先决条件 – 指令格式
1. 三地址指令:
三地址指令是机器指令的一种格式。它有一个操作码和三个地址字段。一个地址字段用于目的地,两个地址字段用于源。
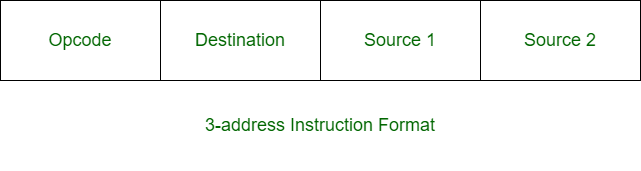
例子 –
X = (A + B) x (C + D) 解决方案:
ADD R1, A, B R1 <- M[A] + M[B]
ADD R2, C, D R2 <- M[C] + M[D]
MUL X, R1, R2 M[X] <- R1 x R2 2. 二地址指令:
二地址指令是机器指令的一种格式。它有一个操作码和两个地址字段。一个地址字段是通用的,可用于目标或源,其他地址字段用于源。

例子 –
X = (A + B) x (C + D) 解决方案:
MOV R1, A R1 <- M[A]
ADD R1, B R1 <- R1 + M[B]
MOV R2, C R2 <- M[C]
ADD R2, D R2 <- R2 + D
MUL R1, R2 R1 <- R1 x R2
MOV X, R1 M[X] <- R1 三地址指令和双地址指令的区别:
| THREE-ADDRESS INSTRUCTION | TWO-ADDRESS INSTRUCTION |
|---|---|
| It has four fields. | It has three fields. |
| It has one field for opcode and three fields for address. | It has one field for opcode and two fields for address. |
| It has long instruction length. | It has shorter instruction. |
| It is slower accessing location inside processor than memory. | It is faster accessing location inside processor than memory. |
| There is distinct address fields for destination and source. | There is one address field common for destination and source. |
| In 3-address format, destination address can not contain operand. | While in 2-address format, destination address can have operand. |
| In 3-address format, instructions are less. | While in 2-address format, instructions are more. |
| It generally requires three memory access. | It generally requires two memory access but in some cases it requires three memory access too. |
| In 3-address format, three memory access is required. | While in 2-address format, it eliminated three memory access but not completely. |