- Python|熊猫 dataframe.get()(1)
- Python|熊猫 dataframe.div()
- Python|熊猫 dataframe.div()(1)
- Python|熊猫 dataframe.add()
- Python|熊猫 dataframe.add()(1)
- Python|熊猫 dataframe.max()
- Python|熊猫 dataframe.std()
- Python|熊猫 dataframe.std()(1)
- Python|熊猫 dataframe.min()(1)
- Python|熊猫 dataframe.min()
- Python|熊猫 dataframe.count()
- Python|熊猫 dataframe.count()(1)
- Python|熊猫 dataframe.all()(1)
- Python|熊猫 dataframe.all()
- Python|熊猫 dataframe.sum()(1)
- Python|熊猫 dataframe.sum()
- Python|熊猫 dataframe.equals()
- Python|熊猫 dataframe.equals()(1)
- Python|熊猫 dataframe.filter()(1)
- Python|熊猫 dataframe.filter()
- Python|熊猫 Dataframe.pop()(1)
- Python|熊猫 Dataframe.pop()
- Python|熊猫 dataframe.replace()(1)
- Python|熊猫 dataframe.replace()
- Python|熊猫 dataframe.mod()(1)
- Python|熊猫 dataframe.mod()
- Python|熊猫 dataframe.insert()(1)
- Python|熊猫 dataframe.insert()
- Python|熊猫 dataframe.groupby()(1)
📅 最后修改于: 2020-11-06 05:37:12 🧑 作者: Mango
数据框是二维数据结构,即,数据以表格形式在行和列中对齐。
DataFrame的功能
- 潜在的列是不同类型的
- 大小–可变
- 标记的轴(行和列)
- 可以对行和列执行算术运算
结构体
让我们假设我们正在使用学生的数据创建一个数据框架。
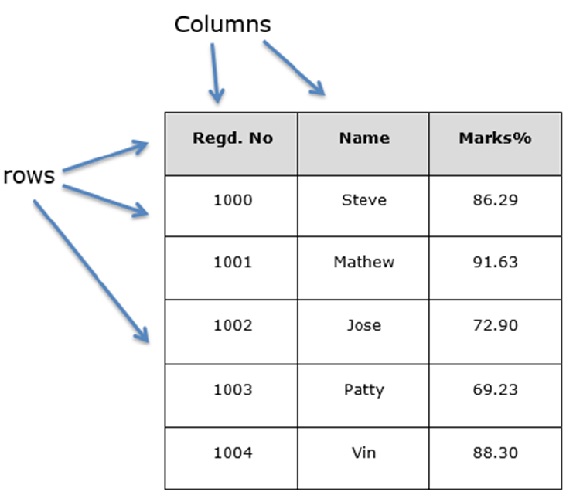
您可以将其视为SQL表或电子表格数据表示形式。
熊猫.DataFrame
可以使用以下构造函数创建pandas DataFrame-
pandas.DataFrame( data, index, columns, dtype, copy)
构造函数的参数如下-
| Sr.No | Parameter & Description |
|---|---|
| 1 |
data data takes various forms like ndarray, series, map, lists, dict, constants and also another DataFrame. |
| 2 |
index For the row labels, the Index to be used for the resulting frame is Optional Default np.arange(n) if no index is passed. |
| 3 |
columns For column labels, the optional default syntax is – np.arange(n). This is only true if no index is passed. |
| 4 |
dtype Data type of each column. |
| 5 |
copy This command (or whatever it is) is used for copying of data, if the default is False. |
创建数据框
可以使用各种输入来创建pandas DataFrame-
- 清单
- 字典
- 系列
- numpy ndarrays
- 另一个数据框
在本章的后续部分中,我们将看到如何使用这些输入来创建DataFrame。
创建一个空的DataFrame
可以创建的基本DataFrame是Empty Dataframe。
例
#import the pandas library and aliasing as pd
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame()
print df
其输出如下-
Empty DataFrame
Columns: []
Index: []
从列表创建一个DataFrame
可以使用单个列表或列表列表创建DataFrame。
例子1
import pandas as pd
data = [1,2,3,4,5]
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
print df
其输出如下-
0
0 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
例子2
import pandas as pd
data = [['Alex',10],['Bob',12],['Clarke',13]]
df = pd.DataFrame(data,columns=['Name','Age'])
print df
其输出如下-
Name Age
0 Alex 10
1 Bob 12
2 Clarke 13
例子3
import pandas as pd
data = [['Alex',10],['Bob',12],['Clarke',13]]
df = pd.DataFrame(data,columns=['Name','Age'],dtype=float)
print df
其输出如下-
Name Age
0 Alex 10.0
1 Bob 12.0
2 Clarke 13.0
注意–请注意, dtype参数将Age列的类型更改为浮点。
从ndarrays / List的Dict创建一个DataFrame
所有ndarray的长度必须相同。如果传递了index,则索引的长度应等于数组的长度。
如果没有传递索引,则默认情况下,索引将是range(n),其中n是数组长度。
例子1
import pandas as pd
data = {'Name':['Tom', 'Jack', 'Steve', 'Ricky'],'Age':[28,34,29,42]}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
print df
其输出如下-
Age Name
0 28 Tom
1 34 Jack
2 29 Steve
3 42 Ricky
注意-遵守值0、1、2、3。它们是使用函数范围(n)分配给每个对象的默认索引。
例子2
现在让我们使用数组创建索引的DataFrame。
import pandas as pd
data = {'Name':['Tom', 'Jack', 'Steve', 'Ricky'],'Age':[28,34,29,42]}
df = pd.DataFrame(data, index=['rank1','rank2','rank3','rank4'])
print df
其输出如下-
Age Name
rank1 28 Tom
rank2 34 Jack
rank3 29 Steve
rank4 42 Ricky
注意–请注意, index参数为每行分配一个索引。
从字典列表创建一个DataFrame
字典列表可以作为输入数据传递以创建DataFrame。默认情况下,字典键被用作列名。
例子1
下面的示例演示如何通过传递字典列表来创建DataFrame。
import pandas as pd
data = [{'a': 1, 'b': 2},{'a': 5, 'b': 10, 'c': 20}]
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
print df
其输出如下-
a b c
0 1 2 NaN
1 5 10 20.0
注意–请注意,缺失区域中将添加NaN(非数字)。
例子2
下面的示例演示如何通过传递字典列表和行索引来创建DataFrame。
import pandas as pd
data = [{'a': 1, 'b': 2},{'a': 5, 'b': 10, 'c': 20}]
df = pd.DataFrame(data, index=['first', 'second'])
print df
其输出如下-
a b c
first 1 2 NaN
second 5 10 20.0
例子3
下面的示例演示如何创建包含字典,行索引和列索引的列表的DataFrame。
import pandas as pd
data = [{'a': 1, 'b': 2},{'a': 5, 'b': 10, 'c': 20}]
#With two column indices, values same as dictionary keys
df1 = pd.DataFrame(data, index=['first', 'second'], columns=['a', 'b'])
#With two column indices with one index with other name
df2 = pd.DataFrame(data, index=['first', 'second'], columns=['a', 'b1'])
print df1
print df2
其输出如下-
#df1 output
a b
first 1 2
second 5 10
#df2 output
a b1
first 1 NaN
second 5 NaN
注–请注意,df2 DataFrame是使用除字典键以外的列索引创建的;因此,将NaN附加到位。而df1是使用与字典键相同的列索引创建的,因此添加了NaN。
从系列字典创建数据框
可以传递系列字典以形成DataFrame。结果索引是所有通过的系列索引的并集。
例
import pandas as pd
d = {'one' : pd.Series([1, 2, 3], index=['a', 'b', 'c']),
'two' : pd.Series([1, 2, 3, 4], index=['a', 'b', 'c', 'd'])}
df = pd.DataFrame(d)
print df
其输出如下-
one two
a 1.0 1
b 2.0 2
c 3.0 3
d NaN 4
注–请注意,对于第一个系列,没有传递标签‘d’ ,但是结果是,对于d标签,NaN附加了NaN。
现在让我们通过示例了解列的选择,添加和删除。
列选择
我们将从DataFrame中选择一列来了解这一点。
例
import pandas as pd
d = {'one' : pd.Series([1, 2, 3], index=['a', 'b', 'c']),
'two' : pd.Series([1, 2, 3, 4], index=['a', 'b', 'c', 'd'])}
df = pd.DataFrame(d)
print df ['one']
其输出如下-
a 1.0
b 2.0
c 3.0
d NaN
Name: one, dtype: float64
列添加
我们将通过在现有数据框中添加新列来理解这一点。
例
import pandas as pd
d = {'one' : pd.Series([1, 2, 3], index=['a', 'b', 'c']),
'two' : pd.Series([1, 2, 3, 4], index=['a', 'b', 'c', 'd'])}
df = pd.DataFrame(d)
# Adding a new column to an existing DataFrame object with column label by passing new series
print ("Adding a new column by passing as Series:")
df['three']=pd.Series([10,20,30],index=['a','b','c'])
print df
print ("Adding a new column using the existing columns in DataFrame:")
df['four']=df['one']+df['three']
print df
其输出如下-
Adding a new column by passing as Series:
one two three
a 1.0 1 10.0
b 2.0 2 20.0
c 3.0 3 30.0
d NaN 4 NaN
Adding a new column using the existing columns in DataFrame:
one two three four
a 1.0 1 10.0 11.0
b 2.0 2 20.0 22.0
c 3.0 3 30.0 33.0
d NaN 4 NaN NaN
列删除
可以删除或弹出列;让我们以一个例子来了解如何。
例
# Using the previous DataFrame, we will delete a column
# using del function
import pandas as pd
d = {'one' : pd.Series([1, 2, 3], index=['a', 'b', 'c']),
'two' : pd.Series([1, 2, 3, 4], index=['a', 'b', 'c', 'd']),
'three' : pd.Series([10,20,30], index=['a','b','c'])}
df = pd.DataFrame(d)
print ("Our dataframe is:")
print df
# using del function
print ("Deleting the first column using DEL function:")
del df['one']
print df
# using pop function
print ("Deleting another column using POP function:")
df.pop('two')
print df
其输出如下-
Our dataframe is:
one three two
a 1.0 10.0 1
b 2.0 20.0 2
c 3.0 30.0 3
d NaN NaN 4
Deleting the first column using DEL function:
three two
a 10.0 1
b 20.0 2
c 30.0 3
d NaN 4
Deleting another column using POP function:
three
a 10.0
b 20.0
c 30.0
d NaN
行选择,添加和删除
现在,我们将通过示例了解行的选择,添加和删除。让我们从选择的概念开始。
按标签选择
可以通过将行标签传递给loc函数来选择行。
import pandas as pd
d = {'one' : pd.Series([1, 2, 3], index=['a', 'b', 'c']),
'two' : pd.Series([1, 2, 3, 4], index=['a', 'b', 'c', 'd'])}
df = pd.DataFrame(d)
print df.loc['b']
其输出如下-
one 2.0
two 2.0
Name: b, dtype: float64
结果是一系列带有标签的标签,作为DataFrame的列名。并且,系列名称是用来检索它的标签。
通过整数位置选择
可以通过将整数位置传递给iloc函数来选择行。
import pandas as pd
d = {'one' : pd.Series([1, 2, 3], index=['a', 'b', 'c']),
'two' : pd.Series([1, 2, 3, 4], index=['a', 'b', 'c', 'd'])}
df = pd.DataFrame(d)
print df.iloc[2]
其输出如下-
one 3.0
two 3.0
Name: c, dtype: float64
切片行
可以使用’:’运算符选择多个行。
import pandas as pd
d = {'one' : pd.Series([1, 2, 3], index=['a', 'b', 'c']),
'two' : pd.Series([1, 2, 3, 4], index=['a', 'b', 'c', 'd'])}
df = pd.DataFrame(d)
print df[2:4]
其输出如下-
one two
c 3.0 3
d NaN 4
行加法
使用append函数将新行添加到DataFrame中。此函数将在行末尾附加行。
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame([[1, 2], [3, 4]], columns = ['a','b'])
df2 = pd.DataFrame([[5, 6], [7, 8]], columns = ['a','b'])
df = df.append(df2)
print df
其输出如下-
a b
0 1 2
1 3 4
0 5 6
1 7 8
删除行
使用索引标签从DataFrame中删除或删除行。如果标签重复,则将删除多行。
如果您观察到,在上面的示例中,标签是重复的。让我们删除标签,然后看看将删除多少行。
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame([[1, 2], [3, 4]], columns = ['a','b'])
df2 = pd.DataFrame([[5, 6], [7, 8]], columns = ['a','b'])
df = df.append(df2)
# Drop rows with label 0
df = df.drop(0)
print df
其输出如下-
a b
1 3 4
1 7 8
在上面的示例中,删除了两行,因为这两行包含相同的标签0。