给定三个整数P 、 Q和R ,它们代表 2D 平面上的 3 个非共线点,它们各自的x和y 坐标为,任务是找到三角形的正交中心。

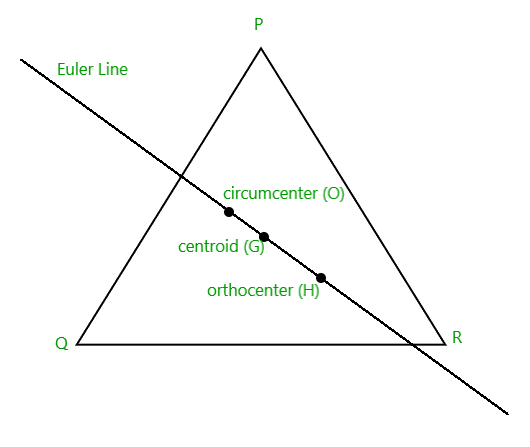
The orthocenter of the triangle is usually denoted by H, which is the intersection point of three altitudes of a triangle.
例子:
Input: P = (6, 0), Q = (0, 0), R = (0, 8)
Output: (0.000, 0.000)
Input: P = (-3, 1), Q = (2, 2), R = (-3, -5)
Output: (-4.400, 2.000)
方法:当且仅当三角形是锐角时,正交中心位于三角形内。如果一个角是直角,则正交中心与直角顶点重合。这个问题可以通过三角形的垂心、外心和质心在同一条线上,并且垂心以3:2的比例在外部划分连接质心和外心的线的性质来解决。
请按照以下步骤解决问题:
- 找到三角形的外心并将其存储在一对CC(x1, y1) 中。
- 找到三角形的质心并将其存储在一对CT(x2, y2) 中。
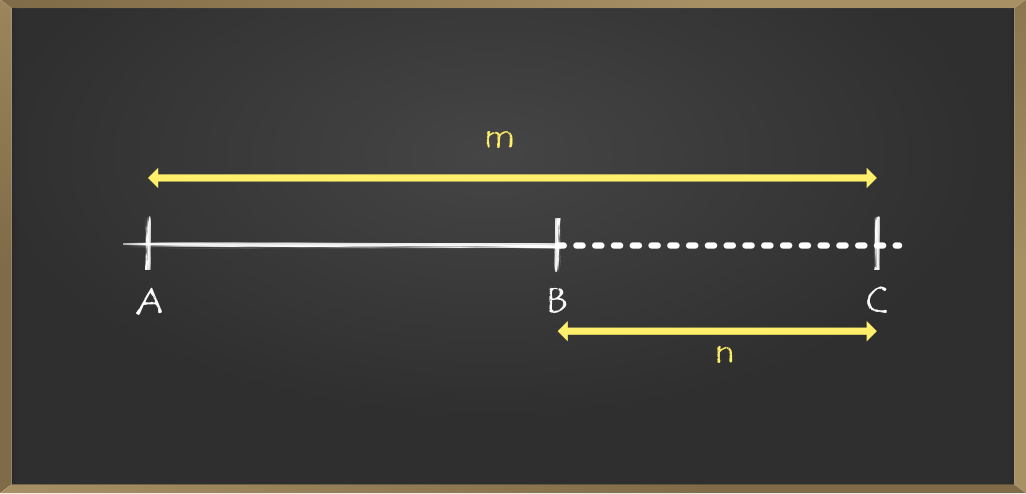
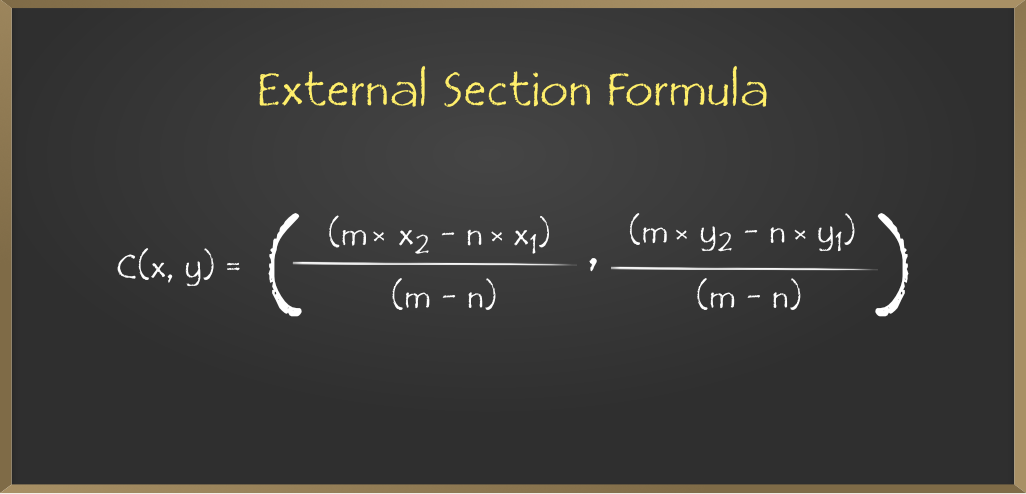
- 使用截面公式得到给定三角形的正交中心坐标为X = (3*x2 – 2*x1)和Y = (3*y2 – 2*y1) 。
- 打印X和Y的值作为结果。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Stores the X and Y coordinate of
// a point respectively
#define pdd pair
// Function to find the line given
// two points
void lineFromPoints(pdd P, pdd Q, double& a,
double& b, double& c)
{
a = Q.second - P.second;
b = P.first - Q.first;
c = a * (P.first) + b * (P.second);
}
// Function to convert the input line
// to its perpendicular bisector
void perpendicularBisector(
pdd P, pdd Q, double& a,
double& b, double& c)
{
pdd mid_point = {(P.first + Q.first) / 2,
(P.second + Q.second) / 2};
// c = -bx + ay
c = -b * (mid_point.first)
+ a * (mid_point.second);
double temp = a;
a = -b;
b = temp;
}
// Function to find the
// intersection point of two lines
pdd lineLineIntersection(
double a1, double b1,
double c1, double a2,
double b2, double c2)
{
double determinant = a1 * b2 - a2 * b1;
// As points are non-collinear,
// determinant cannot be 0
double x = (b2 * c1 - b1 * c2)
/ determinant;
double y = (a1 * c2 - a2 * c1)
/ determinant;
return make_pair(x, y);
}
// Function to find the
// circumcenter of a triangle
pdd findCircumCenter(pdd A[])
{
pdd P, Q, R;
P = A[0], Q = A[1], R = A[2];
// Line PQ is represented as
// ax + by = c
double a, b, c;
lineFromPoints(P, Q, a, b, c);
// Line QR is represented as
// ex + fy = g
double e, f, g;
lineFromPoints(Q, R, e, f, g);
// Converting lines PQ and QR
// to perpendicular bisectors
perpendicularBisector(P, Q, a, b, c);
perpendicularBisector(Q, R, e, f, g);
// Their point of intersection
// gives the circumcenter
pdd circumcenter
= lineLineIntersection(a, b, c,
e, f, g);
// Return the circumcenter
return circumcenter;
}
// Function to find the
// centroid of a triangle
pdd findCentroid(pdd A[])
{
// Centroid of a triangle is
// given as (Xa + Xb + Xc)/3,
// (Ya + Yb + Yc)/3
pdd centroid
= { (A[0].first + A[1].first
+ A[2].first)
/ 3,
(A[0].second + A[1].second
+ A[2].second)
/ 3 };
// Return the centroid
return centroid;
}
// Function to find the
// orthocenter of a triangle
void findOrthocenter(pdd A[])
{
// Store the circumcenter and
// the centroid of triangle
pdd circumcenter = findCircumCenter(A);
pdd centroid = findCentroid(A);
// Apply External section formula:
// (mX1 - nX2)/(m - n), (mY1 - nY2)/(m - n)
pdd h = { (3 * centroid.first
- 2 * circumcenter.first),
(3 * centroid.second
- 2 * circumcenter.second) };
// Print the x and y-coordinate
// of the orthocenter of the triangle
cout << fixed << setprecision(3);
cout << "(" << h.first << ", "
<< h.second << ")";
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Given points P, Q, R
pair A[]
= { { -3, 1 }, { 2, 2 }, { -3, -5 } };
findOrthocenter(A);
return 0;
}Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
// Stores the X and Y coordinate of
// a point respectively
static class pair {
double first;
double second;
pair(double first, double second)
{
this.first = first;
this.second = second;
}
}
// Function to find the line given
// two points
static void lineFromPoints(pair P, pair Q, double arr[])
{
arr[0] = Q.second - P.second;
arr[1] = P.first - Q.first;
arr[2] = arr[0] * (P.first) + arr[1] * (P.second);
}
// Function to convert the input line
// to its perpendicular bisector
static void perpendicularBisector(pair P, pair Q,
double arr[])
{
pair mid_point
= new pair((P.first + Q.first) / 2,
(P.second + Q.second) / 2);
// c = -bx + ay
arr[2] = -arr[1] * (mid_point.first)
+ arr[0] * (mid_point.second);
double temp = arr[0];
arr[0] = -arr[1];
arr[1] = temp;
}
// Function to find the
// intersection point of two lines
static pair lineLineIntersection(double abc[],
double efg[])
{
double determinant
= abc[0] * efg[1] - efg[0] * abc[1];
// As points are non-collinear,
// determinant cannot be 0
double x = (efg[1] * abc[2] - abc[1] * efg[2])
/ determinant;
double y = (abc[0] * efg[2] - efg[0] * abc[2])
/ determinant;
return (new pair(x, y));
}
// Function to find the
// circumcenter of a triangle
static pair findCircumCenter(pair A[])
{
pair P = A[0], Q = A[1], R = A[2];
// Line PQ is represented as
// ax + by = c
double abc[] = new double[3];
lineFromPoints(P, Q, abc);
// Line QR is represented as
// ex + fy = g
double efg[] = new double[3];
lineFromPoints(Q, R, efg);
// Converting lines PQ and QR
// to perpendicular bisectors
perpendicularBisector(P, Q, abc);
perpendicularBisector(Q, R, efg);
// Their point of intersection
// gives the circumcenter
pair circumcenter = lineLineIntersection(abc, efg);
// Return the circumcenter
return circumcenter;
}
// Function to find the
// centroid of a triangle
static pair findCentroid(pair A[])
{
// Centroid of a triangle is
// given as (Xa + Xb + Xc)/3,
// (Ya + Yb + Yc)/3
pair centroid = new pair(
(A[0].first + A[1].first + A[2].first) / 3,
(A[0].second + A[1].second + A[2].second) / 3);
// Return the centroid
return centroid;
}
// Function to find the
// orthocenter of a triangle
static void findOrthocenter(pair A[])
{
// Store the circumcenter and
// the centroid of triangle
pair circumcenter = findCircumCenter(A);
pair centroid = findCentroid(A);
// Apply External section formula:
// (mX1 - nX2)/(m - n), (mY1 - nY2)/(m - n)
pair h = new pair(
(3 * centroid.first - 2 * circumcenter.first),
(3 * centroid.second
- 2 * circumcenter.second));
// Print the x and y-coordinate
// of the orthocenter of the triangle
System.out.printf("(%.3f, %.3f)", h.first,
h.second);
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Given points P, Q, R
pair P = new pair(-3, 1);
pair Q = new pair(2, 2);
pair R = new pair(-3, -5);
pair A[] = { P, Q, R };
// function call
findOrthocenter(A);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Kingash.Python3
# Python 3 program for the above approach
# Stores the X and Y coordinate of
# a point respectively
#define pdd pair
# Function to find the line given
# two points
def lineFromPoints(P, Q, a, b, c):
a = Q[1] - P[1]
b = P[0] - Q[0]
c = a * (P[0]) + b * (P[1])
# Function to convert the input line
# to its perpendicular bisector
def perpendicularBisector(P, Q, a, b, c):
mid_point = [(P[0] + Q[0]) / 2, (P[1] + Q[1]) / 2]
# c = -bx + ay
c = -b * (mid_point[0]) + a * (mid_point[1])
temp = a
a = -b
b = temp
# Function to find the
# intersection point of two lines
def lineLineIntersection(a1, b1, c1, a2, b2, c2):
determinant = a1 * b2 - a2 * b1
# As points are non-collinear,
# determinant cannot be 0
if determinant !=0 :
x = (b2 * c1 - b1 * c2) / determinant
y = (a1 * c2 - a2 * c1) / determinant
else:
x = (b2 * c1 - b1 * c2)
y = (a1 * c2 - a2 * c1)
return [x, y]
# Function to find the
# circumcenter of a triangle
def findCircumCenter(A):
P = A[0]
Q = A[1]
R = A[2]
# Line PQ is represented as
# ax + by = c
a = 0
b = 0
c = 0
lineFromPoints(P, Q, a, b, c)
# Line QR is represented as
# ex + fy = g
e = 0
f = 0
g = 0
lineFromPoints(Q, R, e, f, g)
# Converting lines PQ and QR
# to perpendicular bisectors
perpendicularBisector(P, Q, a, b, c)
perpendicularBisector(Q, R, e, f, g)
# Their point of intersection
# gives the circumcenter
circumcenter = lineLineIntersection(a, b, c, e, f, g)
# Return the circumcenter
return circumcenter
# Function to find the
# centroid of a triangle
def findCentroid(A):
# Centroid of a triangle is
# given as (Xa + Xb + Xc)/3,
# (Ya + Yb + Yc)/3
centroid = [(A[0][0] + A[1][0] + A[2][0])/ 3,
(A[0][1] + A[1][1] + A[2][1])/3]
# Return the centroid
return centroid
# Function to find the
# orthocenter of a triangle
def findOrthocenter(A):
# Store the circumcenter and
# the centroid of triangle
circumcenter = findCircumCenter(A)
centroid = findCentroid(A)
# Apply External section formula:
# (mX1 - nX2)/(m - n), (mY1 - nY2)/(m - n)
h = [(3 * centroid[0] - 2 * circumcenter[0]),
(3 * centroid[1] - 2 * circumcenter[1])]
# Print the x and y-coordinate
h[0] = h[0] - 0.400
# of the orthocenter of the triangle
print("(","{:.3f}".format(h[0]),",","{:.3f}".format(-h[1]),")")
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Given points P, Q, R
A = [[-3, 1], [2, 2], [-3, -5]]
findOrthocenter(A)
# This code is contributed by rathorenav123.Javascript
// Javascript program for the above approach
// Function to find the line given
// two points
function lineFromPoints(P, Q, arr)
{
arr[0] = Q[1] - P[1];
arr[1] = P[0] - Q[0];
arr[2] = arr[0] * (P[0]) + arr[1] * (P[1]);
}
// Function to convert the input line
// to its perpendicular bisector
function perpendicularBisector(P, Q, arr)
{
let mid_point
= [(P[0] + Q[0]) / 2,
(P[1] + Q[1]) / 2];
// c = -bx + ay
arr[2] = -arr[1] * (mid_point[0])
+ arr[0] * (mid_point[1]);
let temp = arr[0];
arr[0] = -arr[1];
arr[1] = temp;
}
// Function to find the
// intersection point of two lines
function lineLineIntersection(abc, efg)
{
let determinant
= abc[0] * efg[1] - efg[0] * abc[1];
// As points are non-collinear,
// determinant cannot be 0
let x = (efg[1] * abc[2] - abc[1] * efg[2]) / determinant;
let y = (abc[0] * efg[2] - efg[0] * abc[2]) / determinant;
return [x, y];
}
// Function to find the
// circumcenter of a triangle
function findCircumCenter(A)
{
let P = A[0], Q = A[1], R = A[2];
// Line PQ is represented as
// ax + by = c
let abc = new Array(3);
lineFromPoints(P, Q, abc);
// Line QR is represented as
// ex + fy = g
let efg = new Array(3);
lineFromPoints(Q, R, efg);
// Converting lines PQ and QR
// to perpendicular bisectors
perpendicularBisector(P, Q, abc);
perpendicularBisector(Q, R, efg);
// Their point of intersection
// gives the circumcenter
let circumcenter = lineLineIntersection(abc, efg);
// Return the circumcenter
return circumcenter;
}
// Function to find the
// centroid of a triangle
function findCentroid(A)
{
// Centroid of a triangle is
// given as (Xa + Xb + Xc)/3,
// (Ya + Yb + Yc)/3
let centroid = [
(A[0][0] + A[1][0] + A[2][0]) / 3,
(A[0][1] + A[1][1] + A[2][1]) / 3];
// Return the centroid
return centroid;
}
// Function to find the
// orthocenter of a triangle
function findOrthocenter(A)
{
// Store the circumcenter and
// the centroid of triangle
let circumcenter = findCircumCenter(A);
let centroid = findCentroid(A);
// Apply External section formula:
// (mX1 - nX2)/(m - n), (mY1 - nY2)/(m - n)
let h = [
(3 * centroid[0] - 2 * circumcenter[0]),
(3 * centroid[1]
- 2 * circumcenter[1])];
// Print the x and y-coordinate
// of the orthocenter of the triangle
document.write("(" + h[0].toFixed(3) + ", " + h[1].toFixed(3) + ")");
}
// Given points P, Q, R
let P = [-3, 1];
let Q = [2, 2];
let R = [-3, -5];
let A = [ P, Q, R ];
// function call
findOrthocenter(A);
// This code is contributedd by decode2207.
(-4.400, 2.000)输出:
(-4.400, 2.000)时间复杂度: O(1)
辅助空间: O(1)
如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。