给定一个无向和未加权的连通图,在该图中找到一个简单的环(如果存在)。
简单循环:
A simple cycle is a cycle in a Graph with no repeated vertices (except for the beginning and ending vertex).
Basically, if a cycle can’t be broken down to two or more cycles, then it is a simple cycle.
For better understanding, refer to the following image:
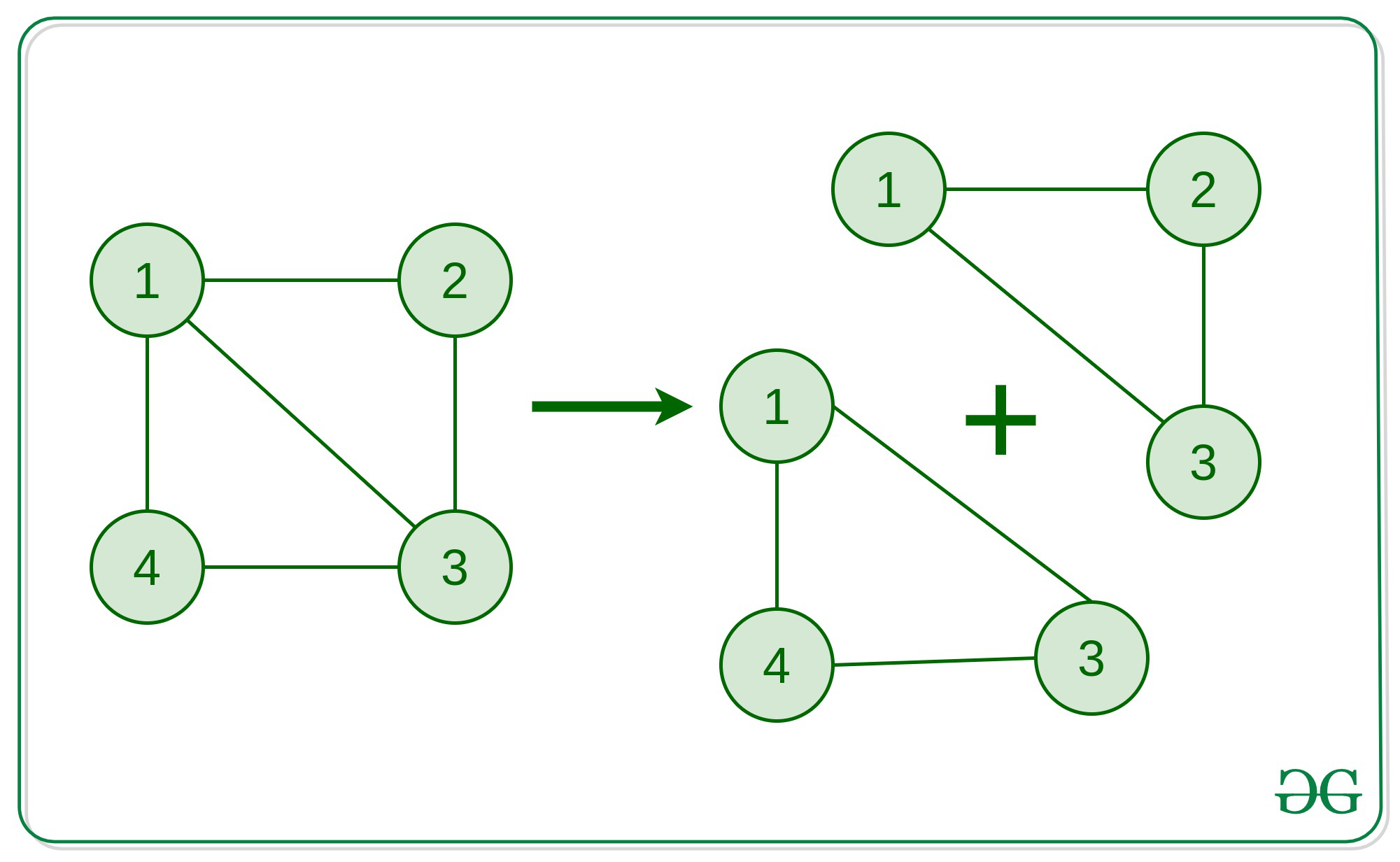
The graph in the above picture explains how the cycle 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 1 isn’t a simple cycle
because, it can be broken into 2 simple cycles 1 -> 3 -> 4 -> 1 and 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 1.
例子:
Input: edges[] = {(1, 2), (2, 3), (2, 4), (3, 4)}
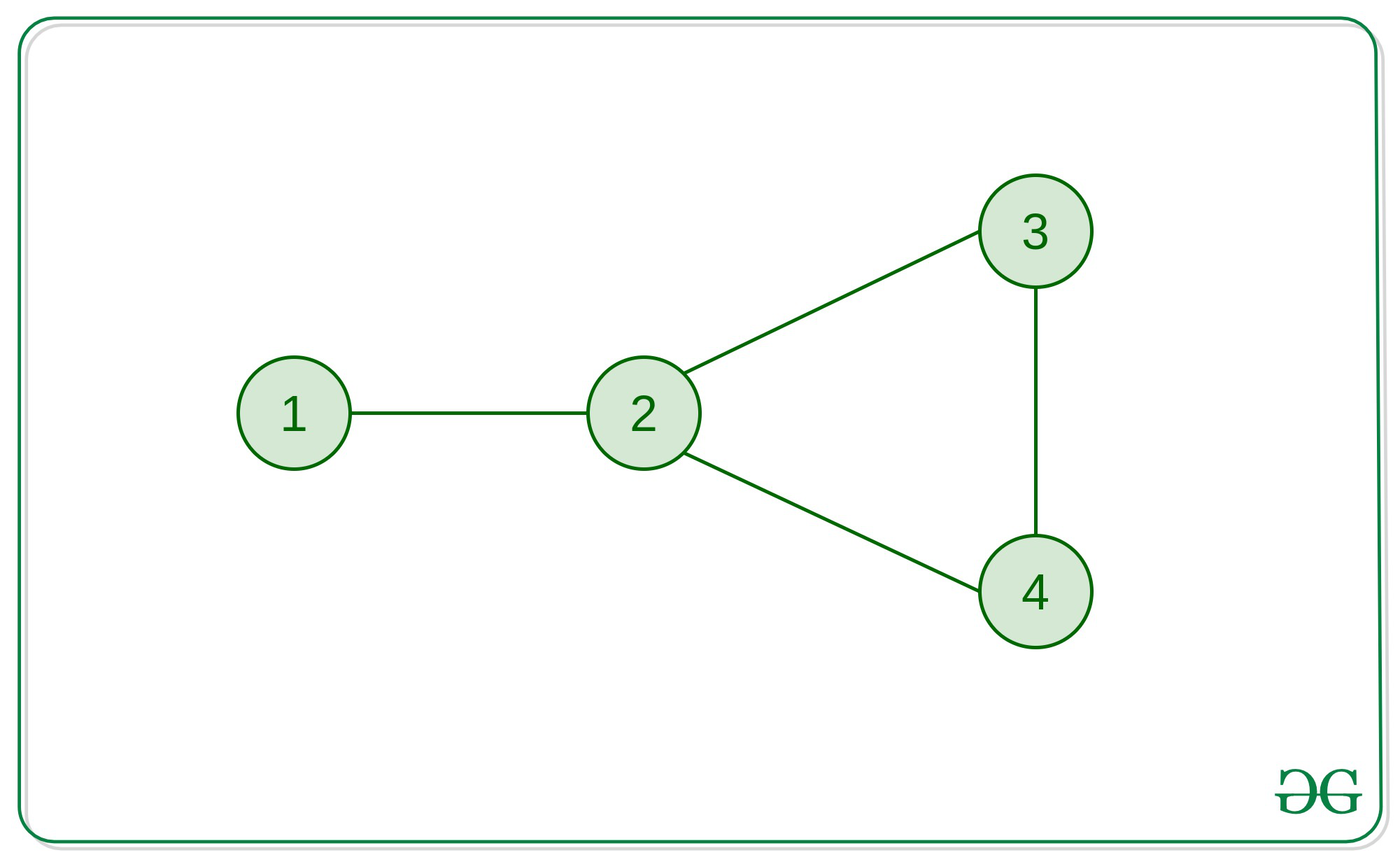
Output: 2 => 3 => 4 => 2
Explanation:
This graph has only one cycle of length 3 which is a simple cycle.
Input: edges[] = {(1, 2), (2, 3), (3, 4), (1, 4), (1, 3)}
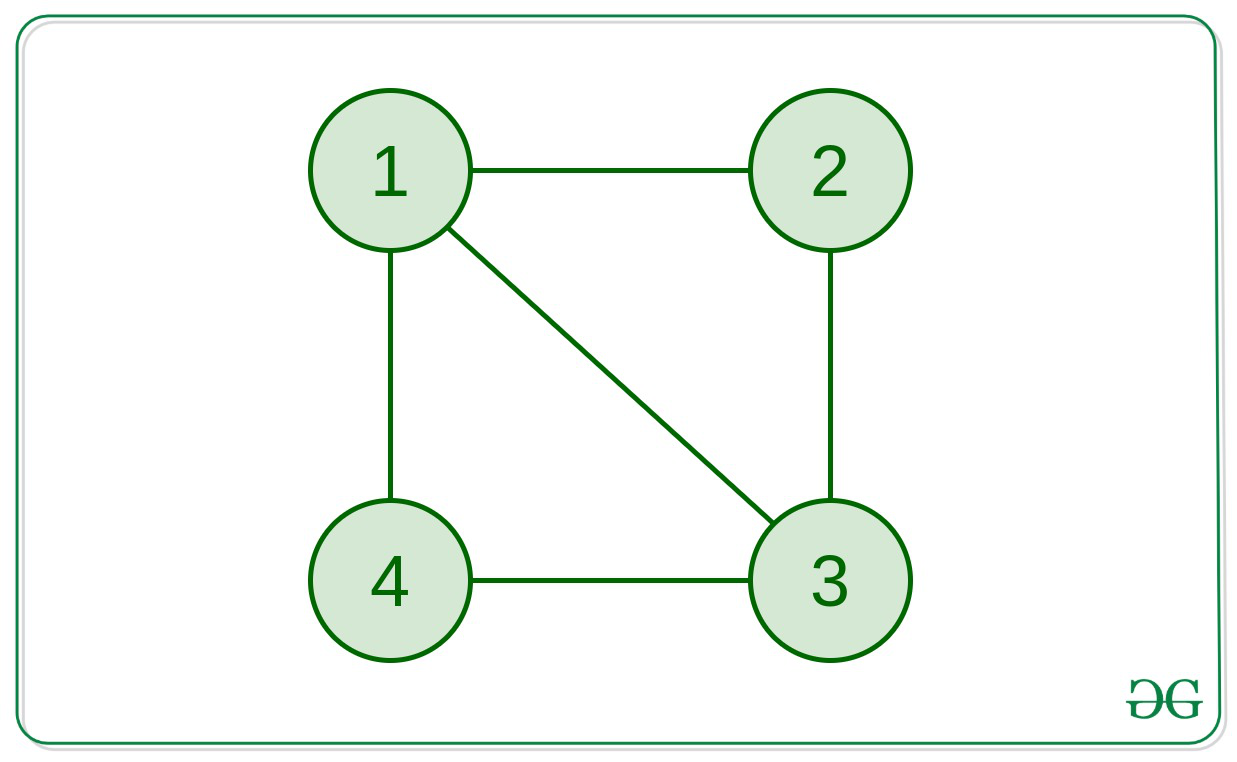
Output: 1 => 3 => 4 => 1
方法:这个想法是检查图形是否包含循环。这可以通过简单地使用 DFS 来完成。
现在,如果图包含一个循环,我们可以从 DFS 本身获取该循环的结束顶点(比如 a 和 b)。现在,如果我们从 a 到 b 运行 BFS(忽略 a 和 b 之间的直接边),我们将能够获得从 a 到 b 的最短路径,这将给我们包含点的最短循环路径a和b 。可以使用父数组轻松跟踪路径。这个最短的周期将是一个简单的周期。
证明最短的循环将是一个简单的循环:
我们可以用矛盾来证明这一点。假设在这个循环中存在另一个简单的循环。这意味着内部简单循环的长度较短,因此可以说从 a 到 b 的路径较短。但是我们已经使用 BFS 找到了从 a 到 b 的最短路径。因此,不存在更短的路径并且找到的路径是最短的。因此,在我们发现的循环内部不存在内部循环。
因此,这个循环是一个简单的循环。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ implementation to find the
// simple cycle in the given path
#include
using namespace std;
#define MAXN 1005
// Declaration of the Graph
vector > adj(MAXN);
// Declaration of visited array
vector vis(MAXN);
int a, b;
// Function to add edges
// connecting 'a' and 'b'
// to the graph
void addedge(int a, int b)
{
adj[a].push_back(b);
adj[b].push_back(a);
}
// Function to detect if the
// graph contains a cycle or not
bool detect_cycle(int node, int par)
{
// Marking the current node visited
vis[node] = 1;
// Traversing to the childs
// of the current node
// Simple DFS approach
for (auto child : adj[node]) {
if (vis[child] == 0) {
if (detect_cycle(child, node))
return true;
}
// Checking for a back-edge
else if (child != par) {
// A cycle is detected
// Marking the end-vertices
// of the cycle
a = child;
b = node;
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
vector simple_cycle;
// Function to get the simple cycle from the
// end-vertices of the cycle we found from DFS
void find_simple_cycle(int a, int b)
{
// Parent array to get the path
vector par(MAXN, -1);
// Queue for BFS
queue q;
q.push(a);
bool ok = true;
while (!q.empty()) {
int node = q.front();
q.pop();
vis[node] = 1;
for (auto child : adj[node]) {
if (node == a && child == b)
// Ignoring the direct edge
// between a and b
continue;
if (vis[child] == 0) {
// Updating the parent array
par[child] = node;
if (child == b) {
// If b is reached,
// we've found the
// shortest path from
// a to b already
ok = false;
break;
}
q.push(child);
vis[child] = 1;
}
}
// If required task is done
if (ok == false)
break;
}
// Cycle starting from a
simple_cycle.push_back(a);
int x = b;
// Until we reach a again
while (x != a) {
simple_cycle.push_back(x);
x = par[x];
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Creating the graph
addedge(1, 2);
addedge(2, 3);
addedge(3, 4);
addedge(4, 1);
addedge(1, 3);
if (detect_cycle(1, -1) == true) {
// If cycle is present
// Resetting the visited array
// for simple cycle finding
vis = vector(MAXN, false);
find_simple_cycle(a, b);
// Printing the simple cycle
cout << "A simple cycle: ";
for (auto& node : simple_cycle) {
cout << node << " => ";
}
cout << a;
cout << "\n";
}
else {
cout << "The Graph doesn't "
<< "contain a cycle.\n";
}
return 0;
} Java
// Java implementation to
// find the simple cycle
// in the given path
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
static final int MAXN = 1005;
// Declaration of the
// Graph
static Vector []adj =
new Vector[MAXN];
// Declaration of visited
// array
static boolean []vis =
new boolean[MAXN];
static int a, b;
// Function to add edges
// connecting 'a' and 'b'
// to the graph
static void addedge(int a,
int b)
{
adj[a].add(b);
adj[b].add(a);
}
// Function to detect if the
// graph contains a cycle or not
static boolean detect_cycle(int node,
int par)
{
// Marking the current
// node visited
vis[node] = true;
// Traversing to the childs
// of the current node
// Simple DFS approach
for (int child : adj[node])
{
if (vis[child] == false)
{
if (detect_cycle(child,
node))
return true;
}
// Checking for a back-edge
else if (child != par)
{
// A cycle is detected
// Marking the end-vertices
// of the cycle
a = child;
b = node;
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
static Vector simple_cycle =
new Vector<>();
// Function to get the simple
// cycle from the end-vertices
//of the cycle we found from DFS
static void find_simple_cycle(int a,
int b)
{
// Parent array to get the path
int []par = new int[MAXN];
// Queue for BFS
Queue q =
new LinkedList<>();
q.add(a);
boolean ok = true;
while (!q.isEmpty())
{
int node = q.peek();
q.remove();
vis[node] = true;
for (int child : adj[node])
{
if (node == a &&
child == b)
// Ignoring the direct edge
// between a and b
continue;
if (vis[child] == false)
{
// Updating the parent
// array
par[child] = node;
if (child == b)
{
// If b is reached,
// we've found the
// shortest path from
// a to b already
ok = false;
break;
}
q.add(child);
vis[child] = true;
}
}
// If required task
// is done
if (ok == false)
break;
}
// Cycle starting from a
simple_cycle.add(a);
int x = b;
// Until we reach
// a again
while (x != a)
{
simple_cycle.add(x);
x = par[x];
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
for (int i = 0; i < adj.length; i++)
adj[i] = new Vector();
// Creating the graph
addedge(1, 2);
addedge(2, 3);
addedge(3, 4);
addedge(4, 1);
addedge(1, 3);
if (detect_cycle(1, -1) == true)
{
// If cycle is present
// Resetting the visited array
// for simple cycle finding
Arrays.fill(vis, false);
find_simple_cycle(a, b);
// Printing the simple cycle
System.out.print("A simple cycle: ");
for (int node : simple_cycle)
{
System.out.print(node + " => ");
}
System.out.print(a);
System.out.print("\n");
}
else
{
System.out.print("The Graph doesn't " +
"contain a cycle.\n");
}
}
}
// This code is contributed by shikhasingrajput Python3
# Python3 implementation to find the
# simple cycle in the given path
MAXN = 1005
# Declaration of the Graph
adj = [[] for i in range(MAXN)]
# Declaration of visited array
vis = [False for i in range(MAXN)]
aa = 0
bb = 0
# Function to add edges
# connecting 'a' and 'b'
# to the graph
def addedge(a, b):
adj[a].append(b);
adj[b].append(a);
# Function to detect if the
# graph contains a cycle or not
def detect_cycle(node, par):
global aa, bb
# Marking the current node visited
vis[node] = True;
# Traversing to the childs
# of the current node
# Simple DFS approach
for child in adj[node]:
if (vis[child] == False):
if (detect_cycle(child, node)):
return True;
# Checking for a back-edge
elif (child != par):
# A cycle is detected
# Marking the end-vertices
# of the cycle
aa = child;
bb = node;
return True;
return False;
simple_cycle = []
# Function to get the simple cycle from the
# end-vertices of the cycle we found from DFS
def find_simple_cycle(a, b):
# Parent array to get the path
par = [0 for i in range(MAXN)]
# Queue for BFS
q = []
q.append(a);
ok = True;
while(len(q) != 0):
node = q[0];
q.pop(0);
vis[node] = True;
for child in adj[node]:
if (node == a and child == b):
# Ignoring the direct edge
# between a and b
continue;
if (vis[child] == False):
# Updating the parent array
par[child] = node;
if (child == b):
# If b is reached,
# we've found the
# shortest path from
# a to b already
ok = False;
break;
q.append(child);
vis[child] = True;
# If required task is done
if (ok == False):
break;
# Cycle starting from a
simple_cycle.append(a);
x = b;
# Until we reach a again
while (x != a):
simple_cycle.append(x);
x = par[x];
# Driver Code
if __name__=='__main__':
# Creating the graph
addedge(1, 2);
addedge(2, 3);
addedge(3, 4);
addedge(4, 1);
addedge(1, 3);
if (detect_cycle(1, -1) == True):
# If cycle is present
# Resetting the visited array
# for simple cycle finding
for i in range(MAXN):
vis[i] = False
find_simple_cycle(aa, bb);
# Printing the simple cycle
print("A simple cycle: ", end = '')
for node in simple_cycle:
print(node, end = " => ")
print(aa)
else:
print("The Graph doesn't contain a cycle.")
# This code is contributed by rutvik_56C#
// C# implementation to
// find the simple cycle
// in the given path
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG{
static readonly int MAXN = 1005;
// Declaration of the
// Graph
static List []adj = new List[MAXN];
// Declaration of visited
// array
static bool []vis = new bool[MAXN];
static int a, b;
// Function to add edges
// connecting 'a' and 'b'
// to the graph
static void addedge(int a, int b)
{
adj[a].Add(b);
adj[b].Add(a);
}
// Function to detect if the
// graph contains a cycle or not
static bool detect_cycle(int node,
int par)
{
// Marking the current
// node visited
vis[node] = true;
// Traversing to the childs
// of the current node
// Simple DFS approach
foreach(int child in adj[node])
{
if (vis[child] == false)
{
if (detect_cycle(child,
node))
return true;
}
// Checking for a back-edge
else if (child != par)
{
// A cycle is detected
// Marking the end-vertices
// of the cycle
a = child;
b = node;
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
static List simple_cycle = new List();
// Function to get the simple
// cycle from the end-vertices
//of the cycle we found from DFS
static void find_simple_cycle(int a,
int b)
{
// Parent array to get the path
int []par = new int[MAXN];
// Queue for BFS
Queue q = new Queue();
q.Enqueue(a);
bool ok = true;
while (q.Count != 0)
{
int node = q.Peek();
q.Dequeue();
vis[node] = true;
foreach(int child in adj[node])
{
if (node == a &&
child == b)
// Ignoring the direct edge
// between a and b
continue;
if (vis[child] == false)
{
// Updating the parent
// array
par[child] = node;
if (child == b)
{
// If b is reached,
// we've found the
// shortest path from
// a to b already
ok = false;
break;
}
q.Enqueue(child);
vis[child] = true;
}
}
// If required task
// is done
if (ok == false)
break;
}
// Cycle starting from a
simple_cycle.Add(a);
int x = b;
// Until we reach
// a again
while (x != a)
{
simple_cycle.Add(x);
x = par[x];
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
for(int i = 0; i < adj.Length; i++)
adj[i] = new List();
// Creating the graph
addedge(1, 2);
addedge(2, 3);
addedge(3, 4);
addedge(4, 1);
addedge(1, 3);
if (detect_cycle(1, -1) == true)
{
// If cycle is present
// Resetting the visited array
// for simple cycle finding
for(int i = 0; i < vis.Length; i++)
vis[i] = false;
find_simple_cycle(a, b);
// Printing the simple cycle
Console.Write("A simple cycle: ");
foreach(int node in simple_cycle)
{
Console.Write(node + " => ");
}
Console.Write(a);
Console.Write("\n");
}
else
{
Console.Write("The Graph doesn't " +
"contain a cycle.\n");
}
}
}
// This code is contributed by gauravrajput1 Javascript
A simple cycle: 1 => 4 => 3 => 1