二叉树中每个水平级别的叶节点总和
给定一棵二叉树,任务是找到给定树每一层的叶子节点的总和。
例子:
Input:
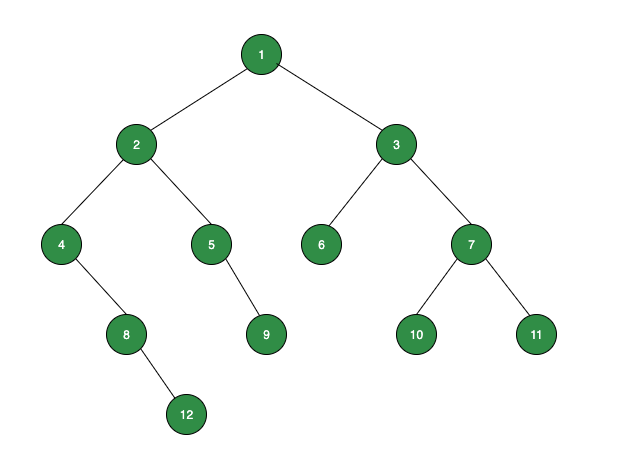
Output:
0
0
6
30
12
Explanation:
Level 1: No leaf node, so sum = 0
Level 2: No leaf node, so sum = 0
Level 3: One leaf node: 6, so sum = 6
Level 4: Three leaf nodes: 9, 10, 11, so sum = 30
Level 5: One leaf node: 12, so sum = 12
Input:
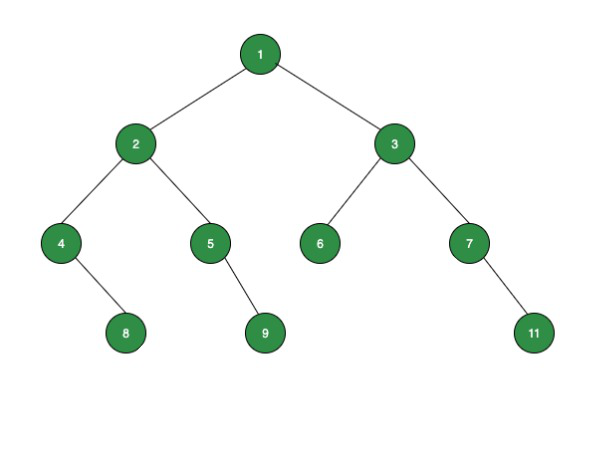
Output:
0
0
6
28
方法:给定的问题可以通过使用水平顺序遍历来解决。请按照以下步骤解决给定的问题:
- 创建一个队列qu ,将节点存储在其级别旁边。此外,创建一个地图来存储每个级别的总和。
- 从根节点开始进行级别顺序遍历,将每个节点及其级别存储在队列中,同时检查当前节点是否为叶子节点。如果它是叶节点,则将其值添加到与其级别对应的映射中。
- 完成上述步骤后,将映射中的值打印为给定树的每个级别的总和。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Tree node structure
class Node {
public:
int data;
Node *left, *right;
Node(int data)
{
this->data = data;
left = right = NULL;
}
};
// Function to print the sum of leaf nodes
// at each horizontal level
void printLevelSum(Node* root)
{
if (root == NULL) {
cout << "No nodes present\n";
return;
}
// Map to hold sum at each level
map mp;
// Queue to hold tree node with level
queue > q;
// Root node is at level 1
q.push({ root, 1 });
pair p;
// Level Order Traversal of tree
while (!q.empty()) {
p = q.front();
q.pop();
// Create a key for each level
// in the map
if (mp.find(p.second) == mp.end()) {
mp[p.second] = 0;
}
// If current node is a leaf node
if (p.first->left == NULL
&& p.first->right == NULL) {
// Adding value in the map
// corresponding to its level
mp[p.second] += p.first->data;
}
if (p.first->left)
q.push({ p.first->left, p.second + 1 });
if (p.first->right)
q.push({ p.first->right, p.second + 1 });
}
// Print the sum at each level
for (auto i : mp) {
cout << i.second << endl;
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
Node* root = new Node(1);
root->left = new Node(2);
root->right = new Node(3);
root->left->left = new Node(4);
root->left->right = new Node(5);
root->right->left = new Node(6);
root->right->right = new Node(7);
root->left->left->right = new Node(8);
root->left->right->right = new Node(9);
root->right->right->left = new Node(10);
root->right->right->right = new Node(11);
root->left->left->right->right = new Node(12);
printLevelSum(root);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class Print_Level_Sum_Btree {
/* A tree node structure */
static class Node {
int data;
Node left;
Node right;
Node(int data){
this.data = data;
left = null;
right = null;
}
}
// User defined class Pair to hold
// the node and its level
static class Pair{
Node n;
int i;
Pair(Node n, int i){
this.n = n;
this.i = i;
}
}
// Function to print the sum of leaf nodes
// at each horizontal level
static void printLevelSum(Node root)
{
if (root == null)
{
System.out.println("No nodes present");
return;
}
// hashmap to hold sum at each level
HashMap map = new HashMap<>();
// queue to hold tree node with level
Queue q = new LinkedList();
// Root node is at level 1
q.add(new Pair(root, 1));
Pair p;
// Level Order Traversal of tree
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
p = q.peek();
q.remove();
// Create a key for each level
// in the map
if (!map.containsKey(p.i))
map.put(p.i, 0);
// If current node is a leaf node
if (p.n.left == null && p.n.right == null)
{
// Adding value in the map
// corresponding to its level
map.put(p.i, map.get(p.i) + p.n.data);
}
if (p.n.left != null)
q.add(new Pair(p.n.left, p.i + 1));
if (p.n.right != null)
q.add(new Pair(p.n.right, p.i + 1));
}
// Print the sum at each level
for (Map.Entry mapElement : map.entrySet()) {
int value = ((int)mapElement.getValue());
System.out.println(value);
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String args[])
{
Node root = null;
root = new Node(1);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(3);
root.left.left = new Node(4);
root.left.right = new Node(5);
root.right.left = new Node(6);
root.right.right = new Node(7);
root.left.left.right = new Node(8);
root.left.right.right = new Node(9);
root.right.right.left = new Node(10);
root.right.right.right = new Node(11);
root.left.left.right.right = new Node(12);
printLevelSum(root);
}
}
// This code is contributed by vineetsharma36. Python3
# Python3 program for the above approach
class newNode:
# Construct to create a new node
def __init__(self, key):
self.data = key
self.left = None
self.right = None
# Function to print the sum of leaf nodes
# at each horizontal level
def printLevelSum(root):
if (not root):
print("No nodes present")
return
# Dictionary to hold sum at each level
dict = {}
# queue to hold tree node with level
q = []
# Root node is at level 1
q.append([root, 1])
p = []
# Level order Traversal of Tree
while (len(q)):
p=q[0]
q.pop(0)
# Create a key for each level
# in the dictionary
if (p[1] not in dict.keys()):
dict[p[1]] = 0
# If current node is a leaf node
if (not p[0].left and not p[0].right):
# Adding value in the dictionary
# corresponding to its level
dict[p[1]] = p[0].data + dict.get(p[1])
if (p[0].left):
q.append([p[0].left, p[1] + 1])
if (p[0].right):
q.append([p[0].right, p[1] + 1])
# Print the sum at each level
for sum in dict.values():
print(sum)
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
root = newNode(1)
root.left = newNode(2)
root.right = newNode(3)
root.left.left = newNode(4)
root.left.right = newNode(5)
root.right.left = newNode(6)
root.right.right = newNode(7)
root.left.left.right = newNode(8)
root.left.right.right = newNode(9)
root.right.right.left = newNode(10)
root.right.right.right = newNode(11)
root.left.left.right.right = newNode(12)
printLevelSum(root)
# This code is contributed by vineetsharma36.C#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class Print_Level_Sum_Btree {
/* A tree node structure */
public class Node {
public int data;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node(int data){
this.data = data;
left = null;
right = null;
}
}
// User defined class Pair to hold
// the node and its level
public class Pair{
public Node n;
public int i;
public Pair(Node n, int i){
this.n = n;
this.i = i;
}
}
// Function to print the sum of leaf nodes
// at each horizontal level
static void printLevelSum(Node root)
{
if (root == null)
{
Console.WriteLine("No nodes present");
return;
}
// hashmap to hold sum at each level
Dictionary map = new Dictionary();
// queue to hold tree node with level
Queue q = new Queue();
// Root node is at level 1
q.Enqueue(new Pair(root, 1));
Pair p;
// Level Order Traversal of tree
while (q.Count!=0) {
p = q.Peek();
q.Dequeue();
// Create a key for each level
// in the map
if (!map.ContainsKey(p.i))
map.Add(p.i, 0);
// If current node is a leaf node
if (p.n.left == null && p.n.right == null)
{
// Adding value in the map
// corresponding to its level
map[p.i]= map[p.i] + p.n.data;
}
if (p.n.left != null)
q.Enqueue(new Pair(p.n.left, p.i + 1));
if (p.n.right != null)
q.Enqueue(new Pair(p.n.right, p.i + 1));
}
// Print the sum at each level
foreach(KeyValuePair entry in map){
int value = (entry.Value);
Console.WriteLine(value);
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String []args)
{
Node root = null;
root = new Node(1);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(3);
root.left.left = new Node(4);
root.left.right = new Node(5);
root.right.left = new Node(6);
root.right.right = new Node(7);
root.left.left.right = new Node(8);
root.left.right.right = new Node(9);
root.right.right.left = new Node(10);
root.right.right.right = new Node(11);
root.left.left.right.right = new Node(12);
printLevelSum(root);
}
}
// This code is contributed by umadevi9616 Javascript
输出
0
0
6
30
12时间复杂度: O(N)
辅助空间: O(N)