给定两个数字N和M ,任务是找到可以使用前N 个自然数形成大小为M的排序数组的数量,如果每个数字可以被取任意次数。
例子:
Input: N = 4, M = 2
Output: 10
Explanation: All such possible arrays are {1, 1}, {1, 2}, {1, 2}, {1, 4}, {2, 2}, {2, 3}, {2, 4}, {3, 3}, {3, 4}, {4, 4}.
Input: N = 2, M = 4
Output: 5
Explanation: All such possible arrays are {1, 1, 1, 1}, {1, 1, 1, 2}, {1, 1, 2, 2}, {1, 2, 2, 2}, {2, 2, 2, 2}.
朴素的方法:每个数字都有两个选择,可以取或可以留下。此外,一个号码可以多次使用。
- 多次获取的元素在数组中应该是连续的,因为数组应该被排序。
- 如果一个元素被留下并已移动到另一个元素,则该元素不能再次被采用。
递归方法:
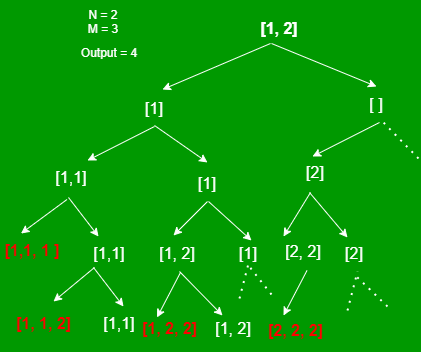
左分支表示该元素被采用,右分支表示该元素在左并且指针移动到下一个元素。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Function to find the number of
// M-length sorted arrays possible
// using numbers from the range [1, N]
int countSortedArrays(int start, int m,
int size, int n)
{
// If size becomes equal to m,
// that means an array is found
if (size == m)
return 1;
if (start > n)
return 0;
int notTaken = 0, taken = 0;
// Include current element, increase
// size by 1 and remain on the same
// element as it can be included again
taken = countSortedArrays(start, m,
size + 1, n);
// Exclude current element
notTaken = countSortedArrays(start + 1,
m, size, n);
// Return the sum obtained
// in both the cases
return taken + notTaken;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Given Input
int n = 2, m = 3;
// Function Call
cout << countSortedArrays(1, m, 0, n);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.util.*;
import java.lang.*;
class GFG{
// Function to find the number of
// M-length sorted arrays possible
// using numbers from the range [1, N]
static int countSortedArrays(int start, int m,
int size, int n)
{
// If size becomes equal to m,
// that means an array is found
if (size == m)
return 1;
if (start > n)
return 0;
int notTaken = 0, taken = 0;
// Include current element, increase
// size by 1 and remain on the same
// element as it can be included again
taken = countSortedArrays(start, m,
size + 1, n);
// Exclude current element
notTaken = countSortedArrays(start + 1,
m, size, n);
// Return the sum obtained
// in both the cases
return taken + notTaken;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Given Input
int n = 2, m = 3;
// Function Call
System.out.println(countSortedArrays(1, m, 0, n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by sanjoy_62Python3
# Python3 program for the above approach
# Function to find the number of
# M-length sorted arrays possible
# using numbers from the range [1, N]
def countSortedArrays(start, m, size, n):
# If size becomes equal to m,
# that means an array is found
if (size == m):
return 1
if (start > n):
return 0
notTaken, taken = 0, 0
# Include current element, increase
# size by 1 and remain on the same
# element as it can be included again
taken = countSortedArrays(start, m,
size + 1, n)
# Exclude current element
notTaken = countSortedArrays(start + 1,
m, size, n)
# Return the sum obtained
# in both the cases
return taken + notTaken
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Given Input
n, m = 2, 3
# Function Call
print (countSortedArrays(1, m, 0, n))
# This code is contributed by mohit kumar 29C#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
class GFG{
// Function to find the number of
// M-length sorted arrays possible
// using numbers from the range [1, N]
static int countSortedArrays(int start, int m,
int size, int n)
{
// If size becomes equal to m,
// that means an array is found
if (size == m)
return 1;
if (start > n)
return 0;
int notTaken = 0, taken = 0;
// Include current element, increase
// size by 1 and remain on the same
// element as it can be included again
taken = countSortedArrays(start, m,
size + 1, n);
// Exclude current element
notTaken = countSortedArrays(start + 1,
m, size, n);
// Return the sum obtained
// in both the cases
return taken + notTaken;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main()
{
// Given Input
int n = 2, m = 3;
// Function Call
Console.WriteLine(countSortedArrays(1, m, 0, n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by susmitakundugoaldangaJavascript
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Function to find the number of
// M-length sorted arrays possible
// using numbers from the range [1, N]
void countSortedArrays(int st, int n,
int m, int& ans, int size)
{
// If size becomes equal to m
// one sorted array is found
if (size == m) {
ans += 1;
return;
}
// Traverse over the range [st, N]
for (int i = st; i <= n; i++) {
// Find all sorted arrays
// starting from i
countSortedArrays(i, n, m,
ans, size + 1);
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Given Input
int n = 2, m = 3;
// Store the required result
int ans = 0;
// Function Call
countSortedArrays(1, n, m, ans, 0);
// Print the result
cout << ans;
return 0;
} Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.io.*;
class GFG{
// Function to find the number of
// M-length sorted arrays possible
// using numbers from the range [1, N]
static int countSortedArrays(int st, int n,
int m, int ans,
int size)
{
// If size becomes equal to m
// one sorted array is found
if (size == m)
{
ans += 1;
System.out.println(ans);
return ans;
}
// Traverse over the range [st, N]
for(int i = st; i <= n; i++)
{
// Find all sorted arrays
// starting from i
ans = countSortedArrays(i, n, m,
ans, size + 1);
}
return ans;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Given Input
int n = 2, m = 3;
// Store the required result
int ans = 0;
// Function Call
ans = countSortedArrays(1, n, m, ans, 0);
// Print the result
System.out.println(ans);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Dharanendra L V.Python3
# Python program for the above approach
# Function to find the number of
# M-length sorted arrays possible
# using numbers from the range [1, N]
def countSortedArrays( st, n, m, ans, size):
# If size becomes equal to m
# one sorted array is found
if (size == m):
ans += 1
return ans
# Traverse over the range [st, N]
for i in range(st,n+1):
# Find all sorted arrays
# starting from i
ans = countSortedArrays(i, n, m, ans, size + 1)
return ans
# Given Input
n = 2
m = 3
# Store the required result
ans = 0
# Function Call
ans = countSortedArrays(1, n, m, ans, 0)
# Print the result
print(ans)
# This code is contributed by unknown2108.C#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
class GFG{
// Function to find the number of
// M-length sorted arrays possible
// using numbers from the range [1, N]
static int countSortedArrays(int st, int n,
int m, int ans,
int size)
{
// If size becomes equal to m
// one sorted array is found
if (size == m)
{
ans += 1;
return ans;
}
// Traverse over the range [st, N]
for(int i = st; i <= n; i++)
{
// Find all sorted arrays
// starting from i
ans = countSortedArrays(i, n, m,
ans, size + 1);
}
return ans;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// Given Input
int n = 2, m = 3;
// Store the required result
int ans = 0;
// Function Call
ans = countSortedArrays(1, n, m, ans, 0);
// Print the result
Console.Write(ans);
}
}
// This code is contributed by shivanisinghss2110Javascript
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Function to find the number of
// M-length sorted arrays possible
// using numbers from the range [1, N]
int countSortedArrays(vector >& dp,
int m, int n)
{
// Base cases
if (m == 0) {
return 1;
}
if (n <= 0)
return 0;
// If the result is already computed,
// return the result of the state
if (dp[m][n] != -1)
return dp[m][n];
int taken = 0, notTaken = 0;
// Include current element, decrease
// required size by 1 and remain on the
// same element, as it can be taken again
taken = countSortedArrays(dp, m - 1, n);
// If element is not included
notTaken = countSortedArrays(dp, m, n - 1);
// Store the result and return it
return dp[m][n] = taken + notTaken;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Given Input
int n = 2, m = 3;
// Create an 2D array for memoization
vector > dp(m + 1,
vector(n + 1, -1));
// Function Call
cout << countSortedArrays(dp, m, n);
return 0;
} C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Function to find the number of
// M-length sorted arrays possible
// using numbers from the range [1, N]
int countSortedArrays(int n, int m)
{
// Create an array of size M+1
vector dp(m + 1, 0);
// Base cases
dp[0] = 1;
// Fill the dp table
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++) {
// dp[j] will be equal to maximum
// number of sorted array of size j
// when elements are taken from 1 to i
dp[j] = dp[j - 1] + dp[j];
}
// Here dp[m] will be equal to the
// maximum number of sorted arrays when
// element are taken from 1 to i
}
// Return the result
return dp[m];
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Given Input
int n = 2, m = 3;
// Function Call
cout << countSortedArrays(n, m);
return 0;
} C#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
class GFG {
// Function to find the number of
// M-length sorted arrays possible
// using numbers from the range [1, N]
static int countSortedArrays(int n, int m)
{
// Create an array of size M+1
int[] dp = new int[(m + 1)];
// Base cases
dp[0] = 1;
// Fill the dp table
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++) {
// dp[j] will be equal to maximum
// number of sorted array of size j
// when elements are taken from 1 to i
dp[j] = dp[j - 1] + dp[j];
}
// Here dp[m] will be equal to the
// maximum number of sorted arrays when
// element are taken from 1 to i
}
// Return the result
return dp[m];
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main()
{
// Given Input
int n = 2, m = 3;
// Function Call
Console.WriteLine(countSortedArrays(n, m));
}
}
// This code is contributed by ukasp.Javascript
4时间复杂度: O(2 N )
辅助空间: O(1)
递归优化方法:
- 遍历每个元素并尝试从该元素开始查找所有可能的数组。
- 在右分支的前一种方法中,元素首先离开,然后在下一步中移动到下一个元素。
- 在这种方式中,不是先离开元素再移动到下一个元素,而是直接转到下一个元素,所以函数调用会更少。
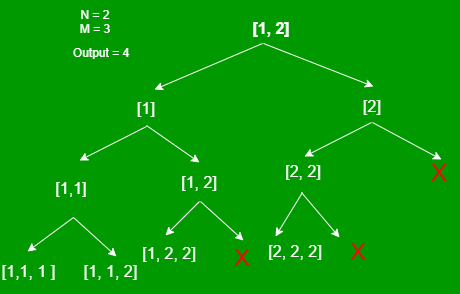
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Function to find the number of
// M-length sorted arrays possible
// using numbers from the range [1, N]
void countSortedArrays(int st, int n,
int m, int& ans, int size)
{
// If size becomes equal to m
// one sorted array is found
if (size == m) {
ans += 1;
return;
}
// Traverse over the range [st, N]
for (int i = st; i <= n; i++) {
// Find all sorted arrays
// starting from i
countSortedArrays(i, n, m,
ans, size + 1);
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Given Input
int n = 2, m = 3;
// Store the required result
int ans = 0;
// Function Call
countSortedArrays(1, n, m, ans, 0);
// Print the result
cout << ans;
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.io.*;
class GFG{
// Function to find the number of
// M-length sorted arrays possible
// using numbers from the range [1, N]
static int countSortedArrays(int st, int n,
int m, int ans,
int size)
{
// If size becomes equal to m
// one sorted array is found
if (size == m)
{
ans += 1;
System.out.println(ans);
return ans;
}
// Traverse over the range [st, N]
for(int i = st; i <= n; i++)
{
// Find all sorted arrays
// starting from i
ans = countSortedArrays(i, n, m,
ans, size + 1);
}
return ans;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Given Input
int n = 2, m = 3;
// Store the required result
int ans = 0;
// Function Call
ans = countSortedArrays(1, n, m, ans, 0);
// Print the result
System.out.println(ans);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Dharanendra L V.
蟒蛇3
# Python program for the above approach
# Function to find the number of
# M-length sorted arrays possible
# using numbers from the range [1, N]
def countSortedArrays( st, n, m, ans, size):
# If size becomes equal to m
# one sorted array is found
if (size == m):
ans += 1
return ans
# Traverse over the range [st, N]
for i in range(st,n+1):
# Find all sorted arrays
# starting from i
ans = countSortedArrays(i, n, m, ans, size + 1)
return ans
# Given Input
n = 2
m = 3
# Store the required result
ans = 0
# Function Call
ans = countSortedArrays(1, n, m, ans, 0)
# Print the result
print(ans)
# This code is contributed by unknown2108.
C#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
class GFG{
// Function to find the number of
// M-length sorted arrays possible
// using numbers from the range [1, N]
static int countSortedArrays(int st, int n,
int m, int ans,
int size)
{
// If size becomes equal to m
// one sorted array is found
if (size == m)
{
ans += 1;
return ans;
}
// Traverse over the range [st, N]
for(int i = st; i <= n; i++)
{
// Find all sorted arrays
// starting from i
ans = countSortedArrays(i, n, m,
ans, size + 1);
}
return ans;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// Given Input
int n = 2, m = 3;
// Store the required result
int ans = 0;
// Function Call
ans = countSortedArrays(1, n, m, ans, 0);
// Print the result
Console.Write(ans);
}
}
// This code is contributed by shivanisinghss2110
Javascript
4时间复杂度: O(2 N )
辅助空间: O(1)
动态规划方法:可以看出,该问题具有重叠子问题和最优子结构性质,即它同时满足动态规划的两个性质。因此,我们的想法是使用 2D 表来记住函数调用期间的结果。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Function to find the number of
// M-length sorted arrays possible
// using numbers from the range [1, N]
int countSortedArrays(vector >& dp,
int m, int n)
{
// Base cases
if (m == 0) {
return 1;
}
if (n <= 0)
return 0;
// If the result is already computed,
// return the result of the state
if (dp[m][n] != -1)
return dp[m][n];
int taken = 0, notTaken = 0;
// Include current element, decrease
// required size by 1 and remain on the
// same element, as it can be taken again
taken = countSortedArrays(dp, m - 1, n);
// If element is not included
notTaken = countSortedArrays(dp, m, n - 1);
// Store the result and return it
return dp[m][n] = taken + notTaken;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Given Input
int n = 2, m = 3;
// Create an 2D array for memoization
vector > dp(m + 1,
vector(n + 1, -1));
// Function Call
cout << countSortedArrays(dp, m, n);
return 0;
}
4时间复杂度: O(N*M)
辅助空间: O(N*M)
空间优化迭代动态规划方法:
- 由于所有元素都可以根据需要多次使用,因此无需保存前一行的值,因此可以使用同一行中的值。
- 因此可以使用一维数组来保存以前的结果。
- 创建一个大小为M的数组dp ,其中dp[i]存储大小为i的排序数组的最大数量,该数组可以由范围[1, N] 中的数字组成。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Function to find the number of
// M-length sorted arrays possible
// using numbers from the range [1, N]
int countSortedArrays(int n, int m)
{
// Create an array of size M+1
vector dp(m + 1, 0);
// Base cases
dp[0] = 1;
// Fill the dp table
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++) {
// dp[j] will be equal to maximum
// number of sorted array of size j
// when elements are taken from 1 to i
dp[j] = dp[j - 1] + dp[j];
}
// Here dp[m] will be equal to the
// maximum number of sorted arrays when
// element are taken from 1 to i
}
// Return the result
return dp[m];
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Given Input
int n = 2, m = 3;
// Function Call
cout << countSortedArrays(n, m);
return 0;
}
C#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
class GFG {
// Function to find the number of
// M-length sorted arrays possible
// using numbers from the range [1, N]
static int countSortedArrays(int n, int m)
{
// Create an array of size M+1
int[] dp = new int[(m + 1)];
// Base cases
dp[0] = 1;
// Fill the dp table
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++) {
// dp[j] will be equal to maximum
// number of sorted array of size j
// when elements are taken from 1 to i
dp[j] = dp[j - 1] + dp[j];
}
// Here dp[m] will be equal to the
// maximum number of sorted arrays when
// element are taken from 1 to i
}
// Return the result
return dp[m];
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main()
{
// Given Input
int n = 2, m = 3;
// Function Call
Console.WriteLine(countSortedArrays(n, m));
}
}
// This code is contributed by ukasp.
Javascript
4时间复杂度: O(N*M)
辅助空间: O(M)
如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。