通过将第一个和最后一个替换为 max 和 min 来排列 Array 中剩余数字的排名
给定一个大小为N的数组arr[ ] ,任务是在执行给定操作后找到数组中剩余元素的秩:
- 在每个操作中,从两端选择元素并删除它们,并将这些值的最大值插入左侧元素的位置,然后从两端向中心移动一步,并继续执行此操作。
- 在下一个循环中继续执行相同的操作,但这次插入元素的最小值而不是最大值。
- 交替循环执行此操作,直到数组中只剩下一个元素。
- 秩是原始数组中剩余元素按升序排序时的位置。 (具有相同值的元素仅考虑排序顺序)
例子:
Input: arr = {4, 5, 3, 56, 3, 24, 5, 6, 22, 4, 55, 50, 89}
Output: 6
Explanation: See the diagram given below
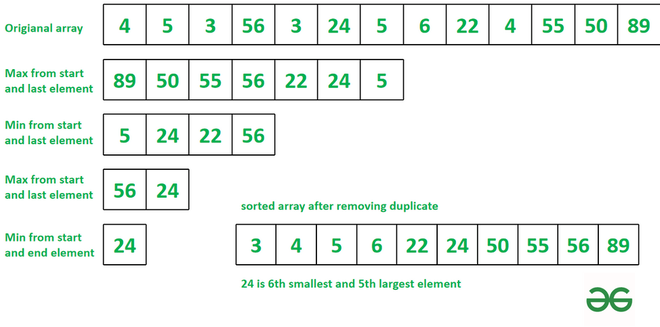
24 is th 6th smallest element. The elements with same values are considered once.
Input: N = {20, 4, 5, 35, 6, 22, 4, 34}
Output: 6
方法:该解决方案基于两个指针方法。请按照以下步骤操作:
- 取c 为 1 ,表示迭代次数。
- 取 2 个指针,从零开始,以N-1结束。
- 比较索引s和e处的元素。
- 如果c 是奇数,则取元素的最大值,否则取元素的最小值并存储在数组中。
- 增加s ,减少e并重复直到s != e 。
- 将 c 增加 1
- 重复步骤 2,直到 arr 的长度变为 1。
- 从arr[]中删除重复项并对其进行排序,现在找到剩余元素的排名。
下面是上述方法的实现。
C++
// C++ code for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Function to find rank of number in array
int rankOfNum(vector& num)
{
// Copying array to S
vector S = num;
// c count no of iterations
int c = 1;
while (S.size() != 1) {
// s is starting index
int s = 0;
// e is ending index
int e = S.size() - 1;
// Empty array to store
// result of comparisons.
vector l;
// loop till s <= e
while (s <= e) {
// In odd iterations take
// maximum of element.
if (c % 2 == 1)
l.push_back(max(S[s], S[e]));
// In even Iterations
// take minimum of element.
else {
l.push_back(min(S[s], S[e]));
}
// Increment s by 1
// and decrement e by 1
s += 1;
e -= 1;
}
// Assigning l to S
S = l;
// Increment iteration value by 1
c += 1;
}
// Converting list into set and again to list
// so that all duplicate will get removed
set setx;
for (auto dt : num)
setx.insert(dt);
// Finding index of remained element
int p = distance(setx.begin(), setx.find(S[0]));
// Returning the rank of element
return p + 1;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
// Original array
vector arr
= { 4, 5, 3, 56, 3, 24, 5, 6, 22, 4, 55, 50, 89 };
// Calling function
int s = rankOfNum(arr);
// Print its rank
cout << s;
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by rakeshsahni Java
// Java code for the above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
// Function to find rank of number in array
static int rankOfNum(Integer[] num)
{
// Copying array to S
List S = Arrays.asList(num);
// c count no of iterations
int c = 1;
while (S.size() != 1) {
// s is starting index
int s = 0;
// e is ending index
int e = S.size() - 1;
// Empty array to store
// result of comparisons.
ArrayList l = new ArrayList();
// loop till s <= e
while (s <= e) {
// In odd iterations take
// maximum of element.
if (c % 2 == 1)
l.add(Math.max(S.get(s), S.get(e)));
// In even Iterations
// take minimum of element.
else {
l.add(Math.min(S.get(s), S.get(e)));
}
// Increment s by 1
// and decrement e by 1
s += 1;
e -= 1;
}
// Assigning l to S
S = l;
// Increment iteration value by 1
c += 1;
}
// Converting list into set and again to list
// so that all duplicate will get removed
HashSet setx = new HashSet();
for (int dt : num)
setx.add(dt);
// Finding index of remained element
List l = new LinkedList<>(setx);
Collections.sort(l);
int p = l.indexOf(S.get(0));
// Returning the rank of element
return p + 1;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Original array
Integer[] arr
= { 4, 5, 3, 56, 3, 24, 5, 6, 22, 4, 55, 50, 89 };
// Calling function
int s = rankOfNum(arr);
// Print its rank
System.out.print(s);
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar Python3
# Python code to implement above approach
# Function to find rank of number in array
def rankOfNum(num):
# Copying array to S
S = num[:]
# c count no of iterations
c = 1
while len(S) != 1:
# s is starting index
s = 0
# e is ending index
e = len(S) - 1
# Empty array to store
# result of comparisons.
l = []
# loop till s <= e
while s <= e:
# In odd iterations take
# maximum of element.
if c % 2 == 1:
l.append(max(S[s], S[e]))
# In even Iterations
# take minimum of element.
else:
l.append(min(S[s], S[e]))
# Increment s by 1
# and decrement e by 1
s += 1
e -= 1
# Assigning l to S
S = l
# Increment iteration value by 1
c += 1
# Converting list into set and again to list
# so that all duplicate will get removed
setx = list(set(num))
# Sorting to get rank
setx.sort()
# Finding index of remained element
p = setx.index(S[0])
# Returning the rank of element
return p + 1
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Original array
arr = [4, 5, 3, 56, 3, 24, 5, 6, 22, 4, 55, 50, 89]
# Calling function
s = rankOfNum(arr)
# Print its rank
print(str(s))C#
// C# code for the above approach
using System;
using System.Linq;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG {
// Function to find rank of number in array
static int rankOfNum(List num)
{
// Copying array to S
List S = num;
// c count no of iterations
int c = 1;
while (S.Count != 1) {
// s is starting index
int s = 0;
// e is ending index
int e = S.Count - 1;
// Empty array to store
// result of comparisons.
List l = new List();
// loop till s <= e
while (s <= e) {
// In odd iterations take
// maximum of element.
if (c % 2 == 1)
l.Add(Math.Max(S[s], S[e]));
// In even Iterations
// take minimum of element.
else {
l.Add(Math.Min(S[s], S[e]));
}
// Increment s by 1
// and decrement e by 1
s += 1;
e -= 1;
}
// Assigning l to S
S = l;
// Increment iteration value by 1
c += 1;
}
// Converting list into set and again to list
// so that all duplicate will get removed
HashSet setx = new HashSet();
foreach(var dt in num) setx.Add(dt);
// Finding index of remained element
List setxList = setx.ToList();
setxList.Sort();
int p = setxList.IndexOf(S[0]);
// Returning the rank of element
return p + 1;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main()
{
// Original array
List arr = new List() {
4, 5, 3, 56, 3, 24, 5, 6, 22, 4, 55, 50, 89
};
// Calling function
int s = rankOfNum(arr);
// Print its rank
Console.Write(s);
}
}
// This code is contributed by ukasp. Javascript
输出
6时间复杂度: O(N)
空间复杂度: O(N)