在 R 编程中使用相关图可视化相关矩阵
相关矩阵的图称为Correlogram 。这通常用于突出显示数据集或数据表中最相关的变量。图中的相关系数根据值着色。根据变量之间的关联程度,我们可以对相关矩阵进行相应的重新排序。
R中的相关图
在 R 中,我们将使用“corrplot”包来实现相关图。因此,要从 R 控制台安装软件包,我们应该执行以下命令:
install.packages("corrplot")
一旦我们正确安装了包,我们将使用library()函数在我们的 R 脚本中加载包,如下所示:
library("corrplot")
我们现在将看到如何在 R 编程中实现相关图。我们将通过一个例子一步一步地看到实现的详细解释。
例子:
第 1 步:[用于相关分析的数据]:第一项工作是选择合适的数据集来实现该概念。对于我们的示例,我们将使用“mtcars”数据集,它是 R 的内置数据集。我们将看到该数据集中的一些数据。
R
# Correlogram in R
# including the required packages
library(corrplot)
head(mtcars)R
# Correlogram in R
# required packages
library(corrplot)
head(mtcars)
#correlation matrix
M<-cor(mtcars)
head(round(M,2))R
# Correlogram in R
# required packages
library(corrplot)
head(mtcars)
#correlation matrix
M<-cor(mtcars)
head(round(M,2))
#visualizing correlogram
#as circle
corrplot(M, method="circle")
# as pie
corrplot(M, method="pie")
# as colour
corrplot(M, method="color")
# as number
corrplot(M, method="number")R
# Correlogram in R
# required package
library(corrplot)
head(mtcars)
# correlation matrix
M<-cor(mtcars)
head(round(M,2))
# types
# upper triangular matrix
corrplot(M, type="upper")
# lower triangular matrix
corrplot(M, type="lower")R
# Correlogram in R
# required packages
library(corrplot)
head(mtcars)
# correlation matrix
M<-cor(mtcars)
head(round(M, 2))
# reordering
# correlogram with hclust reordering
corrplot(M, type = "upper", order = "hclust")
# Using different color spectrum
col<- colorRampPalette(c("red", "white", "blue"))(20)
corrplot(M, type="upper", order = "hclust", col = col)
# Change background color to lightblue
corrplot(M, type="upper", order="hclust",
col = c("black", "white"),
bg = "lightblue")R
# Correlogram in R
# required package
library(corrplot)
library(RColorBrewer)
head(mtcars)
# correlation matrix
M<-cor(mtcars)
head(round(M, 2))
# changing colour of the correlogram
corrplot(M, type="upper", order = "hclust",
col=brewer.pal(n = 8, name = "RdBu"))
corrplot(M, type="upper", order = "hclust",
col=brewer.pal(n = 8, name = "RdYlBu"))
corrplot(M, type="upper", order = "hclust",
col=brewer.pal(n = 8, name = "PuOr"))R
# Correlogram in R
# required packages
library(corrplot)
library(RColorBrewer)
head(mtcars)
# correlation matrix
M<-cor(mtcars)
head(round(M, 2))
# changing the colour and
# rotation of the text labels
corrplot(M, type = "upper", order = "hclust",
tl.col = "black", tl.srt = 45)R
# Correlogram in R
# required package
library(corrplot)
head(mtcars)
M<-cor(mtcars)
head(round(M,2))
# mat : is a matrix of data
# ... : further arguments to pass
# to the native R cor.test function
cor.mtest <- function(mat, ...)
{
mat <- as.matrix(mat)
n <- ncol(mat)
p.mat<- matrix(NA, n, n)
diag(p.mat) <- 0
for (i in 1:(n - 1))
{
for (j in (i + 1):n)
{
tmp <- cor.test(mat[, i], mat[, j], ...)
p.mat[i, j] <- p.mat[j, i] <- tmp$p.value
}
}
colnames(p.mat) <- rownames(p.mat) <- colnames(mat)
p.mat
}
# matrix of the p-value of the correlation
p.mat <- cor.mtest(mtcars)
head(p.mat[, 1:5])R
# Correlogram in R
# required package
library(corrplot)
head(mtcars)
M<-cor(mtcars)
head(round(M, 2))
library(corrplot)
# mat : is a matrix of data
# ... : further arguments to pass
# to the native R cor.test function
cor.mtest <- function(mat, ...)
{
mat <- as.matrix(mat)
n <- ncol(mat)
p.mat<- matrix(NA, n, n)
diag(p.mat) <- 0
for (i in 1:(n - 1))
{
for (j in (i + 1):n)
{
tmp <- cor.test(mat[, i], mat[, j], ...)
p.mat[i, j] <- p.mat[j, i] <- tmp$p.value
}
}
colnames(p.mat) <- rownames(p.mat) <- colnames(mat)
p.mat
}
# matrix of the p-value of the correlation
p.mat <- cor.mtest(mtcars)
head(p.mat[, 1:5])
# Specialized the insignificant value
# according to the significant level
corrplot(M, type = "upper", order = "hclust",
p.mat = p.mat, sig.level = 0.01)
# Leave blank on no significant coefficient
corrplot(M, type = "upper", order = "hclust",
p.mat = p.mat, sig.level = 0.01,
insig = "blank")R
# Correlogram in R
# required package
library(corrplot)
library(RColorBrewer)
head(mtcars)
M<-cor(mtcars)
head(round(M,2))
# customize the correlogram
library(corrplot)
col <- colorRampPalette(c("#BB4444", "#EE9988",
"#FFFFFF", "#77AADD",
"#4477AA"))
corrplot(M, method = "color", col = col(200),
type = "upper", order = "hclust",
addCoef.col = "black", # Add coefficient of correlation
tl.col="black", tl.srt = 45, # Text label color and rotation
# Combine with significance
p.mat = p.mat, sig.level = 0.01, insig = "blank",
# hide correlation coefficient
# on the principal diagonal
diag = FALSE
)输出:
head(mtcars)
mpg cyl disp hp drat wt qsec vs am gear carb
Mazda RX4 21.0 6 160 110 3.90 2.620 16.46 0 1 4 4
Mazda RX4 Wag 21.0 6 160 110 3.90 2.875 17.02 0 1 4 4
Datsun 710 22.8 4 108 93 3.85 2.320 18.61 1 1 4 1
Hornet 4 Drive 21.4 6 258 110 3.08 3.215 19.44 1 0 3 1
Hornet Sportabout 18.7 8 360 175 3.15 3.440 17.02 0 0 3 2
Valiant 18.1 6 225 105 2.76 3.460 20.22 1 0 3 1
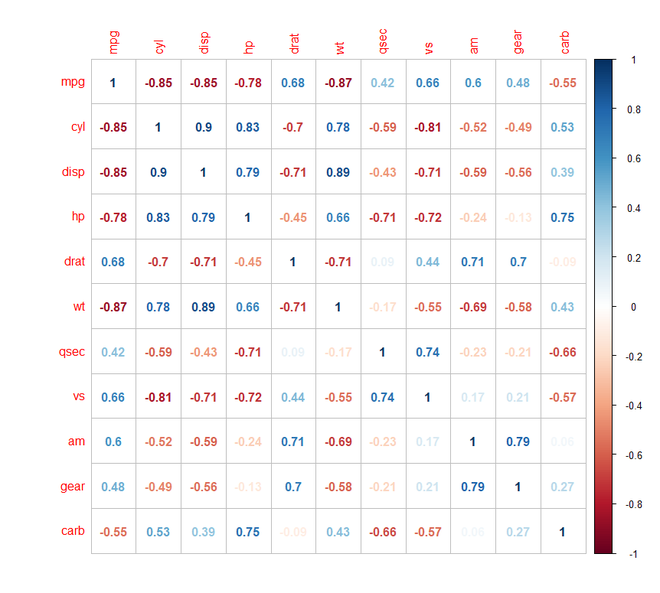
第 2 步:[计算相关矩阵]:我们现在将计算一个相关矩阵,我们要为其绘制相关图。我们将使用cor()函数来计算相关矩阵。
R
# Correlogram in R
# required packages
library(corrplot)
head(mtcars)
#correlation matrix
M<-cor(mtcars)
head(round(M,2))
输出:
head(round(M,2))
mpg cyl disp hp drat wt qsec vs am gear carb
mpg 1.00 -0.85 -0.85 -0.78 0.68 -0.87 0.42 0.66 0.60 0.48 -0.55
cyl -0.85 1.00 0.90 0.83 -0.70 0.78 -0.59 -0.81 -0.52 -0.49 0.53
disp -0.85 0.90 1.00 0.79 -0.71 0.89 -0.43 -0.71 -0.59 -0.56 0.39
hp -0.78 0.83 0.79 1.00 -0.45 0.66 -0.71 -0.72 -0.24 -0.13 0.75
drat 0.68 -0.70 -0.71 -0.45 1.00 -0.71 0.09 0.44 0.71 0.70 -0.09
wt -0.87 0.78 0.89 0.66 -0.71 1.00 -0.17 -0.55 -0.69 -0.58 0.43
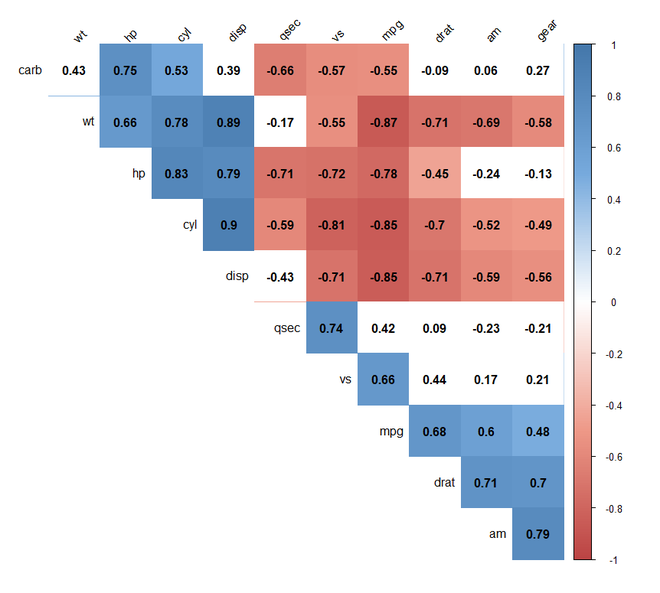
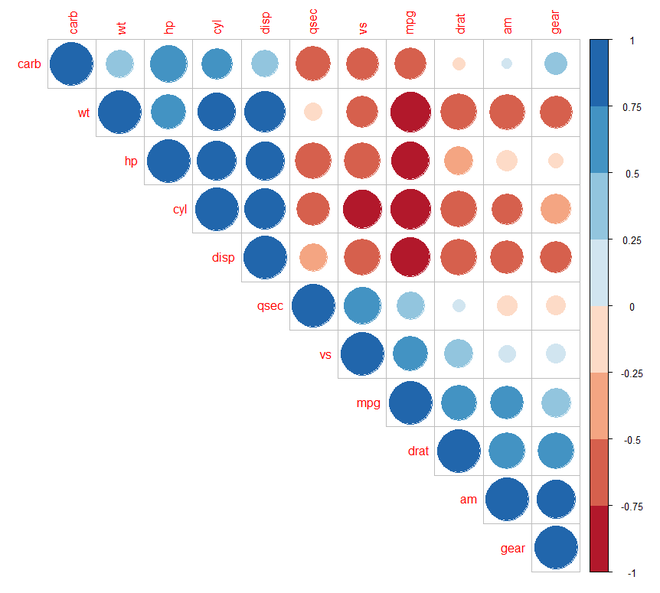
第 3 步:[使用方法参数可视化]:首先,我们将了解如何将相关图可视化为不同形状,如圆形、饼形、椭圆形等。我们将使用corrplot()函数并在其方法参数中提及形状。
R
# Correlogram in R
# required packages
library(corrplot)
head(mtcars)
#correlation matrix
M<-cor(mtcars)
head(round(M,2))
#visualizing correlogram
#as circle
corrplot(M, method="circle")
# as pie
corrplot(M, method="pie")
# as colour
corrplot(M, method="color")
# as number
corrplot(M, method="number")
输出:

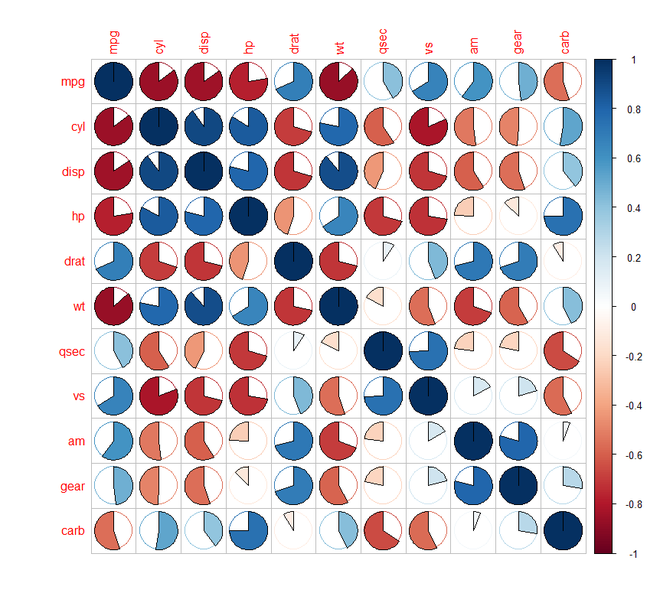

第 4 步:[使用类型参数可视化]:我们将了解如何可视化不同类型的相关图,例如上三角矩阵和下三角矩阵。我们将使用corrplot()函数并提及类型参数。
R
# Correlogram in R
# required package
library(corrplot)
head(mtcars)
# correlation matrix
M<-cor(mtcars)
head(round(M,2))
# types
# upper triangular matrix
corrplot(M, type="upper")
# lower triangular matrix
corrplot(M, type="lower")
输出:


第 5 步:[重新排序相关图]:我们将了解如何重新排序相关图。我们将使用corrplot()函数并提及order 参数。我们将使用“hclust”排序进行层次聚类。
R
# Correlogram in R
# required packages
library(corrplot)
head(mtcars)
# correlation matrix
M<-cor(mtcars)
head(round(M, 2))
# reordering
# correlogram with hclust reordering
corrplot(M, type = "upper", order = "hclust")
# Using different color spectrum
col<- colorRampPalette(c("red", "white", "blue"))(20)
corrplot(M, type="upper", order = "hclust", col = col)
# Change background color to lightblue
corrplot(M, type="upper", order="hclust",
col = c("black", "white"),
bg = "lightblue")
输出:



第 6 步:[更改相关图中的颜色]:现在我们将了解如何更改相关图中的颜色。为此,我们安装了“RColorBrewer”包并将其添加到我们的 R 脚本中以使用其调色板颜色。
R
# Correlogram in R
# required package
library(corrplot)
library(RColorBrewer)
head(mtcars)
# correlation matrix
M<-cor(mtcars)
head(round(M, 2))
# changing colour of the correlogram
corrplot(M, type="upper", order = "hclust",
col=brewer.pal(n = 8, name = "RdBu"))
corrplot(M, type="upper", order = "hclust",
col=brewer.pal(n = 8, name = "RdYlBu"))
corrplot(M, type="upper", order = "hclust",
col=brewer.pal(n = 8, name = "PuOr"))
输出:

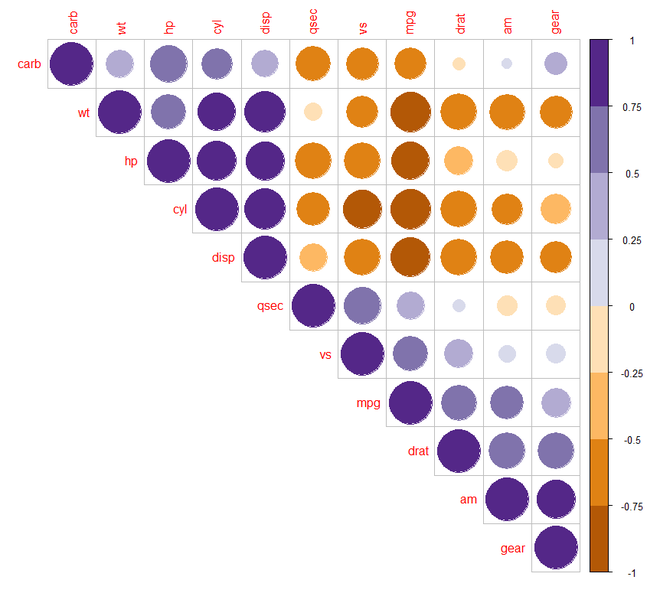
第 7 步:[更改文本标签的颜色和旋转]:为此,我们将在corrplot()函数中包含tl.col 和 tl.str参数。
R
# Correlogram in R
# required packages
library(corrplot)
library(RColorBrewer)
head(mtcars)
# correlation matrix
M<-cor(mtcars)
head(round(M, 2))
# changing the colour and
# rotation of the text labels
corrplot(M, type = "upper", order = "hclust",
tl.col = "black", tl.srt = 45)
输出:

第 8 步:[计算相关性的 p 值]:在向相关图添加显着性检验之前,我们将使用自定义 R函数计算相关性的p 值,如下所示:
R
# Correlogram in R
# required package
library(corrplot)
head(mtcars)
M<-cor(mtcars)
head(round(M,2))
# mat : is a matrix of data
# ... : further arguments to pass
# to the native R cor.test function
cor.mtest <- function(mat, ...)
{
mat <- as.matrix(mat)
n <- ncol(mat)
p.mat<- matrix(NA, n, n)
diag(p.mat) <- 0
for (i in 1:(n - 1))
{
for (j in (i + 1):n)
{
tmp <- cor.test(mat[, i], mat[, j], ...)
p.mat[i, j] <- p.mat[j, i] <- tmp$p.value
}
}
colnames(p.mat) <- rownames(p.mat) <- colnames(mat)
p.mat
}
# matrix of the p-value of the correlation
p.mat <- cor.mtest(mtcars)
head(p.mat[, 1:5])
输出:
head(p.mat[, 1:5])
mpg cyl disp hp drat
mpg 0.000000e+00 6.112687e-10 9.380327e-10 1.787835e-07 1.776240e-05
cyl 6.112687e-10 0.000000e+00 1.802838e-12 3.477861e-09 8.244636e-06
disp 9.380327e-10 1.802838e-12 0.000000e+00 7.142679e-08 5.282022e-06
hp 1.787835e-07 3.477861e-09 7.142679e-08 0.000000e+00 9.988772e-03
drat 1.776240e-05 8.244636e-06 5.282022e-06 9.988772e-03 0.000000e+00
wt 1.293959e-10 1.217567e-07 1.222320e-11 4.145827e-05 4.784260e-06
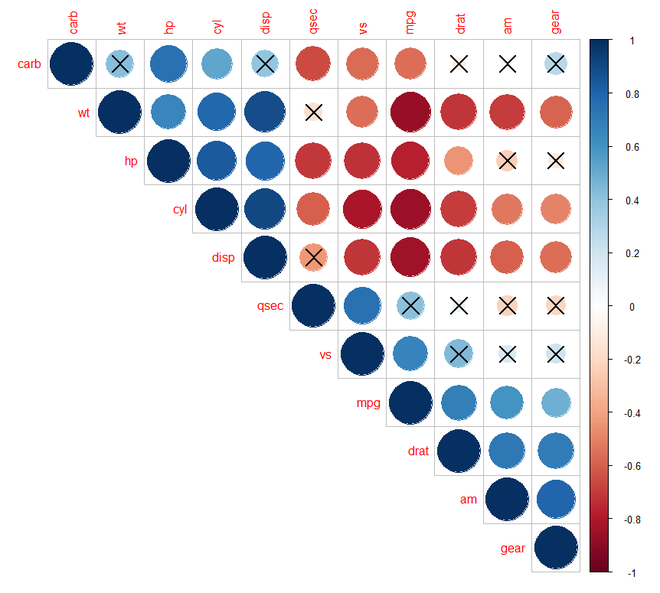
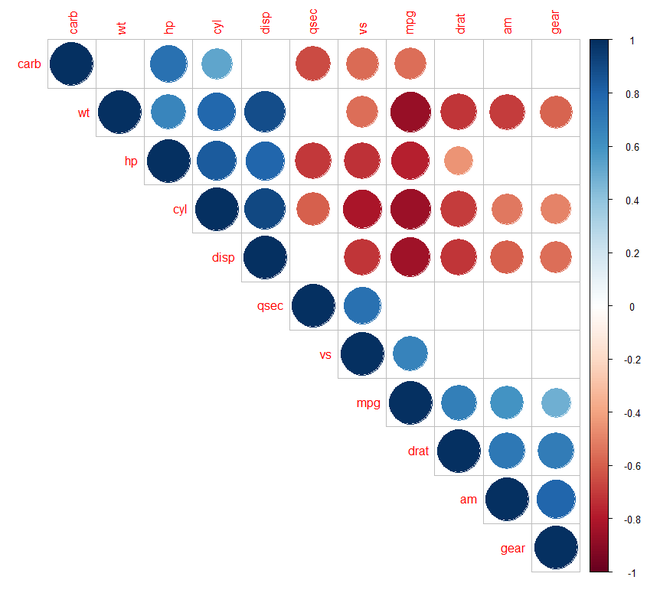
第 9 步:[添加显着性测试]:我们需要在corrplot()函数中添加sig.level 和 insig 参数。如果 p 值大于 0.01,则它是一个无关紧要的值,单元格要么是空白要么是交叉。
R
# Correlogram in R
# required package
library(corrplot)
head(mtcars)
M<-cor(mtcars)
head(round(M, 2))
library(corrplot)
# mat : is a matrix of data
# ... : further arguments to pass
# to the native R cor.test function
cor.mtest <- function(mat, ...)
{
mat <- as.matrix(mat)
n <- ncol(mat)
p.mat<- matrix(NA, n, n)
diag(p.mat) <- 0
for (i in 1:(n - 1))
{
for (j in (i + 1):n)
{
tmp <- cor.test(mat[, i], mat[, j], ...)
p.mat[i, j] <- p.mat[j, i] <- tmp$p.value
}
}
colnames(p.mat) <- rownames(p.mat) <- colnames(mat)
p.mat
}
# matrix of the p-value of the correlation
p.mat <- cor.mtest(mtcars)
head(p.mat[, 1:5])
# Specialized the insignificant value
# according to the significant level
corrplot(M, type = "upper", order = "hclust",
p.mat = p.mat, sig.level = 0.01)
# Leave blank on no significant coefficient
corrplot(M, type = "upper", order = "hclust",
p.mat = p.mat, sig.level = 0.01,
insig = "blank")
输出:
第 10 步:[自定义相关图]:我们可以使用corrplot()函数中所需的参数并调整它们的值来自定义我们的相关图。
R
# Correlogram in R
# required package
library(corrplot)
library(RColorBrewer)
head(mtcars)
M<-cor(mtcars)
head(round(M,2))
# customize the correlogram
library(corrplot)
col <- colorRampPalette(c("#BB4444", "#EE9988",
"#FFFFFF", "#77AADD",
"#4477AA"))
corrplot(M, method = "color", col = col(200),
type = "upper", order = "hclust",
addCoef.col = "black", # Add coefficient of correlation
tl.col="black", tl.srt = 45, # Text label color and rotation
# Combine with significance
p.mat = p.mat, sig.level = 0.01, insig = "blank",
# hide correlation coefficient
# on the principal diagonal
diag = FALSE
)
输出: