Servlet – 国际化示例
默认情况下,网页以英语提供。它可以通过Java技术中的“国际化”概念以用户选择的语言提供。国际化(i18n)帮助用户根据他们的国籍或访问的位置查看页面。请求者的语言环境可以由 servlet 检索,具体取决于他们的国籍,它将返回 Locale 对象。
java.util.Locale request.getLocale()
有不同的方法可用于检测语言环境 S.N Method Description1 getCountry() It helps to return “country/region” code in UPPER CASE for the locale in ISO 3166 2-letter format. 2 getDisplayCountry() It helps to return a “NAME” for the locale’s country and it is appropriate for display to the user. 3 getLanguage() It helps to return the “LANGUAGE CODE” in lower case for the locale in ISO 639 format. 4 getDisplayLanguage() It helps to return a “NAME FOR LOCALE’s LANGUAGE” and it is appropriate for display to the user. 5. getISO3Country() It helps to return a three-letter abbreviation for the locale’s country. 6 getISO3Language() It helps to return a three-letter abbreviation for the locale’s language.
例子
让我们看看不同的例子来显示请求的语言和相关国家
示例 1:
Java
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.util.Locale;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
// Servlet implementation class SearchServlet
@WebServlet("/getCurrentLocationInformation")
public class GetLocationServlet extends HttpServlet {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
public GetLocationServlet() {
super();
}
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
// Get the Locale information
// by using java.util.Locale
Locale locale = request.getLocale();
// language
String localeLanguage = locale.getLanguage();
// country
String localeCountry = locale.getCountry();
// Print the response content type
// below by using PrintWriter object
response.setContentType("text/html");
PrintWriter printWriter = response.getWriter();
String title = "Locale detection";
String docType =
"\n";
printWriter.println(docType +
"\n" +
"" + title + " \n" +
"\n" +
" " + "" + "Language : " + localeLanguage + "" + "
\n" +
"" + "" + "Country : " + localeCountry + "" + "
\n" +
"" +
""
);
}
}Java
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
// Print the response content type below
// by using PrintWriter object
response.setContentType("text/html");
PrintWriter printWriter = response.getWriter();
// Set spanish language code. In this place, we need
// to provide the required language setting
response.setHeader("Content-Language", "es");
String title = "En Español";
String docType =
"\n";
// As it is spanish, the messages
// also given in spanish
printWriter.println(docType +
"\n" +
"" + title + " \n" +
"\n" +
"" + "" + "En Español:" + "" + "
\n" +
"" + "" + "Bienvenido a GeeksForGeeks!" + "" + "
\n" +
""+
"");
}Java
// import java.text.DateFormat as it is getting used
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
// Set response content type
response.setContentType("text/html");
PrintWriter printWriter = response.getWriter();
// Get the client's Locale by using request.getLocale()
Locale locale = request.getLocale( );
String date = DateFormat.getDateTimeInstance(DateFormat.FULL,
DateFormat.SHORT, locale).format(new Date( ));
String title = "Displaying Locale Specific Dates";
String docType =
"\n";
printWriter.println(docType +
"\n" +
"" + title + " \n" +
"\n" +
"" + "" + "Locale specific date : " + date + "" + "
\n" +
"" +
""
);
}Java
// import java.text.NumberFormat; has to be imported
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
// Set response content type
response.setContentType("text/html");
PrintWriter printWriter = response.getWriter();
// Get the current Locale information
Locale currentLocale = request.getLocale( );
NumberFormat numberFormat = NumberFormat.getCurrencyInstance(currentLocale);
String formattedCurrency = numberFormat.format(100000);
String title = "Displaying Locale Specific Currency";
String docType =
"\n";
printWriter.println(docType +
"\n" +
"" + title + " \n" +
"\n" +
"" + "" + "Currency : " +formattedCurrency + "" +"
\n" +
""+
""
);
}通过执行上面的代码,我们可以得到如下输出
输出:
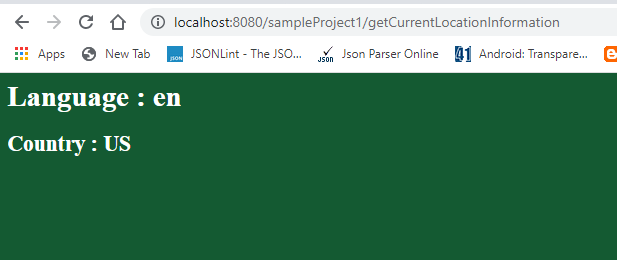
默认语言设置
如果我们想将语言设置为不同的语言,可以通过语言设置来完成。
// In order to set spanish language code.
response.setHeader("Content-Language", "es");
// Similarly we can set different language codes in this way
// http://www.mathguide.de/info/tools/languagecode.html provides various language code示例 2:
Java
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
// Print the response content type below
// by using PrintWriter object
response.setContentType("text/html");
PrintWriter printWriter = response.getWriter();
// Set spanish language code. In this place, we need
// to provide the required language setting
response.setHeader("Content-Language", "es");
String title = "En Español";
String docType =
"\n";
// As it is spanish, the messages
// also given in spanish
printWriter.println(docType +
"\n" +
"" + title + " \n" +
"\n" +
"" + "" + "En Español:" + "" + "
\n" +
"" + "" + "Bienvenido a GeeksForGeeks!" + "" + "
\n" +
""+
"");
}
输出:
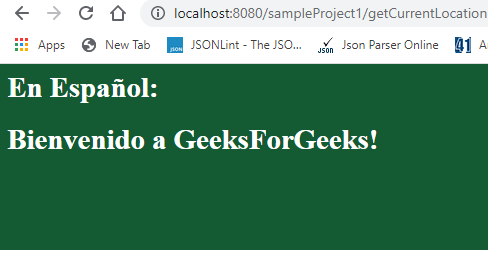
设置为西班牙语
示例 3:
具体到 locale ,通过使用Java.text.DateFormat 类和 getDateTimeInstance() 方法,我们可以格式化日期和时间
Java
// import java.text.DateFormat as it is getting used
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
// Set response content type
response.setContentType("text/html");
PrintWriter printWriter = response.getWriter();
// Get the client's Locale by using request.getLocale()
Locale locale = request.getLocale( );
String date = DateFormat.getDateTimeInstance(DateFormat.FULL,
DateFormat.SHORT, locale).format(new Date( ));
String title = "Displaying Locale Specific Dates";
String docType =
"\n";
printWriter.println(docType +
"\n" +
"" + title + " \n" +
"\n" +
"" + "" + "Locale specific date : " + date + "" + "
\n" +
"" +
""
);
}
输出:

显示地区日期
示例 4:
特定于 locale ,通过使用Java.txt.NumberFormat 类和 getCurrencyInstance() 方法,我们可以格式化货币
Java
// import java.text.NumberFormat; has to be imported
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
// Set response content type
response.setContentType("text/html");
PrintWriter printWriter = response.getWriter();
// Get the current Locale information
Locale currentLocale = request.getLocale( );
NumberFormat numberFormat = NumberFormat.getCurrencyInstance(currentLocale);
String formattedCurrency = numberFormat.format(100000);
String title = "Displaying Locale Specific Currency";
String docType =
"\n";
printWriter.println(docType +
"\n" +
"" + title + " \n" +
"\n" +
"" + "" + "Currency : " +formattedCurrency + "" +"
\n" +
""+
""
);
}
输出:
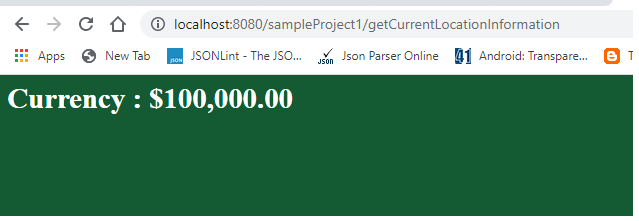
国际化的优势
- 占领国外市场更容易。
- 呈现与语言环境无关的结果
- 一开始,如果实施,软件在全球市场的扩展会更容易。
结论
任何旨在在全球市场上开发的软件,都只能以国际方式进行准备。在Java中,我们可以使用上述方法来实现国际化。