给定 n 个骰子,每个骰子有 m 个面,编号从 1 到 m,求求和 X 的方法数。X 是当所有骰子都掷出时每个面上的值的总和。
朴素的方法是从 n 个骰子中找到所有可能的值组合,并继续计算总和为 X 的结果。
使用动态规划 (DP)可以有效地解决此问题。
Let the function to find X from n dice is: Sum(m, n, X)
The function can be represented as:
Sum(m, n, X) = Finding Sum (X - 1) from (n - 1) dice plus 1 from nth dice
+ Finding Sum (X - 2) from (n - 1) dice plus 2 from nth dice
+ Finding Sum (X - 3) from (n - 1) dice plus 3 from nth dice
...................................................
...................................................
...................................................
+ Finding Sum (X - m) from (n - 1) dice plus m from nth dice
So we can recursively write Sum(m, n, x) as following
Sum(m, n, X) = Sum(m, n - 1, X - 1) +
Sum(m, n - 1, X - 2) +
.................... +
Sum(m, n - 1, X - m)为什么采用 DP 方法?
上述问题表现出重叠的子问题。见下图。另请参阅此递归实现。假设有 3 个骰子,每个骰子有 6 个面,我们需要找到求和 8 的方法数:
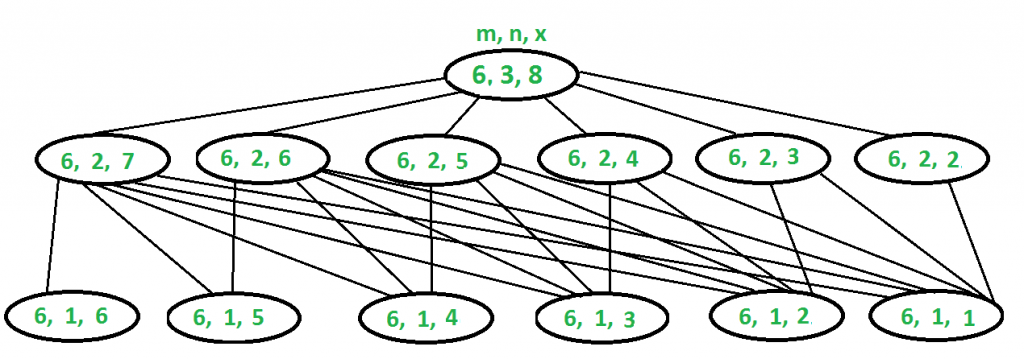
Sum(6, 3, 8) = Sum(6, 2, 7) + Sum(6, 2, 6) + Sum(6, 2, 5) +
Sum(6, 2, 4) + Sum(6, 2, 3) + Sum(6, 2, 2)
To evaluate Sum(6, 3, 8), we need to evaluate Sum(6, 2, 7) which can
recursively written as following:
Sum(6, 2, 7) = Sum(6, 1, 6) + Sum(6, 1, 5) + Sum(6, 1, 4) +
Sum(6, 1, 3) + Sum(6, 1, 2) + Sum(6, 1, 1)
We also need to evaluate Sum(6, 2, 6) which can recursively written
as following:
Sum(6, 2, 6) = Sum(6, 1, 5) + Sum(6, 1, 4) + Sum(6, 1, 3) +
Sum(6, 1, 2) + Sum(6, 1, 1)
..............................................
..............................................
Sum(6, 2, 2) = Sum(6, 1, 1)请仔细看看上面的递归。 RED中的子问题第一次解决, BLUE中的子问题再次解决(展示重叠的子问题)。因此,存储解决的子问题的结果可以节省时间。
以下是动态规划方法的实现。
C++
// C++ program to find number of ways to get sum 'x' with 'n'
// dice where every dice has 'm' faces
#include
#include
using namespace std;
// The main function that returns number of ways to get sum 'x'
// with 'n' dice and 'm' with m faces.
int findWays(int m, int n, int x)
{
// Create a table to store results of subproblems. One extra
// row and column are used for simpilicity (Number of dice
// is directly used as row index and sum is directly used
// as column index). The entries in 0th row and 0th column
// are never used.
int table[n + 1][x + 1];
memset(table, 0, sizeof(table)); // Initialize all entries as 0
// Table entries for only one dice
for (int j = 1; j <= m && j <= x; j++)
table[1][j] = 1;
// Fill rest of the entries in table using recursive relation
// i: number of dice, j: sum
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = 1; j <= x; j++)
for (int k = 1; k <= m && k < j; k++)
table[i][j] += table[i-1][j-k];
/* Uncomment these lines to see content of table
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j <= x; j++)
cout << table[i][j] << " ";
cout << endl;
} */
return table[n][x];
}
// Driver program to test above functions
int main()
{
cout << findWays(4, 2, 1) << endl;
cout << findWays(2, 2, 3) << endl;
cout << findWays(6, 3, 8) << endl;
cout << findWays(4, 2, 5) << endl;
cout << findWays(4, 3, 5) << endl;
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to find number of ways to get sum 'x' with 'n'
// dice where every dice has 'm' faces
import java.util.*;
import java.lang.*;
import java.io.*;
class GFG {
/* The main function that returns the number of ways to get sum 'x' with 'n' dice and 'm' with m faces. */
public static long findWays(int m, int n, int x){
/* Create a table to store the results of subproblems.
One extra row and column are used for simplicity
(Number of dice is directly used as row index and sum is directly used as column index).
The entries in 0th row and 0th column are never used. */
long[][] table = new long[n+1][x+1];
/* Table entries for only one dice */
for(int j = 1; j <= m && j <= x; j++)
table[1][j] = 1;
/* Fill rest of the entries in table using recursive relation
i: number of dice, j: sum */
for(int i = 2; i <= n;i ++){
for(int j = 1; j <= x; j++){
for(int k = 1; k < j && k <= m; k++)
table[i][j] += table[i-1][j-k];
}
}
/* Uncomment these lines to see content of table
for(int i = 0; i< n+1; i++){
for(int j = 0; j< x+1; j++)
System.out.print(dt[i][j] + " ");
System.out.println();
} */
return table[n][x];
}
// Driver Code
public static void main (String[] args) {
System.out.println(findWays(4, 2, 1));
System.out.println(findWays(2, 2, 3));
System.out.println(findWays(6, 3, 8));
System.out.println(findWays(4, 2, 5));
System.out.println(findWays(4, 3, 5));
}
}
// This code is contributed by MaheshwariPiyushPython3
# Python3 program to find the number of ways to get sum 'x' with 'n' dice
# where every dice has 'm' faces
# The main function that returns number of ways to get sum 'x'
# with 'n' dice and 'm' with m faces.
def findWays(m,n,x):
# Create a table to store results of subproblems. One extra
# row and column are used for simpilicity (Number of dice
# is directly used as row index and sum is directly used
# as column index). The entries in 0th row and 0th column
# are never used.
table=[[0]*(x+1) for i in range(n+1)] #Initialize all entries as 0
for j in range(1,min(m+1,x+1)): #Table entries for only one dice
table[1][j]=1
# Fill rest of the entries in table using recursive relation
# i: number of dice, j: sum
for i in range(2,n+1):
for j in range(1,x+1):
for k in range(1,min(m+1,j)):
table[i][j]+=table[i-1][j-k]
#print(dt)
# Uncomment above line to see content of table
return table[-1][-1]
# Driver code
print(findWays(4,2,1))
print(findWays(2,2,3))
print(findWays(6,3,8))
print(findWays(4,2,5))
print(findWays(4,3,5))
# This code is contributed by MaheshwariPiyushC#
// C# program to find number
// of ways to get sum 'x'
// with 'n' dice where every
// dice has 'm' faces
using System;
class GFG
{
// The main function that returns
// number of ways to get sum 'x'
// with 'n' dice and 'm' with m faces.
static int findWays(int m,
int n, int x)
{
// Create a table to store
// results of subproblems.
// row and column are used
// for simpilicity (Number
// of dice is directly used
// as row index and sum is
// directly used as column
// index). The entries in 0th
// row and 0th column are
// never used.
int[,] table = new int[n + 1,
x + 1];
// Initialize all
// entries as 0
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = 0; j <= x; j++)
table[i, j] = 0;
// Table entries for
// only one dice
for (int j = 1;
j <= m && j <= x; j++)
table[1, j] = 1;
// Fill rest of the entries
// in table using recursive
// relation i: number of
// dice, j: sum
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = 1; j <= x; j++)
for (int k = 1;
k <= m && k < j; k++)
table[i, j] += table[i - 1,
j - k];
/* Uncomment these lines to
see content of table
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j <= x; j++)
cout << table[i][j] << " ";
cout << endl;
} */
return table[n, x];
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main()
{
Console.WriteLine(findWays(4, 2, 1));
Console.WriteLine(findWays(2, 2, 3));
Console.WriteLine(findWays(6, 3, 8));
Console.WriteLine(findWays(4, 2, 5));
Console.WriteLine(findWays(4, 3, 5));
}
}
// This code is contributed by mits.PHP
Javascript
C++
// When x is so high that sum can not go beyond x even when we
// get maximum value in every dice throw.
if (m*n <= x)
return (m*n == x);
// When x is too low
if (n >= x)
return (n == x);C++
// C++ program
// The main function that returns number of ways to get sum 'x'
// with 'n' dice and 'm' with m faces.
#include
using namespace std;
long findWays(int f, int d, int s)
{
// Create a table to store results of subproblems. One extra
// row and column are used for simpilicity (Number of dice
// is directly used as row index and sum is directly used
// as column index). The entries in 0th row and 0th column
// are never used.
long mem[d + 1][s + 1];
memset(mem,0,sizeof mem);
// Table entries for no dices
// If you do not have any data, then the value must be 0, so the result is 1
mem[0][0] = 1;
// Iterate over dices
for (int i = 1; i <= d; i++)
{
// Iterate over sum
for (int j = i; j <= s; j++)
{
// The result is obtained in two ways, pin the current dice and spending 1 of the value,
// so we have mem[i-1][j-1] remaining combinations, to find the remaining combinations we
// would have to pin the values ??above 1 then we use mem[i][j-1] to sum all combinations
// that pin the remaining j-1's. But there is a way, when "j-f-1> = 0" we would be adding
// extra combinations, so we remove the combinations that only pin the extrapolated dice face and
// subtract the extrapolated combinations.
mem[i][j] = mem[i][j - 1] + mem[i - 1][j - 1];
if (j - f - 1 >= 0)
mem[i][j] -= mem[i - 1][j - f - 1];
}
}
return mem[d][s];
}
// Driver code
int main(void)
{
cout << findWays(4, 2, 1) << endl;
cout << findWays(2, 2, 3) << endl;
cout << findWays(6, 3, 8) << endl;
cout << findWays(4, 2, 5) << endl;
cout << findWays(4, 3, 5) << endl;
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by ankush_953 Java
/**
* The main function that returns number of ways to get sum 'x'
* with 'n' dice and 'm' with m faces.
*
* @author Pedro H. Chaves
*/
public class GFG {
/**
* Count ways
*
* @param f
* @param d
* @param s
* @return
*/
public static long findWays(int f, int d, int s) {
// Create a table to store results of subproblems. One extra
// row and column are used for simpilicity (Number of dice
// is directly used as row index and sum is directly used
// as column index). The entries in 0th row and 0th column
// are never used.
long mem[][] = new long[d + 1][s + 1];
// Table entries for no dices
// If you do not have any data, then the value must be 0, so the result is 1
mem[0][0] = 1;
// Iterate over dices
for(int i=1; i<=d; i++) {
// Iterate over sum
for(int j=i; j<=s; j++) {
// The result is obtained in two ways, pin the current dice and spending 1 of the value,
// so we have mem[i-1][j-1] remaining combinations, to find the remaining combinations we
// would have to pin the values ??above 1 then we use mem[i][j-1] to sum all combinations
// that pin the remaining j-1's. But there is a way, when "j-f-1> = 0" we would be adding
// extra combinations, so we remove the combinations that only pin the extrapolated dice face and
// subtract the extrapolated combinations.
mem[i][j] = mem[i][j-1] + mem[i-1][j-1];
if(j-f-1 >= 0)
mem[i][j] -= mem[i-1][j-f-1];
}
}
return mem[d][s];
}
/**
* Main
*
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(findWays(4, 2, 1));
System.out.println(findWays(2, 2, 3));
System.out.println(findWays(6, 3, 8));
System.out.println(findWays(4, 2, 5));
System.out.println(findWays(4, 3, 5));
}
} Python3
# Python program
# The main function that returns number of ways to get sum 'x'
# with 'n' dice and 'm' with m faces.
def findWays(f, d, s):
# Create a table to store results of subproblems. One extra
# row and column are used for simpilicity (Number of dice
# is directly used as row index and sum is directly used
# as column index). The entries in 0th row and 0th column
# are never used.
mem = [[0 for i in range(s+1)] for j in range(d+1)]
# Table entries for no dices
# If you do not have any data, then the value must be 0, so the result is 1
mem[0][0] = 1
# Iterate over dices
for i in range(1, d+1):
# Iterate over sum
for j in range(1, s+1):
# The result is obtained in two ways, pin the current dice and spending 1 of the value,
# so we have mem[i-1][j-1] remaining combinations, to find the remaining combinations we
# would have to pin the values ??above 1 then we use mem[i][j-1] to sum all combinations
# that pin the remaining j-1's. But there is a way, when "j-f-1> = 0" we would be adding
# extra combinations, so we remove the combinations that only pin the extrapolated dice face and
# subtract the extrapolated combinations.
mem[i][j] = mem[i][j - 1] + mem[i - 1][j - 1]
if j - f - 1 >= 0:
mem[i][j] -= mem[i - 1][j - f - 1]
return mem[d][s]
# Driver code
print(findWays(4, 2, 1))
print(findWays(2, 2, 3))
print(findWays(6, 3, 8))
print(findWays(4, 2, 5))
print(findWays(4, 3, 5))
# This code is contributed by ankush_953C#
// C# program
// The main function that returns number of ways to get sum 'x'
// with 'n' dice and 'm' with m faces.
using System;
class GFG
{
/**
* Count ways
*
* @param f
* @param d
* @param s
* @return
*/
public static long findWays(int f, int d, int s)
{
// Create a table to store results of subproblems. One extra
// row and column are used for simpilicity (Number of dice
// is directly used as row index and sum is directly used
// as column index). The entries in 0th row and 0th column
// are never used.
long [,]mem = new long[d + 1,s + 1];
// Table entries for no dices
// If you do not have any data, then the value must be 0, so the result is 1
mem[0,0] = 1;
// Iterate over dices
for(int i = 1; i <= d; i++)
{
// Iterate over sum
for(int j = i; j <= s; j++)
{
// The result is obtained in two ways, pin the current dice and spending 1 of the value,
// so we have mem[i-1,j-1] remaining combinations, to find the remaining combinations we
// would have to pin the values ??above 1 then we use mem[i,j-1] to sum all combinations
// that pin the remaining j-1's. But there is a way, when "j-f-1> = 0" we would be adding
// extra combinations, so we remove the combinations that only pin the extrapolated dice face and
// subtract the extrapolated combinations.
mem[i,j] = mem[i,j-1] + mem[i-1,j-1];
if(j-f-1 >= 0)
mem[i,j] -= mem[i-1,j-f-1];
}
}
return mem[d,s];
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine(findWays(4, 2, 1));
Console.WriteLine(findWays(2, 2, 3));
Console.WriteLine(findWays(6, 3, 8));
Console.WriteLine(findWays(4, 2, 5));
Console.WriteLine(findWays(4, 3, 5));
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumarJavascript
输出 :
0
2
21
4
6时间复杂度: O(m * n * x),其中 m 是面数,n 是骰子数,x 是总和。
我们可以在 findWays() 的开头添加以下两个条件来提高程序在极端情况下的性能(x 太高或 x 太低)
C++
// When x is so high that sum can not go beyond x even when we
// get maximum value in every dice throw.
if (m*n <= x)
return (m*n == x);
// When x is too low
if (n >= x)
return (n == x);
添加上述条件后,当 x >= m*n 或 x <= n 时,时间复杂度变为 O(1)。
以下是优化动态规划方法的实现。
C++
// C++ program
// The main function that returns number of ways to get sum 'x'
// with 'n' dice and 'm' with m faces.
#include
using namespace std;
long findWays(int f, int d, int s)
{
// Create a table to store results of subproblems. One extra
// row and column are used for simpilicity (Number of dice
// is directly used as row index and sum is directly used
// as column index). The entries in 0th row and 0th column
// are never used.
long mem[d + 1][s + 1];
memset(mem,0,sizeof mem);
// Table entries for no dices
// If you do not have any data, then the value must be 0, so the result is 1
mem[0][0] = 1;
// Iterate over dices
for (int i = 1; i <= d; i++)
{
// Iterate over sum
for (int j = i; j <= s; j++)
{
// The result is obtained in two ways, pin the current dice and spending 1 of the value,
// so we have mem[i-1][j-1] remaining combinations, to find the remaining combinations we
// would have to pin the values ??above 1 then we use mem[i][j-1] to sum all combinations
// that pin the remaining j-1's. But there is a way, when "j-f-1> = 0" we would be adding
// extra combinations, so we remove the combinations that only pin the extrapolated dice face and
// subtract the extrapolated combinations.
mem[i][j] = mem[i][j - 1] + mem[i - 1][j - 1];
if (j - f - 1 >= 0)
mem[i][j] -= mem[i - 1][j - f - 1];
}
}
return mem[d][s];
}
// Driver code
int main(void)
{
cout << findWays(4, 2, 1) << endl;
cout << findWays(2, 2, 3) << endl;
cout << findWays(6, 3, 8) << endl;
cout << findWays(4, 2, 5) << endl;
cout << findWays(4, 3, 5) << endl;
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by ankush_953
Java
/**
* The main function that returns number of ways to get sum 'x'
* with 'n' dice and 'm' with m faces.
*
* @author Pedro H. Chaves
*/
public class GFG {
/**
* Count ways
*
* @param f
* @param d
* @param s
* @return
*/
public static long findWays(int f, int d, int s) {
// Create a table to store results of subproblems. One extra
// row and column are used for simpilicity (Number of dice
// is directly used as row index and sum is directly used
// as column index). The entries in 0th row and 0th column
// are never used.
long mem[][] = new long[d + 1][s + 1];
// Table entries for no dices
// If you do not have any data, then the value must be 0, so the result is 1
mem[0][0] = 1;
// Iterate over dices
for(int i=1; i<=d; i++) {
// Iterate over sum
for(int j=i; j<=s; j++) {
// The result is obtained in two ways, pin the current dice and spending 1 of the value,
// so we have mem[i-1][j-1] remaining combinations, to find the remaining combinations we
// would have to pin the values ??above 1 then we use mem[i][j-1] to sum all combinations
// that pin the remaining j-1's. But there is a way, when "j-f-1> = 0" we would be adding
// extra combinations, so we remove the combinations that only pin the extrapolated dice face and
// subtract the extrapolated combinations.
mem[i][j] = mem[i][j-1] + mem[i-1][j-1];
if(j-f-1 >= 0)
mem[i][j] -= mem[i-1][j-f-1];
}
}
return mem[d][s];
}
/**
* Main
*
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(findWays(4, 2, 1));
System.out.println(findWays(2, 2, 3));
System.out.println(findWays(6, 3, 8));
System.out.println(findWays(4, 2, 5));
System.out.println(findWays(4, 3, 5));
}
}
蟒蛇3
# Python program
# The main function that returns number of ways to get sum 'x'
# with 'n' dice and 'm' with m faces.
def findWays(f, d, s):
# Create a table to store results of subproblems. One extra
# row and column are used for simpilicity (Number of dice
# is directly used as row index and sum is directly used
# as column index). The entries in 0th row and 0th column
# are never used.
mem = [[0 for i in range(s+1)] for j in range(d+1)]
# Table entries for no dices
# If you do not have any data, then the value must be 0, so the result is 1
mem[0][0] = 1
# Iterate over dices
for i in range(1, d+1):
# Iterate over sum
for j in range(1, s+1):
# The result is obtained in two ways, pin the current dice and spending 1 of the value,
# so we have mem[i-1][j-1] remaining combinations, to find the remaining combinations we
# would have to pin the values ??above 1 then we use mem[i][j-1] to sum all combinations
# that pin the remaining j-1's. But there is a way, when "j-f-1> = 0" we would be adding
# extra combinations, so we remove the combinations that only pin the extrapolated dice face and
# subtract the extrapolated combinations.
mem[i][j] = mem[i][j - 1] + mem[i - 1][j - 1]
if j - f - 1 >= 0:
mem[i][j] -= mem[i - 1][j - f - 1]
return mem[d][s]
# Driver code
print(findWays(4, 2, 1))
print(findWays(2, 2, 3))
print(findWays(6, 3, 8))
print(findWays(4, 2, 5))
print(findWays(4, 3, 5))
# This code is contributed by ankush_953
C#
// C# program
// The main function that returns number of ways to get sum 'x'
// with 'n' dice and 'm' with m faces.
using System;
class GFG
{
/**
* Count ways
*
* @param f
* @param d
* @param s
* @return
*/
public static long findWays(int f, int d, int s)
{
// Create a table to store results of subproblems. One extra
// row and column are used for simpilicity (Number of dice
// is directly used as row index and sum is directly used
// as column index). The entries in 0th row and 0th column
// are never used.
long [,]mem = new long[d + 1,s + 1];
// Table entries for no dices
// If you do not have any data, then the value must be 0, so the result is 1
mem[0,0] = 1;
// Iterate over dices
for(int i = 1; i <= d; i++)
{
// Iterate over sum
for(int j = i; j <= s; j++)
{
// The result is obtained in two ways, pin the current dice and spending 1 of the value,
// so we have mem[i-1,j-1] remaining combinations, to find the remaining combinations we
// would have to pin the values ??above 1 then we use mem[i,j-1] to sum all combinations
// that pin the remaining j-1's. But there is a way, when "j-f-1> = 0" we would be adding
// extra combinations, so we remove the combinations that only pin the extrapolated dice face and
// subtract the extrapolated combinations.
mem[i,j] = mem[i,j-1] + mem[i-1,j-1];
if(j-f-1 >= 0)
mem[i,j] -= mem[i-1,j-f-1];
}
}
return mem[d,s];
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine(findWays(4, 2, 1));
Console.WriteLine(findWays(2, 2, 3));
Console.WriteLine(findWays(6, 3, 8));
Console.WriteLine(findWays(4, 2, 5));
Console.WriteLine(findWays(4, 3, 5));
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar
Javascript
输出 :
0
2
21
4
6如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。