Julia 中的运算符是用于对变量和值执行运算的数学符号。这些符号用于进行算术和逻辑计算。运算符对其执行操作的变量称为Operands 。换句话说,我们可以说运算符操作操作数。
例如,考虑以下语句:
c = a + b;这里,“+”是被称为加法运算符和“a”和“b”是操作数运算符。加法运算符告诉编译器将操作数 ‘a’ 和 ‘b’ 相加。
运算符类型
Julia 中的运算符有六种类型:
- 算术运算符
- 按位运算符
- 逻辑运算符
- 赋值运算符
- 向量化的“点”运算符
- 关系运算符
算术运算符
算术运算运算符用于对操作数执行算术/数学运算。这些运算符包括加、减、乘、除等过程。例如: (+, -, *, /, %, +x, -x)。
算术运算运算符有两种类型:
- 一元运算符:操作或使用单个操作数的运算符是一元运算运算符。例如:(+x, -x) 即一元加和一元减。
- 二元运算符:操作或处理两个操作数的运算符是二元运算符。例如:(+, –, *, /)
| Operator | Description | Syntax |
|---|---|---|
| +(unary plus) | Unary plus: Identity operation | +x |
| -(unary minus) | Unary minus: Performs negation on operand | -x |
| + | Binary plus: adds two operands | x + y |
| – | Binary minus: subtracts two operands | x – y |
| * | Multiplication(times): multiplies two operands | x * y |
| / | Division (float): divides the first operand by the second and returns float value | x / y |
| ÷ | Division (Integer): divides the first operand by the second and returns integer value | x ÷ y |
| \ | Division (Inverse): divides the second operand by the first(y/x) | x \ y |
| ^ | Power: Raises x to the yth power | x ^ y |
| % | Modulus: returns the remainder when first operand is divided by the second | x % y |
| ! | Negation: Changes bool value i.e. from true to false and vice versa | x % y |
# Examples of Arithmetic Operator
a = 9
b = 4
println("a = ", a)
println("b = ", b)
# Addition of numbers
add = a + b
println("Binary Addition: ", add)
# Subtraction of numbers
sub = a - b
println("Binary Subtraction: ", sub)
# Multiplication of number
mul = a * b
println("Binary Multiplication: ", mul)
# Division(float) of number
div1 = a / b
println("Binary Division: ", div1)
# Division(Integer) of number
div2 = a ÷ b
println("Integer Division: ", div2)
# Division(floor) of number
div3 = a \ b
println("Inverse Division: ", div3)
# Power of number
pow = a ^ b
println("Power Operation: ", pow)
# Modulo of both number
mod = a % b
println("Modular Division: ", mod)
输出:
a = 9
b = 4
Binary Addition: 13
Binary Subtraction: 5
Binary Multiplication: 36
Binary Division: 2.25
Integer Division: 2
Inverse Division: 0.4444444444444444
Power Operation: 6561
Modular Division: 1按位运算符
按位运算符用于对数字的各个位进行操作。它们可以与任何整数类型一起使用。示例: (~, &, |, >>, 输出: 逻辑运算符用于组合两个或多个条件/约束或补充考虑原始条件的评估。逻辑运算符是一个布尔值,真或假。例如,当考虑的两个条件都满足时,Julia 中表示为 ‘&&’运算符的逻辑 AND 返回 true。否则,它返回 false。因此,当 a 和 b 都为真(即非零)时, a && b 返回真。 输出: 赋值运算符用于为变量赋值。赋值运算符左侧的操作数是可变的,并且所述赋值运算符右侧的操作数是一个值。右侧的值必须与左侧的变量具有相同的数据类型,否则编译器将引发错误。 输出 “点”运算符(.) 用于执行二元运算,将其用于整个数组,逐个元素,一个接一个。例如,如果将幂 (^)运算符应用于 [4, 5, 6, 7] ^ 2 等数组,将导致错误,因为无法对数组执行“平方”。因此,“点”运算符开始使用。当与.^等二元运算一起使用时,它将对数组的每个元素执行运算。例如 – [4, 5, 6, 7] ^ 2 将导致 [4^2, 5^2, 6^2, 7^2]。 例子: 当在没有“点”运算符的情况下执行指数时,上面的代码将产生错误。这是因为不能对元素数组执行指数。 这些运算符用于检查诸如相等、大于、小于等关系。它们在比较后返回布尔结果,并广泛用于循环语句和条件 if-else 语句。 例子: 输出:
Operator
Description
Syntax
~
Bitwise NOT
~x
&
Bitwise AND
x & y
|
Bitwise OR
x | y
⊻
Bitwise XOR
x ⊻ y
>>>
Logical right shift
x >>> y
>>
Bitwise right shift
x >> y
<<
Bitwise/Logical left shift
x << y
# Examples of Bitwise operators
a = 48
b = 67
# Bitwise NOT operation
println(~a)
# Bitwise AND operation
println(a & b)
# Bitwise OR operation
println(a | b)
# Bitwise XOR operation
println(a ? b)
# Logical right shift operation
println(a >>> 2)
# Bitwise right shift operation
println(a >> 2)
# Bitwise left shift operation
println(a << 2)
-49
0
115
115
12
12
192
逻辑运算符
Operator
Description
Syntax
&&
Logical AND: True if both the operands are true
x && y
||
Logical OR: True if either of the operands is true
x || y
!
Logical NOT: True if operand is false
!x
# Examples of Logical Operator
a = true
b = false
# Print if a and b both are False
println(a && b)
# Print if a or b is True
println(a || b)
# Print if not a is False
println(! a)
false
true
false
赋值运算符
Operator
Description
Syntax
=
Assign value of right side of expression to left side operand
x = y + z
+=
Add AND: Add right side operand with left side operand and then assign to left operand
a += b a = a + b
-=
Subtract AND: Subtract right operand from left operand and then assign to left operand
a -= b a = a – b
*=
Multiply AND: Multiply right operand with left operand and then assign to left operand
a *= b a = a * b
/=
Divide AND: Divide left operand with right operand and then assign to left operand
a /= b a = a / b
\=
Inverse Divide AND: Divide right operand with left operand and then assign to left operand
a \= b a = a \ b
÷=
Integer Divide AND: Divide left operand with right operand and then assign to left operand
a ÷= b a = a ÷ b
%=
Modulus AND: Takes modulus using left and right operands and assign result to left operand
a %= b a = a % b
^=
Exponent AND: Calculate exponent(raise power) value using operands and assign value to left operand
a ^= b a = a ^ b
&=
Performs Bitwise AND on operands and assign value to left operand
a &= b a = a & b
|=
Performs Bitwise OR on operands and assign value to left operand
a |= b a = a | b
⊻=
Performs Bitwise xOR on operands and assign value to left operand
a ⊻= b a = a ⊻ b
>>>=
Performs Logical right shift on operands and assign value to left operand
a>>>=b a=a>>>b
>>=
Performs Bitwise right shift on operands and assign value to left operand
a >>= b a = a >> b
<<=
Performs Bitwise left shift on operands and assign value to left operand
a <<= b a = a << b
# Examples of Assignment Operator
a = 9
b = 4
println("a = ", a)
println("b = ", b)
# Addition of numbers
a += b
println("Binary Addition: ", a)
# Subtraction of numbers
a -= b
println("Binary Subtraction: ", a)
# Multiplication of number
a *= b
println("Binary Multiplication: ", a)
# Division(float) of number
a /= b
println("Binary Division: ", a)
# Division(Integer) of number
a ÷= b
println("Integer Division: ", a)
# Division(floor) of number
a \= b
println("Inverse Division: ", a)
# Power of number
a ^= b
println("Power Operation: ", a)
# Modulo of both number
a %= b
println("Modular Division: ", a)
a = 9
b = 4
Binary Addition: 13
Binary Subtraction: 9
Binary Multiplication: 36
Binary Division: 9.0
Integer Division: 2.0
Inverse Division: 2.0
Power Operation: 16.0
Modular Division: 0.0
向量化的“点”运算符
同样,此点运算符可以与其他二元运算符一起使用,例如 .=、.+、.- 等。# Julia program to illustrate
# use of 'dot' operator
# Creating array
A = [4, 5, 6, 7]
# Performing exponent binary operation
A = A ^ 2
# Performing exponent using 'dot' operation
A = A .^ 2
println(A)
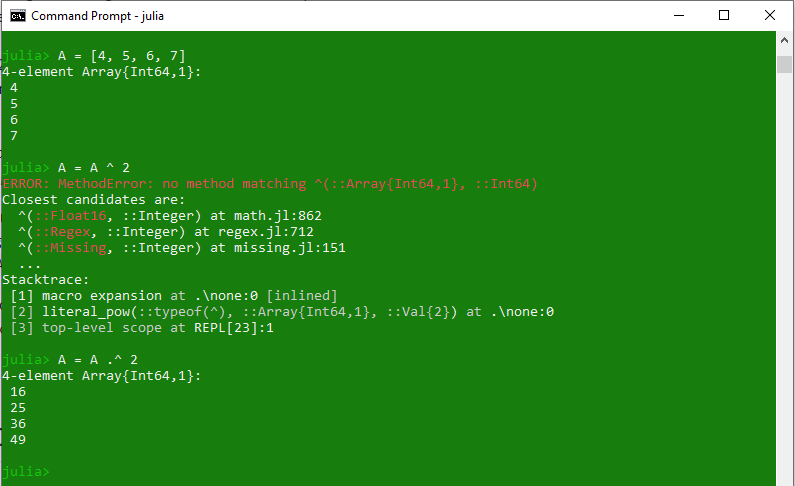
关系运算符
Operator
Description
Syntax
>
Greater than: True if left operand is greater than the right
x > y
<
Less than: True if left operand is less than the right
x < y
==
Equal to: True if both operands are equal
x == y
!=, ≠
Not equal to – True if operands are not equal
x != y or x ≠ y
>=, ≥
Greater than or equal to: True if left operand is greater than or equal to the right
x >= y or x ≥ y
<=, ≤
Less than or equal to: True if left operand is less than or equal to the right
x <= y or x ≤ y
# Examples of Relational Operators
a = 13
b = 33
# a > b is False
println(a > b)
# a < b is True
println(a < b)
# a == b is False
println(a == b)
# a != b is True
println(a != b)
# a >= b is False
println(a >= b)
# a <= b is True
println(a <= b)
false
true
false
true
false
true