给定一个二叉树N个节点和一个整数K,任务是找到所有节点出现在第K个级别的总和。
例子:
Input: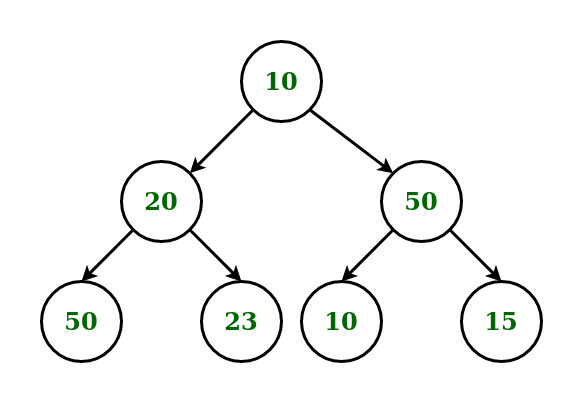
K = 1
Output: 70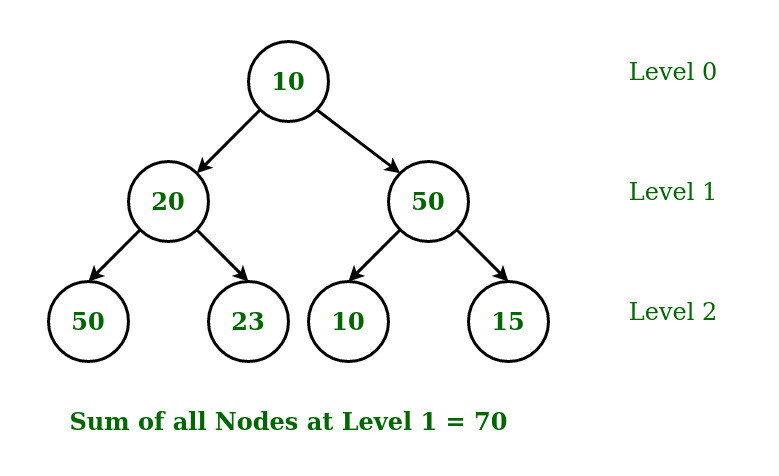
Input: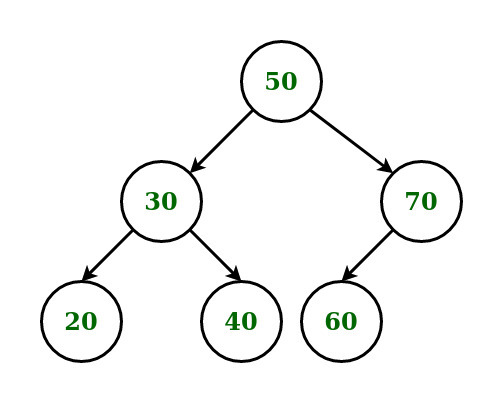
K = 2
Output: 120
方法:
- 使用 Level Order Traversal 和 queue 来遍历二叉树
- 在遍历过程中,将每个元素从队列中弹出并将其子元素(如果可用)推送到队列中。
- 跟踪二叉树的当前级别。
- 要跟踪当前级别,请声明一个变量级别并在从父级遍历子级时增加它。
- 当树的当前级别即变量级别满足所需的第K级时,从队列中弹出元素并计算它们的总和。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ implementation of the approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Binary tree node consists of data, a
// pointer to the left child and a
// pointer to the right child
struct node {
int data;
struct node* left;
struct node* right;
};
// Function to create new Binary Tree node
struct node* newNode(int data)
{
struct node* temp = new struct node;
temp->data = data;
temp->left = nullptr;
temp->right = nullptr;
return temp;
};
// Function to return the sum of all
// the nodes at Kth level using
// level order traversal
int sumOfNodesAtNthLevel(struct node* root,
int k)
{
// If the current node is NULL
if (root == nullptr)
return 0;
// Create Queue
queue que;
// Enqueue the root node
que.push(root);
// Level is used to track
// the current level
int level = 0;
// To store the sum of nodes
// at the Kth level
int sum = 0;
// flag is used to break out of
// the loop after the sum of all
// the nodes at Nth level is found
int flag = 0;
// Iterate the queue till its not empty
while (!que.empty()) {
// Calculate the number of nodes
// in the current level
int size = que.size();
// Process each node of the current
// level and enqueue their left
// and right child to the queue
while (size--) {
struct node* ptr = que.front();
que.pop();
// If the current level matches the
// required level then calculate the
// sum of all the nodes at that level
if (level == k) {
// Flag initialized to 1
// indicates that sum of the
// required level is calculated
flag = 1;
// Calculating the sum of the nodes
sum += ptr->data;
}
else {
// Traverse to the left child
if (ptr->left)
que.push(ptr->left);
// Traverse to the right child
if (ptr->right)
que.push(ptr->right);
}
}
// Increment the variable level
// by 1 for each level
level++;
// Break out from the loop after the sum
// of nodes at K level is found
if (flag == 1)
break;
}
return sum;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
struct node* root = new struct node;
// Tree Construction
root = newNode(50);
root->left = newNode(30);
root->right = newNode(70);
root->left->left = newNode(20);
root->left->right = newNode(40);
root->right->left = newNode(60);
int level = 2;
int result = sumOfNodesAtNthLevel(root, level);
// Printing the result
cout << result;
return 0;
} Java
// Java implementation of the approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
// Binary tree node consists of data, a
// pointer to the left child and a
// pointer to the right child
static class node
{
int data;
node left;
node right;
};
// Function to create new Binary Tree node
static node newNode(int data)
{
node temp = new node();
temp.data = data;
temp.left = null;
temp.right = null;
return temp;
};
// Function to return the sum of all
// the nodes at Kth level using
// level order traversal
static int sumOfNodesAtNthLevel(node root,
int k)
{
// If the current node is null
if (root == null)
return 0;
// Create Queue
Queue que = new LinkedList<>();
// Enqueue the root node
que.add(root);
// Level is used to track
// the current level
int level = 0;
// To store the sum of nodes
// at the Kth level
int sum = 0;
// flag is used to break out of
// the loop after the sum of all
// the nodes at Nth level is found
int flag = 0;
// Iterate the queue till its not empty
while (!que.isEmpty())
{
// Calculate the number of nodes
// in the current level
int size = que.size();
// Process each node of the current
// level and enqueue their left
// and right child to the queue
while (size-- >0)
{
node ptr = que.peek();
que.remove();
// If the current level matches the
// required level then calculate the
// sum of all the nodes at that level
if (level == k)
{
// Flag initialized to 1
// indicates that sum of the
// required level is calculated
flag = 1;
// Calculating the sum of the nodes
sum += ptr.data;
}
else {
// Traverse to the left child
if (ptr.left != null)
que.add(ptr.left);
// Traverse to the right child
if (ptr.right != null)
que.add(ptr.right);
}
}
// Increment the variable level
// by 1 for each level
level++;
// Break out from the loop after the sum
// of nodes at K level is found
if (flag == 1)
break;
}
return sum;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
node root = new node();
// Tree Construction
root = newNode(50);
root.left = newNode(30);
root.right = newNode(70);
root.left.left = newNode(20);
root.left.right = newNode(40);
root.right.left = newNode(60);
int level = 2;
int result = sumOfNodesAtNthLevel(root, level);
// Printing the result
System.out.print(result);
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar Python3
# Python3 implementation of the approach
# Binary tree node consists of data, a
# pointer to the left child and a
# pointer to the right child
class newNode :
def __init__(self, data) :
self.data = data;
self.left = None;
self.right = None;
# Function to return the sum of all
# the nodes at Kth level using
# level order traversal
def sumOfNodesAtNthLevel(root, k) :
# If the current node is NULL
if (root == None) :
return 0;
# Create Queue
que = [];
# Enqueue the root node
que.append(root);
# Level is used to track
# the current level
level = 0;
# To store the sum of nodes
# at the Kth level
sum = 0;
# flag is used to break out of
# the loop after the sum of all
# the nodes at Nth level is found
flag = 0;
# Iterate the queue till its not empty
while (len(que) != 0) :
# Calculate the number of nodes
# in the current level
size = len(que);
# Process each node of the current
# level and enqueue their left
# and right child to the queue
while (size != 0) :
size -= 1;
ptr = que[0];
que.pop(0);
# If the current level matches the
# required level then calculate the
# sum of all the nodes at that level
if (level == k) :
# Flag initialized to 1
# indicates that sum of the
# required level is calculated
flag = 1;
# Calculating the sum of the nodes
sum += ptr.data;
else :
# Traverse to the left child
if (ptr.left) :
que.append(ptr.left);
# Traverse to the right child
if (ptr.right) :
que.append(ptr.right);
# Increment the variable level
# by 1 for each level
level += 1;
# Break out from the loop after the sum
# of nodes at K level is found
if (flag == 1) :
break;
return sum;
# Driver code
if __name__ == "__main__" :
# Tree Construction
root = newNode(50);
root.left = newNode(30);
root.right = newNode(70);
root.left.left = newNode(20);
root.left.right = newNode(40);
root.right.left = newNode(60);
level = 2;
result = sumOfNodesAtNthLevel(root, level);
# Printing the result
print(result);
# This code is contributed by AnkitRai01C#
// C# implementation of the approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG
{
// Binary tree node consists of data, a
// pointer to the left child and a
// pointer to the right child
class node
{
public int data;
public node left;
public node right;
};
// Function to create new Binary Tree node
static node newNode(int data)
{
node temp = new node();
temp.data = data;
temp.left = null;
temp.right = null;
return temp;
}
// Function to return the sum of all
// the nodes at Kth level using
// level order traversal
static int sumOfNodesAtNthLevel(node root,
int k)
{
// If the current node is null
if (root == null)
return 0;
// Create Queue
List que = new List();
// Enqueue the root node
que.Add(root);
// Level is used to track
// the current level
int level = 0;
// To store the sum of nodes
// at the Kth level
int sum = 0;
// flag is used to break out of
// the loop after the sum of all
// the nodes at Nth level is found
int flag = 0;
// Iterate the queue till its not empty
while (que.Count != 0)
{
// Calculate the number of nodes
// in the current level
int size = que.Count;
// Process each node of the current
// level and enqueue their left
// and right child to the queue
while (size-- >0)
{
node ptr = que[0];
que.RemoveAt(0);
// If the current level matches the
// required level then calculate the
// sum of all the nodes at that level
if (level == k)
{
// Flag initialized to 1
// indicates that sum of the
// required level is calculated
flag = 1;
// Calculating the sum of the nodes
sum += ptr.data;
}
else
{
// Traverse to the left child
if (ptr.left != null)
que.Add(ptr.left);
// Traverse to the right child
if (ptr.right != null)
que.Add(ptr.right);
}
}
// Increment the variable level
// by 1 for each level
level++;
// Break out from the loop after the sum
// of nodes at K level is found
if (flag == 1)
break;
}
return sum;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
node root = new node();
// Tree Construction
root = newNode(50);
root.left = newNode(30);
root.right = newNode(70);
root.left.left = newNode(20);
root.left.right = newNode(40);
root.right.left = newNode(60);
int level = 2;
int result = sumOfNodesAtNthLevel(root, level);
// Printing the result
Console.Write(result);
}
}
// This code is contributed by PrinciRaj1992 输出:
120
时间复杂度: O(N)
如果您想与行业专家一起参加直播课程,请参阅Geeks Classes Live