翻转二叉树
给定一棵二叉树,任务是将二叉树朝顺时针的正确方向翻转。请参阅以下示例以查看转换。
在翻转操作中,最左边的节点成为翻转树的根,它的父节点成为它的右孩子,右兄弟成为它的左孩子,并且应该递归地对所有最左边的节点执行相同的操作。
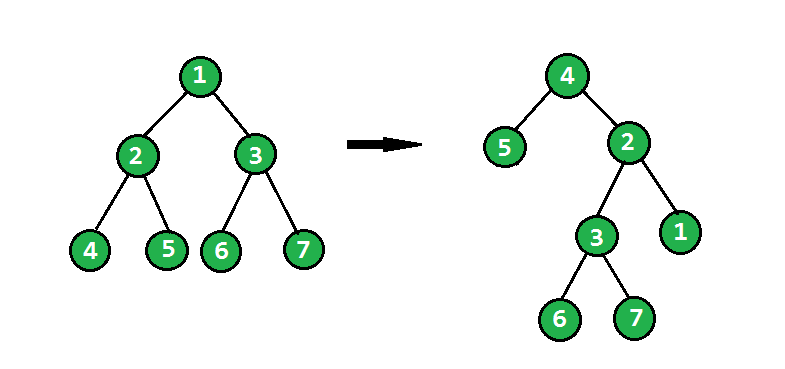
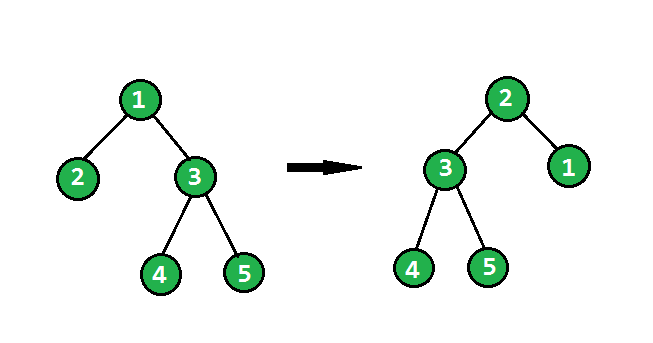
下面是子树的主要旋转代码
root->left->left = root->right;
root->left->right = root;
root->left = NULL;
root->right = NULL; 上面的代码可以通过下图来理解——
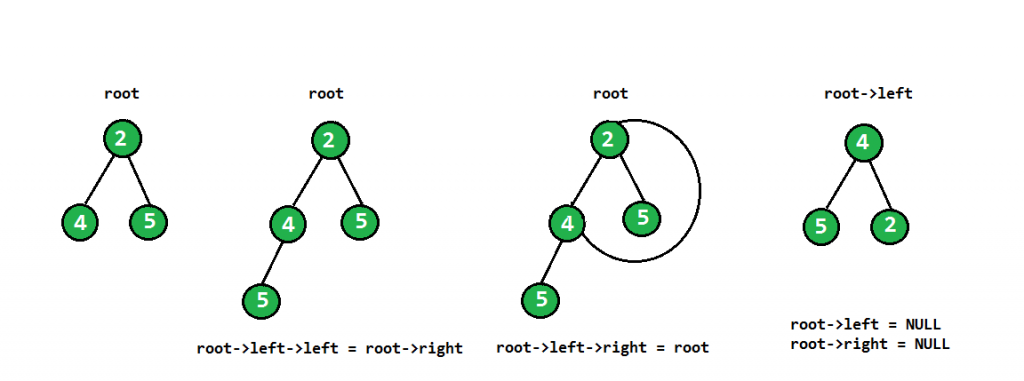
当我们将 root->left 存储在翻转的根中时,翻转的子树存储在每个递归调用中。
C++
/* C/C++ program to flip a binary tree */
#include
using namespace std;
/* A binary tree node structure */
struct Node
{
int data;
Node *left, *right;
};
/* Utility function to create a new Binary
Tree Node */
struct Node* newNode(int data)
{
struct Node *temp = new struct Node;
temp->data = data;
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
return temp;
}
// method to flip the binary tree
Node* flipBinaryTree(Node* root)
{
// Base cases
if (root == NULL)
return root;
if (root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL)
return root;
// recursively call the same method
Node* flippedRoot = flipBinaryTree(root->left);
// rearranging main root Node after returning
// from recursive call
root->left->left = root->right;
root->left->right = root;
root->left = root->right = NULL;
return flippedRoot;
}
// Iterative method to do level order traversal
// line by line
void printLevelOrder(Node *root)
{
// Base Case
if (root == NULL) return;
// Create an empty queue for level order traversal
queue q;
// Enqueue Root and initialize height
q.push(root);
while (1)
{
// nodeCount (queue size) indicates number
// of nodes at current level.
int nodeCount = q.size();
if (nodeCount == 0)
break;
// Dequeue all nodes of current level and
// Enqueue all nodes of next level
while (nodeCount > 0)
{
Node *node = q.front();
cout << node->data << " ";
q.pop();
if (node->left != NULL)
q.push(node->left);
if (node->right != NULL)
q.push(node->right);
nodeCount--;
}
cout << endl;
}
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
Node* root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->right->left = newNode(4);
root->right->right = newNode(5);
cout << "Level order traversal of given tree\n";
printLevelOrder(root);
root = flipBinaryTree(root);
cout << "\nLevel order traversal of the flipped"
" tree\n";
printLevelOrder(root);
return 0;
} Java
/* Java program to flip a binary tree */
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class FlipTree {
// method to flip the binary tree
public static Node flipBinaryTree(Node root)
{
if (root == null)
return root;
if (root.left == null && root.right ==null)
return root;
// recursively call the same method
Node flippedRoot=flipBinaryTree(root.left);
// rearranging main root Node after returning
// from recursive call
root.left.left=root.right;
root.left.right=root;
root.left=root.right=null;
return flippedRoot;
}
// Iterative method to do level order traversal
// line by line
public static void printLevelOrder(Node root)
{
// Base Case
if(root==null)
return ;
// Create an empty queue for level order traversal
Queue q=new LinkedList<>();
// Enqueue Root and initialize height
q.add(root);
while(true)
{
// nodeCount (queue size) indicates number
// of nodes at current level.
int nodeCount = q.size();
if (nodeCount == 0)
break;
// Dequeue all nodes of current level and
// Enqueue all nodes of next level
while (nodeCount > 0)
{
Node node = q.remove();
System.out.print(node.data+" ");
if (node.left != null)
q.add(node.left);
if (node.right != null)
q.add(node.right);
nodeCount--;
}
System.out.println();
}
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
Node root=new Node(1);
root.left=new Node(2);
root.right=new Node(1);
root.right.left = new Node(4);
root.right.right = new Node(5);
System.out.println("Level order traversal of given tree");
printLevelOrder(root);
root = flipBinaryTree(root);
System.out.println("Level order traversal of flipped tree");
printLevelOrder(root);
}
}
/* A binary tree node structure */
class Node
{
int data;
Node left, right;
Node(int data)
{
this.data=data;
}
};
//This code is contributed by Gaurav Tiwari Python3
# Python3 program to flip
# a binary tree
# A binary tree node
class Node:
# Constructor to create
# a new node
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.right = None
self.left = None
def flipBinaryTree(root):
# Base Cases
if root is None:
return root
if (root.left is None and
root.right is None):
return root
# Recursively call the
# same method
flippedRoot = flipBinaryTree(root.left)
# Rearranging main root Node
# after returning from
# recursive call
root.left.left = root.right
root.left.right = root
root.left = root.right = None
return flippedRoot
# Iterative method to do the level
# order traversal line by line
def printLevelOrder(root):
# Base Case
if root is None:
return
# Create an empty queue for
# level order traversal
from Queue import Queue
q = Queue()
# Enqueue root and initialize
# height
q.put(root)
while(True):
# nodeCount (queue size) indicates
# number of nodes at current level
nodeCount = q.qsize()
if nodeCount == 0:
break
# Dequeue all nodes of current
# level and Enqueue all nodes
# of next level
while nodeCount > 0:
node = q.get()
print node.data,
if node.left is not None:
q.put(node.left)
if node.right is not None:
q.put(node.right)
nodeCount -= 1
print
# Driver code
root = Node(1)
root.left = Node(2)
root.right = Node(3)
root.right.left = Node(4)
root.right.right = Node(5)
print "Level order traversal of given tree"
printLevelOrder(root)
root = flipBinaryTree(root)
print "\nLevel order traversal of the flipped tree"
printLevelOrder(root)
# This code is contributed by Nikhil Kumar Singh(nickzuck_007)C#
// C# program to flip a binary tree
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class FlipTree
{
// method to flip the binary tree
public static Node flipBinaryTree(Node root)
{
if (root == null)
return root;
if (root.left == null && root.right ==null)
return root;
// recursively call the same method
Node flippedRoot = flipBinaryTree(root.left);
// rearranging main root Node after returning
// from recursive call
root.left.left = root.right;
root.left.right = root;
root.left = root.right = null;
return flippedRoot;
}
// Iterative method to do level order traversal
// line by line
public static void printLevelOrder(Node root)
{
// Base Case
if(root == null)
return ;
// Create an empty queue for level order traversal
Queue q = new Queue();
// Enqueue Root and initialize height
q.Enqueue(root);
while(true)
{
// nodeCount (queue size) indicates number
// of nodes at current level.
int nodeCount = q.Count;
if (nodeCount == 0)
break;
// Dequeue all nodes of current level and
// Enqueue all nodes of next level
while (nodeCount > 0)
{
Node node = q.Dequeue();
Console.Write(node.data+" ");
if (node.left != null)
q.Enqueue(node.left);
if (node.right != null)
q.Enqueue(node.right);
nodeCount--;
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String []args)
{
Node root = new Node(1);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(1);
root.right.left = new Node(4);
root.right.right = new Node(5);
Console.WriteLine("Level order traversal of given tree");
printLevelOrder(root);
root = flipBinaryTree(root);
Console.WriteLine("Level order traversal of flipped tree");
printLevelOrder(root);
}
}
/* A binary tree node structure */
public class Node
{
public int data;
public Node left, right;
public Node(int data)
{
this.data = data;
}
};
// This code is contributed by Princi Singh Javascript
C++
// C/C++ program to flip a binary tree
#include
using namespace std;
// A binary tree node structure
struct Node
{
int data;
Node *left, *right;
};
// Utility function to create a new Binary
// Tree Node
struct Node* newNode(int data)
{
struct Node *temp = new struct Node;
temp->data = data;
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
return temp;
}
// method to flip the binary tree
Node* flipBinaryTree(Node* root)
{
// Initialization of pointers
Node *curr = root;
Node *next = NULL;
Node *temp = NULL;
Node *prev = NULL;
// Iterate through all left nodes
while(curr)
{
next = curr->left;
// Swapping nodes now, need temp to keep the previous right child
// Making prev's right as curr's left child
curr->left = temp;
// Storing curr's right child
temp = curr->right;
// Making prev as curr's right child
curr->right = prev;
prev = curr;
curr = next;
}
return prev;
}
// Iterative method to do level order traversal
// line by line
void printLevelOrder(Node *root)
{
// Base Case
if (root == NULL) return;
// Create an empty queue for level order traversal
queue q;
// Enqueue Root and initialize height
q.push(root);
while (1)
{
// nodeCount (queue size) indicates number
// of nodes at current level.
int nodeCount = q.size();
if (nodeCount == 0)
break;
// Dequeue all nodes of current level and
// Enqueue all nodes of next level
while (nodeCount > 0)
{
Node *node = q.front();
cout << node->data << " ";
q.pop();
if (node->left != NULL)
q.push(node->left);
if (node->right != NULL)
q.push(node->right);
nodeCount--;
}
cout << endl;
}
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
Node* root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->right->left = newNode(4);
root->right->right = newNode(5);
cout << "Level order traversal of given tree\n";
printLevelOrder(root);
root = flipBinaryTree(root);
cout << "\nLevel order traversal of the flipped"
" tree\n";
printLevelOrder(root);
return 0;
}
// This article is contributed by Pal13 Java
// Java program to flip a binary tree
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
// A binary tree node
static class Node
{
int data;
Node left, right;
};
// Utility function to create
// a new Binary Tree Node
static Node newNode(int data)
{
Node temp = new Node();
temp.data = data;
temp.left = temp.right = null;
return temp;
}
// method to flip the binary tree
static Node flipBinaryTree(Node root)
{
// Initialization of pointers
Node curr = root;
Node next = null;
Node temp = null;
Node prev = null;
// Iterate through all left nodes
while(curr != null)
{
next = curr.left;
// Swapping nodes now, need
// temp to keep the previous
// right child
// Making prev's right
// as curr's left child
curr.left = temp;
// Storing curr's right child
temp = curr.right;
// Making prev as curr's
// right child
curr.right = prev;
prev = curr;
curr = next;
}
return prev;
}
// Iterative method to do
// level order traversal
// line by line
static void printLevelOrder(Node root)
{
// Base Case
if (root == null) return;
// Create an empty queue for
// level order traversal
Queue q = new LinkedList();
// Enqueue Root and
// initialize height
q.add(root);
while (true)
{
// nodeCount (queue size)
// indicates number of nodes
// at current level.
int nodeCount = q.size();
if (nodeCount == 0)
break;
// Dequeue all nodes of current
// level and Enqueue all nodes
// of next level
while (nodeCount > 0)
{
Node node = q.peek();
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
q.remove();
if (node.left != null)
q.add(node.left);
if (node.right != null)
q.add(node.right);
nodeCount--;
}
System.out.println();
}
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String args[])
{
Node root = newNode(1);
root.left = newNode(2);
root.right = newNode(3);
root.right.left = newNode(4);
root.right.right = newNode(5);
System.out.print("Level order traversal " +
"of given tree\n");
printLevelOrder(root);
root = flipBinaryTree(root);
System.out.print("\nLevel order traversal " +
"of the flipped tree\n");
printLevelOrder(root);
}
}
// This code is contributed
// by Arnab Kundu Python3
# Python3 program to flip
# a binary tree
from collections import deque
# A binary tree node structure
class Node:
def __init__(self, key):
self.data = key
self.left = None
self.right = None
# method to flip the
# binary tree
def flipBinaryTree(root):
# Initialization of
# pointers
curr = root
next = None
temp = None
prev = None
# Iterate through all
# left nodes
while(curr):
next = curr.left
# Swapping nodes now, need temp
# to keep the previous right child
# Making prev's right as curr's
# left child
curr.left = temp
# Storing curr's right child
temp = curr.right
# Making prev as curr's right
# child
curr.right = prev
prev = curr
curr = next
return prev
# Iterative method to do level
# order traversal line by line
def printLevelOrder(root):
# Base Case
if (root == None):
return
# Create an empty queue for
# level order traversal
q = deque()
# Enqueue Root and initialize
# height
q.append(root)
while (1):
# nodeCount (queue size) indicates
# number of nodes at current level.
nodeCount = len(q)
if (nodeCount == 0):
break
# Dequeue all nodes of current
# level and Enqueue all nodes
# of next level
while (nodeCount > 0):
node = q.popleft()
print(node.data, end = " ")
if (node.left != None):
q.append(node.left)
if (node.right != None):
q.append(node.right)
nodeCount -= 1
print()
# Driver code
if __name__ == '__main__':
root = Node(1)
root.left = Node(2)
root.right = Node(3)
root.right.left = Node(4)
root.right.right = Node(5)
print("Level order traversal of given tree")
printLevelOrder(root)
root = flipBinaryTree(root)
print("\nLevel order traversal of the flipped"
" tree")
printLevelOrder(root)
# This code is contributed by Mohit Kumar 29C#
// C# program to flip a binary tree
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG
{
// A binary tree node
public class Node
{
public int data;
public Node left, right;
}
// Utility function to create
// a new Binary Tree Node
public static Node newNode(int data)
{
Node temp = new Node();
temp.data = data;
temp.left = temp.right = null;
return temp;
}
// method to flip the binary tree
public static Node flipBinaryTree(Node root)
{
// Initialization of pointers
Node curr = root;
Node next = null;
Node temp = null;
Node prev = null;
// Iterate through all left nodes
while (curr != null)
{
next = curr.left;
// Swapping nodes now, need
// temp to keep the previous
// right child
// Making prev's right
// as curr's left child
curr.left = temp;
// Storing curr's right child
temp = curr.right;
// Making prev as curr's
// right child
curr.right = prev;
prev = curr;
curr = next;
}
return prev;
}
// Iterative method to do level
// order traversal line by line
public static void printLevelOrder(Node root)
{
// Base Case
if (root == null)
{
return;
}
// Create an empty queue for
// level order traversal
LinkedList q = new LinkedList();
// Enqueue Root and
// initialize height
q.AddLast(root);
while (true)
{
// nodeCount (queue size)
// indicates number of nodes
// at current level.
int nodeCount = q.Count;
if (nodeCount == 0)
{
break;
}
// Dequeue all nodes of current
// level and Enqueue all nodes
// of next level
while (nodeCount > 0)
{
Node node = q.First.Value;
Console.Write(node.data + " ");
q.RemoveFirst();
if (node.left != null)
{
q.AddLast(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null)
{
q.AddLast(node.right);
}
nodeCount--;
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
Node root = newNode(1);
root.left = newNode(2);
root.right = newNode(3);
root.right.left = newNode(4);
root.right.right = newNode(5);
Console.Write("Level order traversal " +
"of given tree\n");
printLevelOrder(root);
root = flipBinaryTree(root);
Console.Write("\nLevel order traversal " +
"of the flipped tree\n");
printLevelOrder(root);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Shrikant13 Javascript
输出:
Level order traversal of given tree
1
2 3
4 5
Level order traversal of the flipped tree
2
3 1
4 5 迭代方法
这种方法是由Pal13贡献的。
迭代解法跟递归解法一样,唯一需要注意的是保存会被覆盖的节点信息。
C++
// C/C++ program to flip a binary tree
#include
using namespace std;
// A binary tree node structure
struct Node
{
int data;
Node *left, *right;
};
// Utility function to create a new Binary
// Tree Node
struct Node* newNode(int data)
{
struct Node *temp = new struct Node;
temp->data = data;
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
return temp;
}
// method to flip the binary tree
Node* flipBinaryTree(Node* root)
{
// Initialization of pointers
Node *curr = root;
Node *next = NULL;
Node *temp = NULL;
Node *prev = NULL;
// Iterate through all left nodes
while(curr)
{
next = curr->left;
// Swapping nodes now, need temp to keep the previous right child
// Making prev's right as curr's left child
curr->left = temp;
// Storing curr's right child
temp = curr->right;
// Making prev as curr's right child
curr->right = prev;
prev = curr;
curr = next;
}
return prev;
}
// Iterative method to do level order traversal
// line by line
void printLevelOrder(Node *root)
{
// Base Case
if (root == NULL) return;
// Create an empty queue for level order traversal
queue q;
// Enqueue Root and initialize height
q.push(root);
while (1)
{
// nodeCount (queue size) indicates number
// of nodes at current level.
int nodeCount = q.size();
if (nodeCount == 0)
break;
// Dequeue all nodes of current level and
// Enqueue all nodes of next level
while (nodeCount > 0)
{
Node *node = q.front();
cout << node->data << " ";
q.pop();
if (node->left != NULL)
q.push(node->left);
if (node->right != NULL)
q.push(node->right);
nodeCount--;
}
cout << endl;
}
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
Node* root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->right->left = newNode(4);
root->right->right = newNode(5);
cout << "Level order traversal of given tree\n";
printLevelOrder(root);
root = flipBinaryTree(root);
cout << "\nLevel order traversal of the flipped"
" tree\n";
printLevelOrder(root);
return 0;
}
// This article is contributed by Pal13
Java
// Java program to flip a binary tree
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
// A binary tree node
static class Node
{
int data;
Node left, right;
};
// Utility function to create
// a new Binary Tree Node
static Node newNode(int data)
{
Node temp = new Node();
temp.data = data;
temp.left = temp.right = null;
return temp;
}
// method to flip the binary tree
static Node flipBinaryTree(Node root)
{
// Initialization of pointers
Node curr = root;
Node next = null;
Node temp = null;
Node prev = null;
// Iterate through all left nodes
while(curr != null)
{
next = curr.left;
// Swapping nodes now, need
// temp to keep the previous
// right child
// Making prev's right
// as curr's left child
curr.left = temp;
// Storing curr's right child
temp = curr.right;
// Making prev as curr's
// right child
curr.right = prev;
prev = curr;
curr = next;
}
return prev;
}
// Iterative method to do
// level order traversal
// line by line
static void printLevelOrder(Node root)
{
// Base Case
if (root == null) return;
// Create an empty queue for
// level order traversal
Queue q = new LinkedList();
// Enqueue Root and
// initialize height
q.add(root);
while (true)
{
// nodeCount (queue size)
// indicates number of nodes
// at current level.
int nodeCount = q.size();
if (nodeCount == 0)
break;
// Dequeue all nodes of current
// level and Enqueue all nodes
// of next level
while (nodeCount > 0)
{
Node node = q.peek();
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
q.remove();
if (node.left != null)
q.add(node.left);
if (node.right != null)
q.add(node.right);
nodeCount--;
}
System.out.println();
}
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String args[])
{
Node root = newNode(1);
root.left = newNode(2);
root.right = newNode(3);
root.right.left = newNode(4);
root.right.right = newNode(5);
System.out.print("Level order traversal " +
"of given tree\n");
printLevelOrder(root);
root = flipBinaryTree(root);
System.out.print("\nLevel order traversal " +
"of the flipped tree\n");
printLevelOrder(root);
}
}
// This code is contributed
// by Arnab Kundu
Python3
# Python3 program to flip
# a binary tree
from collections import deque
# A binary tree node structure
class Node:
def __init__(self, key):
self.data = key
self.left = None
self.right = None
# method to flip the
# binary tree
def flipBinaryTree(root):
# Initialization of
# pointers
curr = root
next = None
temp = None
prev = None
# Iterate through all
# left nodes
while(curr):
next = curr.left
# Swapping nodes now, need temp
# to keep the previous right child
# Making prev's right as curr's
# left child
curr.left = temp
# Storing curr's right child
temp = curr.right
# Making prev as curr's right
# child
curr.right = prev
prev = curr
curr = next
return prev
# Iterative method to do level
# order traversal line by line
def printLevelOrder(root):
# Base Case
if (root == None):
return
# Create an empty queue for
# level order traversal
q = deque()
# Enqueue Root and initialize
# height
q.append(root)
while (1):
# nodeCount (queue size) indicates
# number of nodes at current level.
nodeCount = len(q)
if (nodeCount == 0):
break
# Dequeue all nodes of current
# level and Enqueue all nodes
# of next level
while (nodeCount > 0):
node = q.popleft()
print(node.data, end = " ")
if (node.left != None):
q.append(node.left)
if (node.right != None):
q.append(node.right)
nodeCount -= 1
print()
# Driver code
if __name__ == '__main__':
root = Node(1)
root.left = Node(2)
root.right = Node(3)
root.right.left = Node(4)
root.right.right = Node(5)
print("Level order traversal of given tree")
printLevelOrder(root)
root = flipBinaryTree(root)
print("\nLevel order traversal of the flipped"
" tree")
printLevelOrder(root)
# This code is contributed by Mohit Kumar 29
C#
// C# program to flip a binary tree
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG
{
// A binary tree node
public class Node
{
public int data;
public Node left, right;
}
// Utility function to create
// a new Binary Tree Node
public static Node newNode(int data)
{
Node temp = new Node();
temp.data = data;
temp.left = temp.right = null;
return temp;
}
// method to flip the binary tree
public static Node flipBinaryTree(Node root)
{
// Initialization of pointers
Node curr = root;
Node next = null;
Node temp = null;
Node prev = null;
// Iterate through all left nodes
while (curr != null)
{
next = curr.left;
// Swapping nodes now, need
// temp to keep the previous
// right child
// Making prev's right
// as curr's left child
curr.left = temp;
// Storing curr's right child
temp = curr.right;
// Making prev as curr's
// right child
curr.right = prev;
prev = curr;
curr = next;
}
return prev;
}
// Iterative method to do level
// order traversal line by line
public static void printLevelOrder(Node root)
{
// Base Case
if (root == null)
{
return;
}
// Create an empty queue for
// level order traversal
LinkedList q = new LinkedList();
// Enqueue Root and
// initialize height
q.AddLast(root);
while (true)
{
// nodeCount (queue size)
// indicates number of nodes
// at current level.
int nodeCount = q.Count;
if (nodeCount == 0)
{
break;
}
// Dequeue all nodes of current
// level and Enqueue all nodes
// of next level
while (nodeCount > 0)
{
Node node = q.First.Value;
Console.Write(node.data + " ");
q.RemoveFirst();
if (node.left != null)
{
q.AddLast(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null)
{
q.AddLast(node.right);
}
nodeCount--;
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
Node root = newNode(1);
root.left = newNode(2);
root.right = newNode(3);
root.right.left = newNode(4);
root.right.right = newNode(5);
Console.Write("Level order traversal " +
"of given tree\n");
printLevelOrder(root);
root = flipBinaryTree(root);
Console.Write("\nLevel order traversal " +
"of the flipped tree\n");
printLevelOrder(root);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Shrikant13
Javascript
输出:
Level order traversal of given tree
1
2 3
4 5
Level order traversal of the flipped tree
2
3 1
4 5 复杂性分析:
时间复杂度: O(n),在最坏的情况下,二叉树的深度为 n。
辅助空间: O(1)。