = j
if (r < x + n / 2 and c < y + n / 2):
place(x + int(n / 2), y + int(n / 2) - 1, x + int(n / 2), y + int(n / 2), x + int(n / 2) - 1, y + int(n / 2))
elif(r >= x + int(n / 2) and c < y + int(n / 2)):
place(x + int(n / 2) - 1, y + int(n / 2), x + int(n / 2), y + int(n / 2), x + int(n / 2) - 1, y + int(n / 2) - 1)
elif(r < x + int(n / 2) and c >= y + int(n / 2)):
place(x + int(n / 2), y + int(n / 2) - 1, x + int(n / 2), y + int(n / 2), x + int(n / 2) - 1, y + int(n / 2) - 1)
elif(r >= x + int(n / 2) and c >= y + int(n / 2)):
place(x + int(n / 2) - 1, y + int(n / 2), x + int(n / 2), y + int(n / 2) - 1, x + int(n / 2) - 1, y + int(n / 2) - 1)
tile(int(n / 2), x, y + int(n / 2));
tile(int(n / 2), x, y);
tile(int(n / 2), x + int(n / 2), y);
tile(int(n / 2), x + int(n / 2), y + int(n / 2));
return 0
size_of_grid = 8
a = 0
b = 0
arr[a][b] = -1
tile(size_of_grid, 0, 0)
for i in range(size_of_grid):
for j in range(size_of_grid):
print(arr[i][j], end=" ")
print()
# This code is contributed by rag2127输出
-1 9 8 8 4 4 3 3
9 9 7 8 4 2 2 3
10 7 7 11 5 5 2 6
10 10 11 11 1 5 6 6
14 14 13 1 1 19 18 18
14 12 13 13 19 19 17 18
15 12 12 16 20 17 17 21
15 15 16 16 20 20 21 21 时间复杂度:
上述递归算法的递归关系可以写成如下。 C 是常数。
T(n) = 4T(n/2) + C
上述递归可以使用 Master Method 求解,时间复杂度为 O(n 2 )
这是如何运作的?
分治算法的工作原理可以用数学归纳法证明。让输入正方形的大小为 2 k x 2 k ,其中 k >=1。
基本情况:我们知道问题可以在 k = 1 时解决。我们有一个 2 x 2 的正方形,缺少一个单元格。
归纳假设:令问题可解为 k-1。
现在我们需要证明如果问题可以解决k-1,那么问题就可以解决k。对于 k,我们在中间放置了一个 L 形瓷砖,我们有四个尺寸为 2 k-1 x 2 k-1 的子方块,如上图 2 所示。所以如果我们能解 4 个子方格,我们就可以解出完整的方格。
如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。