在完整的二元加权图中找到给定长度 K 的回文路径
给定一个具有N个顶点的完整有向图,其边的权重为“1”或“0”,任务是找到长度正好为K的路径,该路径是回文。如果可能,打印“ YES ”,然后打印路径,否则打印“ NO ”。
例子:
Input: N = 3, K = 4
edges[] = {{{1, 2}, ‘1’}, {{1, 3}, ‘1’}, {{2, 1}, ‘1’}, {{2, 3}, ‘1’}, {{3, 1}, ‘0’}, {{3, 2}, ‘0’}}
Output:
YES
2 1 2 1 2
Explanation:
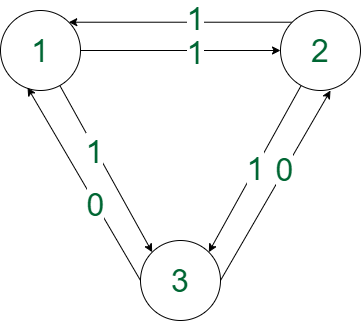
The path followed is “1111” which is palindrome.
Input: N = 2, K = 6
edges[] = { { 1, 2 }, ‘1’ }, { { 2, 1 }, ‘0’ }
Output: NO
方法:可以通过考虑不同的情况并构建相应的答案来解决上述问题。请按照以下步骤解决问题:
- 如果K 是奇数:
- 如果 K 是奇数,则在每种情况下都存在一条回文路径。
- 它可以通过选择任意两个节点并循环它们K次来构造,例如,对于K = 5:“00000”,“11111”,“10101”,“01010”。
- 如果K 是偶数:
- 现在问题可以分为两种情况:
- 如果存在两个节点(i, j)使得边i->j的权重等于边j->i 的权重。然后可以通过遍历它们来构造答案,直到达到路径长度 K。
- 否则,如果存在三个不同的节点(i, j, k)使得边i->j的权重等于边j->k的权重。然后可以将这三个节点放置在路径的中心,例如…i->j-> i->j->k ->j->k…,以创建一个偶数长度的回文。
- 现在问题可以分为两种情况:
- 根据以上观察打印答案。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ implementation for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Function to print the left path
void printLeftPath(int i, int j, int K)
{
if (K & 1) {
// j->i->j->i->j->k->j->k->j
for (int p = 0; p < K; p++) {
if (p & 1) {
cout << i << " ";
}
else {
cout << j << " ";
}
}
}
else {
// i->j->i->j->k->j->k
for (int p = 0; p < K; p++) {
if (p & 1) {
cout << j << " ";
}
else {
cout << i << " ";
}
}
}
}
// Function to print the right path
void printRightPath(int j, int k, int K)
{
if (K & 1) {
// j->i->j->i->j->k->j->k->j
for (int p = 0; p < K; p++) {
if (p & 1) {
cout << k << " ";
}
else {
cout << j << " ";
}
}
}
else {
// i->j->i->j->k->j->k
for (int p = 0; p < K; p++) {
if (p & 1) {
cout << k << " ";
}
else {
cout << j << " ";
}
}
}
}
// Function to check that
// if there exists a palindromic path
// in a binary graph
void constructPalindromicPath(
vector, char> > edges,
int n, int K)
{
// Create adjacency matrix
vector > adj(
n + 1,
vector(n + 1));
for (int i = 0; i < edges.size(); i++) {
adj[edges[i]
.first.first][edges[i]
.first.second]
= edges[i].second;
}
// If K is odd then
// print the path directly by
// choosing node 1 and 2 repeatedly
if (K & 1) {
cout << "YES" << endl;
for (int i = 1; i <= K + 1; i++) {
cout << (i & 1) + 1 << " ";
}
return;
}
// If K is even
// Try to find an edge such that weight of
// edge i->j and j->i is equal
bool found = 0;
int idx1, idx2;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
if (i == j) {
continue;
}
if (adj[i][j] == adj[j][i]) {
// Same weight edges are found
found = 1;
// Store their indexes
idx1 = i, idx2 = j;
}
}
}
if (found) {
// Print the path
cout << "YES" << endl;
for (int i = 1; i <= K + 1; i++) {
if (i & 1) {
cout << idx1 << " ";
}
else {
cout << idx2 << " ";
}
}
return;
}
// If nodes i, j having equal weight
// on edges i->j and j->i can not
// be found then try to find
// three nodes i, j, k such that
// weights of edges i->j
// and j->k are equal
else {
// To store edges with weight '0'
vector mp1[n + 1];
// To store edges with weight '1'
vector mp2[n + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
if (i == j) {
continue;
}
if (adj[i][j] == '0') {
mp1[i].push_back(j);
}
else {
mp2[i].push_back(j);
}
}
}
// Try to find edges i->j and
// j->k having weight 0
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
if (j == i) {
continue;
}
if (adj[i][j] == '0') {
if (mp1[j].size()) {
int k = mp1[j][0];
if (k == i || k == j) {
continue;
}
cout << "YES" << endl;
K -= 2;
K /= 2;
// Print left Path
printLeftPath(i, j, K);
// Print centre
cout << i << " "
<< j << " " << k
<< " ";
// Print right path
printRightPath(j, k, K);
return;
}
}
}
}
// Try to find edges i->j
// and j->k which having
// weight 1
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
if (j == i) {
continue;
}
if (adj[i][j] == '1') {
if (mp1[j].size()) {
int k = mp1[j][0];
// cout<, char> > edges
= { { { 1, 2 }, '1' },
{ { 1, 3 }, '1' },
{ { 2, 1 }, '1' },
{ { 2, 3 }, '1' },
{ { 3, 1 }, '0' },
{ { 3, 2 }, '0' } };
constructPalindromicPath(edges, N, K);
} Python3
# Python implementation for the above approach
# Function to print the left path
def printLeftPath(i, j, K):
if (K & 1):
# j->i->j->i->j->k->j->k->j
for p in range(0, K):
if (p & 1):
print(i, end=" ")
else:
print(j, end=" ")
else:
# i->j->i->j->k->j->k
for p in range(K):
if (p & 1):
print(j, end=" ")
else:
print(i, end=" ")
# Function to print the right path
def printRightPath(j, k, K):
if (K & 1):
# j->i->j->i->j->k->j->k->j
for p in range(K):
if (p & 1):
print(K, end=" ")
else:
print(j, end=" ")
else:
# i->j->i->j->k->j->k
for p in range(K):
if (p & 1):
print(K, end=" ")
else:
print(j, end=" ")
# Function to check that
# if there exists a palindromic path
# in a binary graph
def constructPalindromicPath(edges, n, K):
# Create adjacency matrix
adj = [[0 for i in range(n + 1)] for i in range(n + 1)]
for i in range(len(edges)):
adj[edges[i][0][0]][edges[i][0][1]] = edges[i][1]
# If K is odd then
# print the path directly by
# choosing node 1 and 2 repeatedly
if (K & 1):
print("YES")
for i in range(1, K + 2):
print((i & 1) + 1, end=" ")
return
# If K is even
# Try to find an edge such that weight of
# edge i->j and j->i is equal
found = 0
idx1 = None
idx2 = None
for i in range(1, n + 1):
for j in range(1, n + 1):
if (i == j):
continue
if (adj[i][j] == adj[j][i]):
# Same weight edges are found
found = 1
# Store their indexes
idx1 = i
idx2 = j
if (found):
# Print the path
print("YES")
for i in range(1, K + 2):
if (i & 1):
print(idx1, end=" ")
else:
print(idx2, end=" ")
return
# If nodes i, j having equal weight
# on edges i->j and j->i can not
# be found then try to find
# three nodes i, j, k such that
# weights of edges i->j
# and j->k are equal
else:
# To store edges with weight '0'
mp1 = [[] for i in range*(n + 1)]
# To store edges with weight '1'
mp2 = [[] for i in range(n + 1)]
for i in range(1, n + 1):
for j in range(1, n + 1):
if (i == j):
continue
if (adj[i][j] == '0'):
mp1[i].push(j)
else:
mp2[i].push(j)
# Try to find edges i->j and
# j->k having weight 0
for i in range(1, n + 1):
for j in range(1, n + 1):
if (j == i):
continue
if (adj[i][j] == '0'):
if (len(mp1[j])):
k = mp1[j][0]
if (k == i or k == j):
continue
print("YES")
K -= 2
K = k // 2
# Print left Path
printLeftPath(i, j, K)
# Print centre
print(f"{i} {j} {k}")
# Print right path
printRightPath(j, k, K)
return
# Try to find edges i->j
# and j->k which having
# weight 1
for i in range(1, n + 1):
for j in range(1, n + 1):
if (j == i):
continue
if (adj[i][j] == '1'):
if (len(mp1[j])):
k = mp1[j][0]
# cout<Javascript
输出
YES
2 1 2 1 2 时间复杂度: O(N*N)
辅助空间: O(N*N)