图是一组实体的表示,其中一些实体对通过连接链接。互连实体由称为顶点的点表示,顶点之间的连接称为边。形式上,图是一对集合 (V, E),其中 V 是顶点的集合,E 是连接一对顶点的边的集合。

可以使用邻接矩阵来表示图。

图的初始化:邻接矩阵将使用一个二维数组来描述,一个构造函数将用于分配数组的大小,该数组的每个元素将被初始化为 0。显示图中每个顶点的度数为零。
C++
class Graph {
private:
// number of vertices
int n;
// adjacency matrix
int g[10][10];
public:
// constructor
Graph(int x)
{
n = x;
// initializing each element of the adjacency matrix to zero
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
g[i][j] = 0;
}
}
}
};Java
class Graph {
// number of vertices
private int n;
// adjacency matrix
private int[][] g = new int[10][10];
// constructor
Graph(int x)
{
this.n = x;
int i, j;
// initializing each element of the adjacency matrix to zero
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
for (j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
g[i][j] = 0;
}
}
}
}Python3
class Graph:
# number of vertices
__n = 0
# adjacency matrix
__g =[[0 for x in range(10)] for y in range(10)]
# constructor
def __init__(self, x):
self.__n = x
# initializing each element of the adjacency matrix to zero
for i in range(0, self.__n):
for j in range(0, self.__n):
self.__g[i][j]= 0C#
class Graph{
// Number of vertices
private int n;
// Adjacency matrix
private int[,] g = new int[10, 10];
// Constructor
Graph(int x)
{
this.n = x;
int i, j;
// Initializing each element of
// the adjacency matrix to zero
for(i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
for(j = 0; j < n; ++j)
{
g[i, j] = 0;
}
}
}
}
// This code is contributed by ukaspC++
void displayAdjacencyMatrix()
{
cout << "\n\n Adjacency Matrix:";
// displaying the 2D array
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
cout << "\n";
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
cout << " " << g[i][j];
}
}
}Java
public void displayAdjacencyMatrix()
{
System.out.print("\n\n Adjacency Matrix:");
// displaying the 2D array
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
System.out.println();
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
System.out.print(" " + g[i][j]);
}
}
}Python3
def displayAdjacencyMatrix(self):
print("\n\n Adjacency Matrix:", end ="")
# displaying the 2D array
for i in range(0, self.__n):
print()
for j in range(0, self.__n):
print("", self.__g[i][j], end ="")C++
void addEdge(int x, int y)
{
// checks if the vertex exists in the graph
if ((x >= n) || (y > n)) {
cout << "Vertex does not exists!";
}
// checks if the vertex is connecting to itself
if (x == y) {
cout << "Same Vertex!";
}
else {
// connecting the vertices
g[y][x] = 1;
g[x][y] = 1;
}
}Java
public void addEdge(int x, int y)
{
// checks if the vertex exists in the graph
if ((x >= n) || (y > n)) {
System.out.println("Vertex does not exists!");
}
// checks if the vertex is connecting to itself
if (x == y) {
System.out.println("Same Vertex!");
}
else {
// connecting the vertices
g[y][x] = 1;
g[x][y] = 1;
}
}Python3
def addEdge(self, x, y):
# checks if the vertex exists in the graph
if(x>= self.__n) or (y >= self.__n):
print("Vertex does not exists !")
# checks if the vertex is connecting to itself
if(x == y):
print("Same Vertex !")
else:
# connecting the vertices
self.__g[y][x]= 1
self.__g[x][y]= 1C++
void addVertex()
{
// increasing the number of vertices
n++;
int i;
// initializing the new elements to 0
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
g[i][n - 1] = 0;
g[n - 1][i] = 0;
}
}Java
public void addVertex()
{
// increasing the number of vertices
n++;
int i;
// initializing the new elements to 0
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
g[i][n - 1] = 0;
g[n - 1][i] = 0;
}
}Python3
def addVertex(self):
# increasing the number of vertices
self.__n = self.__n + 1;
# initializing the new elements to 0
for i in range(0, self.__n):
self.__g[i][self.__n-1]= 0
self.__g[self.__n-1][i]= 0C++
void removeVertex(int x)
{
// checking if the vertex is present
if (x > n) {
cout << "\nVertex not present!";
return;
}
else {
int i;
// removing the vertex
while (x < n) {
// shifting the rows to left side
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
g[i][x] = g[i][x + 1];
}
// shifting the columns upwards
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
g[x][i] = g[x + 1][i];
}
x++;
}
// decreasing the number of vertices
n--;
}
}Java
public void removeVertex(int x)
{
// checking if the vertex is present
if (x > n) {
System.out.println("Vertex not present!");
return;
}
else {
int i;
// removing the vertex
while (x < n) {
// shifting the rows to left side
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
g[i][x] = g[i][x + 1];
}
// shifting the columns upwards
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
g[x][i] = g[x + 1][i];
}
x++;
}
// decreasing the number of vertices
n--;
}
}Python3
def removeVertex(self, x):
# checking if the vertex is present
if(x>self.__n):
print("Vertex not present !")
else:
# removing the vertex
while(xC++
// C++ program to add and remove Vertex in Adjacency Matrix
#include
using namespace std;
class Graph {
private:
// number of vertices
int n;
// adjacency matrix
int g[10][10];
public:
// constructor
Graph(int x)
{
n = x;
// initializing each element of the adjacency matrix to zero
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
g[i][j] = 0;
}
}
}
void displayAdjacencyMatrix()
{
cout << "\n\n Adjacency Matrix:";
// displaying the 2D array
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
cout << "\n";
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
cout << " " << g[i][j];
}
}
}
void addEdge(int x, int y)
{
// checks if the vertex exists in the graph
if ((x >= n) || (y > n)) {
cout << "Vertex does not exists!";
}
// checks if the vertex is connecting to itself
if (x == y) {
cout << "Same Vertex!";
}
else {
// connecting the vertices
g[y][x] = 1;
g[x][y] = 1;
}
}
void addVertex()
{
// increasing the number of vertices
n++;
int i;
// initializing the new elements to 0
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
g[i][n - 1] = 0;
g[n - 1][i] = 0;
}
}
void removeVertex(int x)
{
// checking if the vertex is present
if (x > n) {
cout << "\nVertex not present!";
return;
}
else {
int i;
// removing the vertex
while (x < n) {
// shifting the rows to left side
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
g[i][x] = g[i][x + 1];
}
// shifting the columns upwards
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
g[x][i] = g[x + 1][i];
}
x++;
}
// decreasing the number of vertices
n--;
}
}
};
int main()
{
// creating objects of class Graph
Graph obj(4);
// calling methods
obj.addEdge(0, 1);
obj.addEdge(0, 2);
obj.addEdge(1, 2);
obj.addEdge(2, 3);
// the adjacency matrix created
obj.displayAdjacencyMatrix();
// adding a vertex to the graph
obj.addVertex();
// connecting that vertex to other existing vertices
obj.addEdge(4, 1);
obj.addEdge(4, 3);
// the adjacency matrix with a new vertex
obj.displayAdjacencyMatrix();
// removing an existing vertex in the graph
obj.removeVertex(1);
// the adjacency matrix after removing a vertex
obj.displayAdjacencyMatrix();
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to add and remove Vertex in Adjacency Matrix
class Graph
{
// number of vertices
private int n;
// adjacency matrix
private int[][] g = new int[10][10];
// constructor
Graph(int x)
{
this.n = x;
int i, j;
// initializing each element of
// the adjacency matrix to zero
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
for (j = 0; j < n; ++j)
{
g[i][j] = 0;
}
}
}
public void displayAdjacencyMatrix()
{
System.out.print("\n\n Adjacency Matrix:");
// displaying the 2D array
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
System.out.println();
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j)
{
System.out.print(" " + g[i][j]);
}
}
}
public void addEdge(int x, int y)
{
// checks if the vertex exists in the graph
if ((x >= n) || (y > n))
{
System.out.println("Vertex does not exists!");
}
// checks if the vertex is connecting to itself
if (x == y)
{
System.out.println("Same Vertex!");
}
else
{
// connecting the vertices
g[y][x] = 1;
g[x][y] = 1;
}
}
public void addVertex()
{
// increasing the number of vertices
n++;
int i;
// initializing the new elements to 0
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
g[i][n - 1] = 0;
g[n - 1][i] = 0;
}
}
public void removeVertex(int x)
{
// checking if the vertex is present
if (x > n)
{
System.out.println("Vertex not present!");
return;
}
else
{
int i;
// removing the vertex
while (x < n)
{
// shifting the rows to left side
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
g[i][x] = g[i][x + 1];
}
// shifting the columns upwards
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
g[x][i] = g[x + 1][i];
}
x++;
}
// decreasing the number of vertices
n--;
}
}
}
class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// creating objects of class Graph
Graph obj = new Graph(4);
// calling methods
obj.addEdge(0, 1);
obj.addEdge(0, 2);
obj.addEdge(1, 2);
obj.addEdge(2, 3);
// the adjacency matrix created
obj.displayAdjacencyMatrix();
// adding a vertex to the graph
obj.addVertex();
// connecting that vertex to other existing vertices
obj.addEdge(4, 1);
obj.addEdge(4, 3);
// the adjacency matrix with a new vertex
obj.displayAdjacencyMatrix();
// removing an existing vertex in the graph
obj.removeVertex(1);
// the adjacency matrix after removing a vertex
obj.displayAdjacencyMatrix();
}
}Python3
# Python program to add and remove Vertex in Adjacency Matrix
class Graph:
# number of vertices
__n = 0
# adjacency matrix
__g =[[0 for x in range(10)] for y in range(10)]
# constructor
def __init__(self, x):
self.__n = x
# initializing each element of the adjacency matrix to zero
for i in range(0, self.__n):
for j in range(0, self.__n):
self.__g[i][j]= 0
def displayAdjacencyMatrix(self):
print("\n\n Adjacency Matrix:", end ="")
# displaying the 2D array
for i in range(0, self.__n):
print()
for j in range(0, self.__n):
print("", self.__g[i][j], end ="")
def addEdge(self, x, y):
# checks if the vertex exists in the graph
if(x>= self.__n) or (y >= self.__n):
print("Vertex does not exists !")
# checks if the vertex is connecting to itself
if(x == y):
print("Same Vertex !")
else:
# connecting the vertices
self.__g[y][x]= 1
self.__g[x][y]= 1
def addVertex(self):
# increasing the number of vertices
self.__n = self.__n + 1;
# initializing the new elements to 0
for i in range(0, self.__n):
self.__g[i][self.__n-1]= 0
self.__g[self.__n-1][i]= 0
def removeVertex(self, x):
# checking if the vertex is present
if(x>self.__n):
print("Vertex not present !")
else:
# removing the vertex
while(xC#
// C# program to add and remove Vertex in Adjacency Matrix
using System;
public class Graph
{
// number of vertices
private int n;
// adjacency matrix
private int[,] g = new int[10, 10];
// constructor
public Graph(int x)
{
this.n = x;
int i, j;
// initializing each element of the adjacency matrix to zero
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
for (j = 0; j < n; ++j)
{
g[i, j] = 0;
}
}
}
public void displayAdjacencyMatrix()
{
Console.Write("\n\n Adjacency Matrix:");
// displaying the 2D array
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
Console.WriteLine();
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j)
{
Console.Write(" " + g[i, j]);
}
}
}
public void addEdge(int x, int y)
{
// checks if the vertex exists in the graph
if ((x >= n) || (y > n))
{
Console.WriteLine("Vertex does not exists!");
}
// checks if the vertex is connecting to itself
if (x == y)
{
Console.WriteLine("Same Vertex!");
}
else
{
// connecting the vertices
g[y, x] = 1;
g[x, y] = 1;
}
}
public void addVertex()
{
// increasing the number of vertices
n++;
int i;
// initializing the new elements to 0
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
g[i, n - 1] = 0;
g[n - 1, i] = 0;
}
}
public void removeVertex(int x)
{
// checking if the vertex is present
if (x > n)
{
Console.WriteLine("Vertex not present!");
return;
}
else
{
int i;
// removing the vertex
while (x < n)
{
// shifting the rows to left side
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
g[i, x] = g[i, x + 1];
}
// shifting the columns upwards
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
g[x, i] = g[x + 1, i];
}
x++;
}
// decreasing the number of vertices
n--;
}
}
}
public class GFG
{
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// creating objects of class Graph
Graph obj = new Graph(4);
// calling methods
obj.addEdge(0, 1);
obj.addEdge(0, 2);
obj.addEdge(1, 2);
obj.addEdge(2, 3);
// the adjacency matrix created
obj.displayAdjacencyMatrix();
// adding a vertex to the graph
obj.addVertex();
// connecting that vertex to other existing vertices
obj.addEdge(4, 1);
obj.addEdge(4, 3);
// the adjacency matrix with a new vertex
obj.displayAdjacencyMatrix();
// removing an existing vertex in the graph
obj.removeVertex(1);
// the adjacency matrix after removing a vertex
obj.displayAdjacencyMatrix();
}
}
// This code is contributed by PrinciRaj1992Javascript
这里的邻接矩阵是 g[n][n],其中每个顶点的度数为零。
显示图形:使用顶点数为 n 的邻接矩阵 g[n][n] 来描绘图形。显示二维数组(邻接矩阵),其中如果两个顶点 ‘x’ 和 ‘y’ 之间存在边,则 g[x][y] 为 1,否则为 0。
C++
void displayAdjacencyMatrix()
{
cout << "\n\n Adjacency Matrix:";
// displaying the 2D array
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
cout << "\n";
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
cout << " " << g[i][j];
}
}
}
Java
public void displayAdjacencyMatrix()
{
System.out.print("\n\n Adjacency Matrix:");
// displaying the 2D array
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
System.out.println();
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
System.out.print(" " + g[i][j]);
}
}
}
蟒蛇3
def displayAdjacencyMatrix(self):
print("\n\n Adjacency Matrix:", end ="")
# displaying the 2D array
for i in range(0, self.__n):
print()
for j in range(0, self.__n):
print("", self.__g[i][j], end ="")
上述方法是 Graph 类的公共成员函数,它使用邻接矩阵显示图形。
在图中的顶点之间添加边:要在两个现有顶点(例如顶点 ‘x’ 和顶点 ‘y’)之间添加边,则邻接矩阵的元素 g[x][y] 和 g[y][x] 将是指定为 1,表示顶点“x”和顶点“y”之间有一条边。
C++
void addEdge(int x, int y)
{
// checks if the vertex exists in the graph
if ((x >= n) || (y > n)) {
cout << "Vertex does not exists!";
}
// checks if the vertex is connecting to itself
if (x == y) {
cout << "Same Vertex!";
}
else {
// connecting the vertices
g[y][x] = 1;
g[x][y] = 1;
}
}
Java
public void addEdge(int x, int y)
{
// checks if the vertex exists in the graph
if ((x >= n) || (y > n)) {
System.out.println("Vertex does not exists!");
}
// checks if the vertex is connecting to itself
if (x == y) {
System.out.println("Same Vertex!");
}
else {
// connecting the vertices
g[y][x] = 1;
g[x][y] = 1;
}
}
蟒蛇3
def addEdge(self, x, y):
# checks if the vertex exists in the graph
if(x>= self.__n) or (y >= self.__n):
print("Vertex does not exists !")
# checks if the vertex is connecting to itself
if(x == y):
print("Same Vertex !")
else:
# connecting the vertices
self.__g[y][x]= 1
self.__g[x][y]= 1
这里上面的方法是Graph类的一个公共成员函数,它连接Graph中任意两个现有的顶点。
在图中添加一个顶点:要在图中添加一个顶点,我们需要增加现有邻接矩阵的行和列,然后将与该顶点相关的新元素初始化为 0。(即添加的新顶点不是连接到任何其他顶点)
C++
void addVertex()
{
// increasing the number of vertices
n++;
int i;
// initializing the new elements to 0
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
g[i][n - 1] = 0;
g[n - 1][i] = 0;
}
}
Java
public void addVertex()
{
// increasing the number of vertices
n++;
int i;
// initializing the new elements to 0
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
g[i][n - 1] = 0;
g[n - 1][i] = 0;
}
}
蟒蛇3
def addVertex(self):
# increasing the number of vertices
self.__n = self.__n + 1;
# initializing the new elements to 0
for i in range(0, self.__n):
self.__g[i][self.__n-1]= 0
self.__g[self.__n-1][i]= 0
上面的方法是Graph类的一个公共成员函数,它的顶点数加1,新顶点的度数为0。
删除图中的顶点:要从图中删除一个顶点,我们需要检查该顶点是否存在于图中,如果该顶点存在,则需要将行向左移动,将列向上移动邻接矩阵,以便给定顶点的行和列值被下一个顶点的值替换,然后将顶点的数量减少 1。这样特定的顶点将从邻接矩阵中删除。
C++
void removeVertex(int x)
{
// checking if the vertex is present
if (x > n) {
cout << "\nVertex not present!";
return;
}
else {
int i;
// removing the vertex
while (x < n) {
// shifting the rows to left side
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
g[i][x] = g[i][x + 1];
}
// shifting the columns upwards
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
g[x][i] = g[x + 1][i];
}
x++;
}
// decreasing the number of vertices
n--;
}
}
Java
public void removeVertex(int x)
{
// checking if the vertex is present
if (x > n) {
System.out.println("Vertex not present!");
return;
}
else {
int i;
// removing the vertex
while (x < n) {
// shifting the rows to left side
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
g[i][x] = g[i][x + 1];
}
// shifting the columns upwards
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
g[x][i] = g[x + 1][i];
}
x++;
}
// decreasing the number of vertices
n--;
}
}
蟒蛇3
def removeVertex(self, x):
# checking if the vertex is present
if(x>self.__n):
print("Vertex not present !")
else:
# removing the vertex
while(x上面的方法是 Graph 类的一个公共成员函数,它通过将行向左移动并向上移动列以用下一个顶点替换该顶点的行和列值,然后从图中删除现有顶点图中顶点数乘以 1。
以下是一个完整的程序,它在 Graph 中使用了上述所有方法。
C++
// C++ program to add and remove Vertex in Adjacency Matrix
#include
using namespace std;
class Graph {
private:
// number of vertices
int n;
// adjacency matrix
int g[10][10];
public:
// constructor
Graph(int x)
{
n = x;
// initializing each element of the adjacency matrix to zero
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
g[i][j] = 0;
}
}
}
void displayAdjacencyMatrix()
{
cout << "\n\n Adjacency Matrix:";
// displaying the 2D array
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
cout << "\n";
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
cout << " " << g[i][j];
}
}
}
void addEdge(int x, int y)
{
// checks if the vertex exists in the graph
if ((x >= n) || (y > n)) {
cout << "Vertex does not exists!";
}
// checks if the vertex is connecting to itself
if (x == y) {
cout << "Same Vertex!";
}
else {
// connecting the vertices
g[y][x] = 1;
g[x][y] = 1;
}
}
void addVertex()
{
// increasing the number of vertices
n++;
int i;
// initializing the new elements to 0
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
g[i][n - 1] = 0;
g[n - 1][i] = 0;
}
}
void removeVertex(int x)
{
// checking if the vertex is present
if (x > n) {
cout << "\nVertex not present!";
return;
}
else {
int i;
// removing the vertex
while (x < n) {
// shifting the rows to left side
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
g[i][x] = g[i][x + 1];
}
// shifting the columns upwards
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
g[x][i] = g[x + 1][i];
}
x++;
}
// decreasing the number of vertices
n--;
}
}
};
int main()
{
// creating objects of class Graph
Graph obj(4);
// calling methods
obj.addEdge(0, 1);
obj.addEdge(0, 2);
obj.addEdge(1, 2);
obj.addEdge(2, 3);
// the adjacency matrix created
obj.displayAdjacencyMatrix();
// adding a vertex to the graph
obj.addVertex();
// connecting that vertex to other existing vertices
obj.addEdge(4, 1);
obj.addEdge(4, 3);
// the adjacency matrix with a new vertex
obj.displayAdjacencyMatrix();
// removing an existing vertex in the graph
obj.removeVertex(1);
// the adjacency matrix after removing a vertex
obj.displayAdjacencyMatrix();
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program to add and remove Vertex in Adjacency Matrix
class Graph
{
// number of vertices
private int n;
// adjacency matrix
private int[][] g = new int[10][10];
// constructor
Graph(int x)
{
this.n = x;
int i, j;
// initializing each element of
// the adjacency matrix to zero
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
for (j = 0; j < n; ++j)
{
g[i][j] = 0;
}
}
}
public void displayAdjacencyMatrix()
{
System.out.print("\n\n Adjacency Matrix:");
// displaying the 2D array
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
System.out.println();
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j)
{
System.out.print(" " + g[i][j]);
}
}
}
public void addEdge(int x, int y)
{
// checks if the vertex exists in the graph
if ((x >= n) || (y > n))
{
System.out.println("Vertex does not exists!");
}
// checks if the vertex is connecting to itself
if (x == y)
{
System.out.println("Same Vertex!");
}
else
{
// connecting the vertices
g[y][x] = 1;
g[x][y] = 1;
}
}
public void addVertex()
{
// increasing the number of vertices
n++;
int i;
// initializing the new elements to 0
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
g[i][n - 1] = 0;
g[n - 1][i] = 0;
}
}
public void removeVertex(int x)
{
// checking if the vertex is present
if (x > n)
{
System.out.println("Vertex not present!");
return;
}
else
{
int i;
// removing the vertex
while (x < n)
{
// shifting the rows to left side
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
g[i][x] = g[i][x + 1];
}
// shifting the columns upwards
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
g[x][i] = g[x + 1][i];
}
x++;
}
// decreasing the number of vertices
n--;
}
}
}
class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// creating objects of class Graph
Graph obj = new Graph(4);
// calling methods
obj.addEdge(0, 1);
obj.addEdge(0, 2);
obj.addEdge(1, 2);
obj.addEdge(2, 3);
// the adjacency matrix created
obj.displayAdjacencyMatrix();
// adding a vertex to the graph
obj.addVertex();
// connecting that vertex to other existing vertices
obj.addEdge(4, 1);
obj.addEdge(4, 3);
// the adjacency matrix with a new vertex
obj.displayAdjacencyMatrix();
// removing an existing vertex in the graph
obj.removeVertex(1);
// the adjacency matrix after removing a vertex
obj.displayAdjacencyMatrix();
}
}
蟒蛇3
# Python program to add and remove Vertex in Adjacency Matrix
class Graph:
# number of vertices
__n = 0
# adjacency matrix
__g =[[0 for x in range(10)] for y in range(10)]
# constructor
def __init__(self, x):
self.__n = x
# initializing each element of the adjacency matrix to zero
for i in range(0, self.__n):
for j in range(0, self.__n):
self.__g[i][j]= 0
def displayAdjacencyMatrix(self):
print("\n\n Adjacency Matrix:", end ="")
# displaying the 2D array
for i in range(0, self.__n):
print()
for j in range(0, self.__n):
print("", self.__g[i][j], end ="")
def addEdge(self, x, y):
# checks if the vertex exists in the graph
if(x>= self.__n) or (y >= self.__n):
print("Vertex does not exists !")
# checks if the vertex is connecting to itself
if(x == y):
print("Same Vertex !")
else:
# connecting the vertices
self.__g[y][x]= 1
self.__g[x][y]= 1
def addVertex(self):
# increasing the number of vertices
self.__n = self.__n + 1;
# initializing the new elements to 0
for i in range(0, self.__n):
self.__g[i][self.__n-1]= 0
self.__g[self.__n-1][i]= 0
def removeVertex(self, x):
# checking if the vertex is present
if(x>self.__n):
print("Vertex not present !")
else:
# removing the vertex
while(xC#
// C# program to add and remove Vertex in Adjacency Matrix
using System;
public class Graph
{
// number of vertices
private int n;
// adjacency matrix
private int[,] g = new int[10, 10];
// constructor
public Graph(int x)
{
this.n = x;
int i, j;
// initializing each element of the adjacency matrix to zero
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
for (j = 0; j < n; ++j)
{
g[i, j] = 0;
}
}
}
public void displayAdjacencyMatrix()
{
Console.Write("\n\n Adjacency Matrix:");
// displaying the 2D array
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
Console.WriteLine();
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j)
{
Console.Write(" " + g[i, j]);
}
}
}
public void addEdge(int x, int y)
{
// checks if the vertex exists in the graph
if ((x >= n) || (y > n))
{
Console.WriteLine("Vertex does not exists!");
}
// checks if the vertex is connecting to itself
if (x == y)
{
Console.WriteLine("Same Vertex!");
}
else
{
// connecting the vertices
g[y, x] = 1;
g[x, y] = 1;
}
}
public void addVertex()
{
// increasing the number of vertices
n++;
int i;
// initializing the new elements to 0
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
g[i, n - 1] = 0;
g[n - 1, i] = 0;
}
}
public void removeVertex(int x)
{
// checking if the vertex is present
if (x > n)
{
Console.WriteLine("Vertex not present!");
return;
}
else
{
int i;
// removing the vertex
while (x < n)
{
// shifting the rows to left side
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
g[i, x] = g[i, x + 1];
}
// shifting the columns upwards
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
g[x, i] = g[x + 1, i];
}
x++;
}
// decreasing the number of vertices
n--;
}
}
}
public class GFG
{
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// creating objects of class Graph
Graph obj = new Graph(4);
// calling methods
obj.addEdge(0, 1);
obj.addEdge(0, 2);
obj.addEdge(1, 2);
obj.addEdge(2, 3);
// the adjacency matrix created
obj.displayAdjacencyMatrix();
// adding a vertex to the graph
obj.addVertex();
// connecting that vertex to other existing vertices
obj.addEdge(4, 1);
obj.addEdge(4, 3);
// the adjacency matrix with a new vertex
obj.displayAdjacencyMatrix();
// removing an existing vertex in the graph
obj.removeVertex(1);
// the adjacency matrix after removing a vertex
obj.displayAdjacencyMatrix();
}
}
// This code is contributed by PrinciRaj1992
Javascript
输出:
Adjacency Matrix:
0 1 1 0
1 0 1 0
1 1 0 1
0 0 1 0
Adjacency Matrix:
0 1 1 0 0
1 0 1 0 1
1 1 0 1 0
0 0 1 0 1
0 1 0 1 0
Adjacency Matrix:
0 1 0 0
1 0 1 0
0 1 0 1
0 0 1 0邻接矩阵浪费了大量的内存空间。发现这样的矩阵非常稀疏。这种表示需要n*n个元素的空间,addVertex()方法的时间复杂度为O(n),removeVertex()方法的时间复杂度为O(n*n),对于n个顶点的图。
从程序的输出来看,邻接矩阵是:
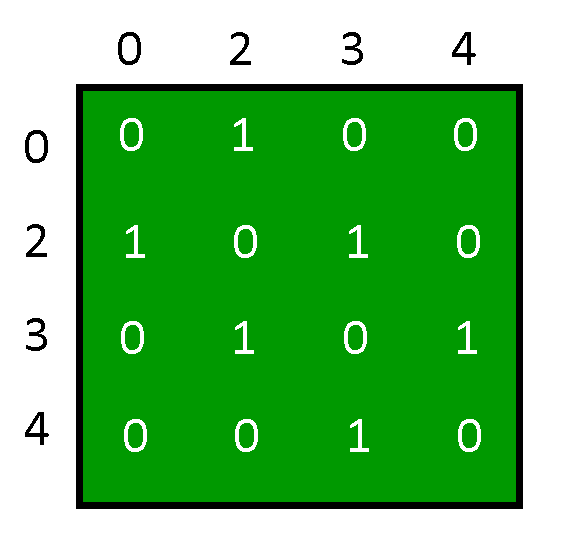
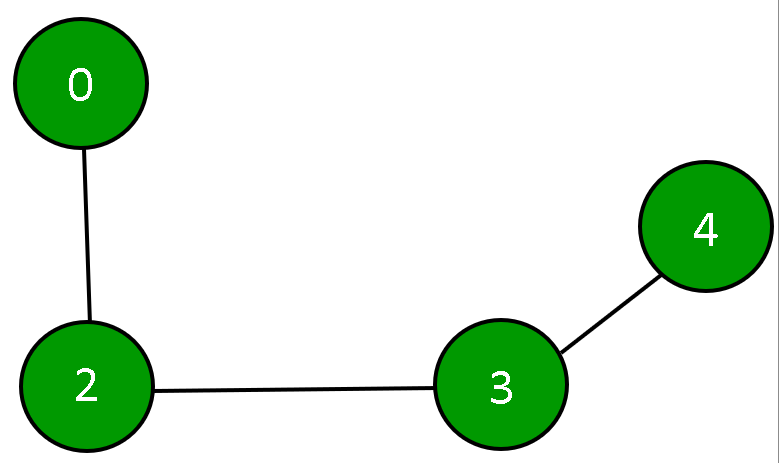
而上述邻接矩阵所描绘的Graph为:
如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。