📌 相关文章
- 国际化 - 任何代码示例
- 国际化测试(1)
- 国际化测试
- Flutter-国际化(1)
- Flutter – 国际化(1)
- Flutter – 国际化
- Flutter – 国际化
- Flutter – 国际化(1)
- Flutter-国际化
- AngularJS-国际化(1)
- AngularJS-国际化
- Java国际化教程
- Java国际化教程(1)
- 讨论JSF
- CodeIgniter-国际化(1)
- CodeIgniter-国际化
- JSF-概述
- JSF-概述(1)
- JSF-Ajax(1)
- JSF-Ajax
- Drupal-国际化
- Drupal-国际化(1)
- Flex-国际化(1)
- Flex-国际化
- Servlet-国际化(1)
- Servlet-国际化
- Symfony-国际化(1)
- Symfony-国际化
- JSF-数据表
📜 JSF-国际化
📅 最后修改于: 2020-10-23 06:49:32 🧑 作者: Mango
国际化是一种在程序中不对状态消息,GUI组件标签,货币,日期进行硬编码的技术。而是将它们存储在源代码之外的资源束中,并进行动态检索。 JSF提供了一种非常方便的方式来处理资源束。
需要以下步骤来内部化JSF应用程序。
步骤1:定义属性文件
为每个语言环境创建属性文件。名称应为<文件名> _ <语言环境> .properties格式。
文件名中可以省略默认语言环境。
messages.properties
greeting = Hello World!
messages_fr.properties
greeting = Bonjour tout le monde!
步骤2:更新faces-config.xml
faces-config.xml
en
fr
com.tutorialspoint.messages
msg
步骤3:使用resource-bundle var
home.xhtml
应用范例
让我们创建一个测试JSF应用程序以测试JSF中的国际化。
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Create a project with a name helloworld under a package com.tutorialspoint.test as explained in the JSF – First Application chapter. |
| 2 | Create resources folder under src → mai folder. |
| 3 | Create com folder under src → main → resources folder. |
| 4 | Create tutorialspoint folder under src → main → resources → com folder. |
| 5 | Create messages.properties file under src → main → resources → com → tutorialspoint folder. Modify it as explained below. |
| 6 | Create messages_fr.properties file under src → main → resources → com → tutorialspoint folder. Modify it as explained below. |
| 7 | Create faces-config.xml in WEB-INFf older as explained below. |
| 8 | Create UserData.java under package com.tutorialspoint.test as explained below. |
| 9 | Modify home.xhtml as explained below. Keep the rest of the files unchanged. |
| 10 | Compile and run the application to make sure the business logic is working as per the requirements. |
| 11 | Finally, build the application in the form of war file and deploy it in Apache Tomcat Webserver. |
| 12 | Launch your web application using appropriate URL as explained below in the last step. |
messages.properties
greeting = Hello World!
messages_fr.properties
greeting = Bonjour tout le monde!
faces-config.xml
en
fr
com.tutorialspoint.messages
msg
UserData.java
package com.tutorialspoint.test;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
import java.util.Locale;
import java.util.Map;
import javax.faces.bean.ManagedBean;
import javax.faces.bean.SessionScoped;
import javax.faces.context.FacesContext;
import javax.faces.event.ValueChangeEvent;
@ManagedBean(name = "userData", eager = true)
@SessionScoped
public class UserData implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private String locale;
private static Map countries;
static {
countries = new LinkedHashMap();
countries.put("English", Locale.ENGLISH);
countries.put("French", Locale.FRENCH);
}
public Map getCountries() {
return countries;
}
public String getLocale() {
return locale;
}
public void setLocale(String locale) {
this.locale = locale;
}
//value change event listener
public void localeChanged(ValueChangeEvent e) {
String newLocaleValue = e.getNewValue().toString();
for (Map.Entry entry : countries.entrySet()) {
if(entry.getValue().toString().equals(newLocaleValue)) {
FacesContext.getCurrentInstance()
.getViewRoot().setLocale((Locale)entry.getValue());
}
}
}
}
home.xhtml
JSF tutorial
Internalization Language Example
准备好所有更改后,让我们像在JSF-First Application一章中那样编译并运行该应用程序。如果您的应用程序一切正常,将产生以下结果。
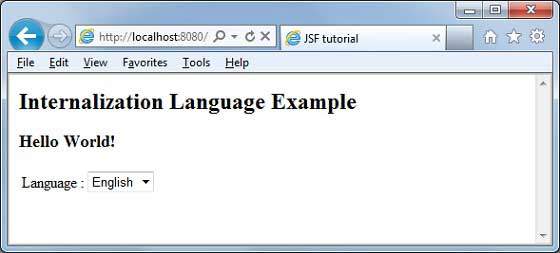
从下拉菜单更改语言。您将看到以下输出。