给定一个图, G由N 个节点、一个源S和一个类型为{u, v}的数组Edges[][2]组成,该数组表示节点u和v之间存在无向边,任务是遍历使用 BFS 按字典顺序绘制图形。
Input: N = 10, M = 10, S = ‘a’, Edges[][2] = { { ‘a’, ‘y’ }, { ‘a’, ‘z’ }, { ‘a’, ‘p’ }, { ‘p’, ‘c’ }, { ‘p’, ‘b’ }, { ‘y’, ‘m’ }, { ‘y’, ‘l’ }, { ‘z’, ‘h’ }, { ‘z’, ‘g’ }, { ‘z’, ‘i’ } }
Output: a p y z b c l m g h i
Explanation:
For the first level visit the node in lexicographical order as shown and print it:
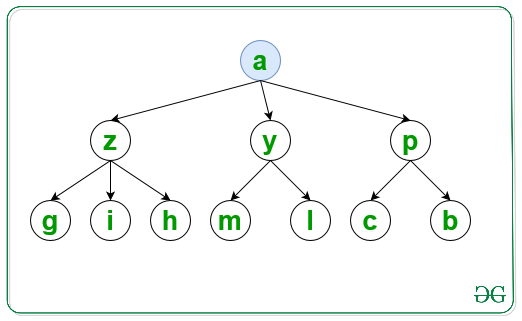
For the second level visit the node in lexicographical order as shown and print it:
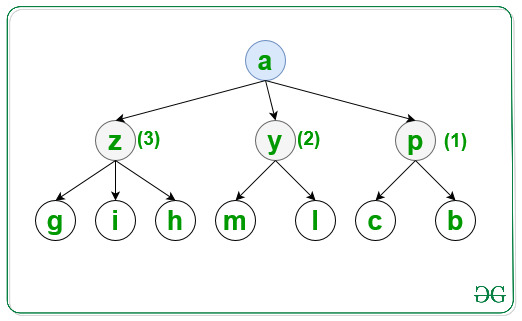
For the third level visit the node in lexicographical order as shown and print it:

Input: N = 6, S = ‘a’, Edges[][2] = { { ‘a’, ‘e’ }, { ‘a’, ‘d’ }, { ‘e’, ‘b’ }, { ‘e’, ‘c’ }, { ‘d’, ‘f’ }, { ‘d’, ‘g’ } }
Output: a d e f g b c
处理方法:按照以下步骤解决问题:
- 初始化一个映射,比如G以根据节点的字典顺序存储一个节点的所有相邻节点。
- 初始化一个地图,比如vis检查一个节点是否已经被遍历。
- 遍历 Edges[][2] 数组,并将图的每个节点的所有相邻节点存储在G 中。
- 最后,使用 BFS 遍历图形并打印图形的访问节点。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program to implement
// the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Function to traverse the graph in
// lexicographical order using BFS
void LexiBFS(map >& G,
char S, map& vis)
{
// Stores nodes of the graph
// at each level
queue q;
// Insert nodes of first level
q.push(S);
// Mark S as
// visited node
vis[S] = true;
// Traverse all nodes of the graph
while (!q.empty()) {
// Stores top node of queue
char top = q.front();
// Print visited nodes of graph
cout << top << " ";
// Insert all adjacent nodes
// of the graph into queue
for (auto i = G[top].begin();
i != G[top].end(); i++) {
// If i is not visited
if (!vis[*i]) {
// Mark i as visited node
vis[*i] = true;
// Insert i into queue
q.push(*i);
}
}
// Pop top element of the queue
q.pop();
}
}
// Utility Function to traverse graph
// in lexicographical order of nodes
void CreateGraph(int N, int M, int S,
char Edges[][2])
{
// Store all the adjacent nodes
// of each node of a graph
map > G;
// Traverse Edges[][2] array
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
G[Edges[i][0]].insert(Edges[i][1]);
}
// Check if a node is already visited or not
map vis;
LexiBFS(G, S, vis);
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int N = 10, M = 10 S = 'a';
char Edges[M][2]
= { { 'a', 'y' }, { 'a', 'z' },
{ 'a', 'p' }, { 'p', 'c' },
{ 'p', 'b' }, { 'y', 'm' },
{ 'y', 'l' }, { 'z', 'h' },
{ 'z', 'g' }, { 'z', 'i' } };
// Function Call
CreateGraph(N, M, S, Edges);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to implement
// the above approach
import java.util.*;
class Graph{
// Function to traverse the graph in
// lexicographical order using BFS
static void LexiBFS(HashMap> G,
char S, HashMap vis)
{
// Stores nodes of the graph
// at each level
Queue q = new LinkedList<>();
// Insert nodes of first level
q.add(S);
// Mark S as
// visited node
vis.put(S, true);
// Traverse all nodes of the graph
while (!q.isEmpty())
{
// Stores top node of queue
char top = q.peek();
// Print visited nodes of graph
System.out.print(top + " ");
// Insert all adjacent nodes
// of the graph into queue
if (G.containsKey(top))
{
for(char i : G.get(top))
{
// If i is not visited
if (vis.containsKey(i))
{
if (!vis.get(i))
{
// Mark i as visited node
vis.put(i, true);
// Insert i into queue
q.add(i);
}
}
else
{
// Mark i as visited node
vis.put(i, true);
// Insert i into queue
q.add(i);
}
}
}
// Pop top element of the queue
q.remove();
}
}
// Utility Function to traverse graph
// in lexicographical order of nodes
static void CreateGraph(int N, int M, char S,
char[][] Edges)
{
// Store all the adjacent nodes
// of each node of a graph
HashMap> G = new HashMap<>();
// Traverse Edges[][2] array
for(int i = 0; i < M; i++)
{
if (G.containsKey(Edges[i][0]))
{
Set temp = G.get(Edges[i][0]);
temp.add(Edges[i][1]);
G.put(Edges[i][0], temp);
}
else
{
Set temp = new HashSet<>();
temp.add(Edges[i][1]);
G.put(Edges[i][0], temp);
}
}
// Check if a node is already visited or not
HashMap vis = new HashMap<>();
LexiBFS(G, S, vis);
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int N = 10, M = 10;
char S = 'a';
char[][] Edges = { { 'a', 'y' }, { 'a', 'z' },
{ 'a', 'p' }, { 'p', 'c' },
{ 'p', 'b' }, { 'y', 'm' },
{ 'y', 'l' }, { 'z', 'h' },
{ 'z', 'g' }, { 'z', 'i' } };
// Function Call
CreateGraph(N, M, S, Edges);
}
}
// This code is contributed by hritikrommie Python3
# Python3 program to implement
# the above approach
from collections import deque
G = [[] for i in range(1000)]
vis = [False for i in range(1000)]
# Function to traverse the graph in
# lexicographical order using BFS
def LexiBFS(S):
global G, vis
# Stores nodes of the graph
# at each level
q = deque()
# Insert nodes of first level
q.append(ord(S))
# Mark S as
# visited node
vis[ord(S)] = True
#a = []
# Traverse all nodes of the graph
while (len(q) > 0):
# Stores top node of queue
top = q.popleft()
print(chr(top), end = " ")
# Insert all adjacent nodes
# of the graph into queue
for i in G[top]:
# If i is not visited
if (not vis[i]):
#print(chr(i),end=" ")
# Mark i as visited node
vis[i] = True
# Insert i into queue
q.append(i)
# Utility Function to traverse graph
# in lexicographical order of nodes
def CreateGraph(N, M, S,Edges):
# Traverse Edges[][2] array
for i in range(M):
G[ord(Edges[i][0])].append(ord(Edges[i][1]))
for i in range(1000):
G[i] = sorted(G[i])
LexiBFS(S)
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
N, M = 10, 10
S = 'a'
Edges = [ [ 'a', 'y' ], [ 'a', 'z' ],
[ 'a', 'p' ], [ 'p', 'c' ],
[ 'p', 'b' ], [ 'y', 'm' ],
[ 'y', 'l' ], [ 'z', 'h' ],
[ 'z', 'g' ], [ 'z', 'i' ] ]
# Function Call
CreateGraph(N, M, S, Edges)
# This code is contributed by mohit kumar 29Javascript
a p y z b c l m g h i时间复杂度: O(N * log(N))
辅助空间: O(N)
如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。