反应速率的温度依赖性
如果在烹饪时将气体保持在低温,则食物会慢慢煮熟。然而,当我们将温度提高到最高设置时,食物会很快煮熟。因此,提高温度会提高反应速率。 Arrhenius 方程有助于解释这种速率-温度关系。让我们看看这个等式,看看它是如何工作的。
反应速率的温度依赖性
激活能量开始发挥作用。根据碰撞理论,当反应物分子相互碰撞时会发生反应。阈值能量是碰撞分子必须具有的最小能量才能使它们的碰撞有效。
活化能是反应物分子为了使其能量等于阈值而吸收的最低附加能量。
阈值能量 = 激活能量 + 拥有的能量。
活化能越低,反应越快。反应物必须克服能量障碍才能转化为产物。反应物分子吸收能量并产生一种称为活化复合物的中间体,它几乎立即分解成产物。
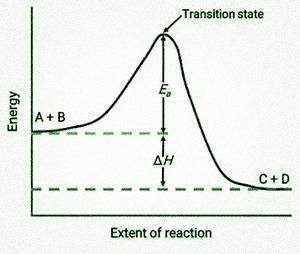
从左到右,查看图表。起初,系统仅包含反应物 (A + B)。当足够的能量反应物分子碰撞时,它们会产生高能活化复合物或过渡态。之后,不稳定的过渡态衰变产生稳定的产物(C + D)。
反应的活化能 E a在图中表示为反应物与过渡态之间的能量差。反应的焓变 (H) 等于反应物和产物之间的能量差。在这个例子中,反应是放热的(H<0),因为它导致系统焓下降。
反应速率的温度依赖性
当温度升高 10 度时,化学过程的速率常数大约翻倍。
温度系数 = T + 10 °时的速率常数 / T ° 时的速率常数
解释
如果在特定温度下根据相应的动能绘制分子分数,则会创建与所描绘的图形相似的图形。最可能的动能由曲线的峰值表示,它表示最大部分分子所拥有的动能。
随着温度的升高
- 曲线的最大值移动到更高的能量值,表明最有可能的动能增加。
- 曲线向右移动,表明有更多具有非常高能量的分子。
由于总概率必须始终为 1,因此曲线下的面积保持不变。在 (t + 10) 处,描绘能量等于或大于活化能的分子比例的区域加倍,导致反应速率加倍。
温度的影响
温度是对化学反应速率有显着影响的变量之一。人们经常发现牛奶在煤气炉上沸腾。一定量的牛奶沸腾的速度取决于炉子的火焰。如果火焰高度设置为最大,牛奶会更快沸腾,而如果火焰高度设置为最小,则需要更长的时间。这里的火焰高度对应于温度。
当温度高时,牛奶沸腾得更快,而当温度低时,牛奶需要更长的时间来煮沸。温度对许多反应都有影响,包括牛奶的沸腾。大多数化学反应的反应速率随着温度的变化而变化。
温度每升高 10 摄氏度,化学反应的速率常数就会增加一倍。直到 1889 年,还没有明确的方法来物理测量化学反应速度对温度的依赖性。Svante Arrhenius 在 1889 年改进了 JH van't Hoff 的工作,提出了一个将温度和过程的速率常数定量联系起来的方程。 Arrhenius 方程是所提出的方程的名称。
阿累尼乌斯方程
Arrhenius 方程可以定量地解释化学过程速率的温度依赖性。
k = Ae -E a /RT
Arrhenius 因子,也称为频率因子或指前因子,用 A 表示。E a是以焦耳/摩尔为单位的活化能,R 是气体常数。
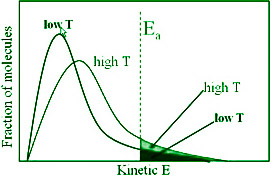
动能大于E a的分子分数由因子e -E a /RT表示。
作为 Arrhenius 方程的结果,已经发现提高温度或降低活化能会导致反应速率增加和速率常数呈指数增加。

取等式自然对数的两边
ln k = -(E a /RT) + ln A
当绘制 ln k 与 1/T = -(E a /R) 且截距 = ln A 时,绘制一条带斜率的直线
在温度 T 1下,方程
ln k 1 = E a /RT 1 + ln A
在温度 T 2 ,方程
ln k 2 = E a /RT 2 + ln A
对于给定的反应,A 是常数。
温度 T 1和 T 2的速率常数值分别为 k 1和 k 2 。
减法方程形式,
ln k 2 – ln k 1 = (E a /RT 1 ) – (E a /RT 2 )
ln (k 2 /k 1 ) = E a /R ((1/T 1 )-(1/T 2 ))
log k 2 /k 1 = (E a /2.303R) × ((1/T 1 )-(1/T 2 ))
log k 2 /k 1 = (E a /2.303R) × ((T 2 -T 1 )/(T 1 T 2 ))
温度影响的图形描述
已经发现,分子的平均动能与温度成正比。根据碰撞理论,双分子反应只有在反应分子以足够的动能和合适的方向碰撞时才会发生。
在给定温度下动能等于或大于 E a的分子部分可能会产生产物。随着温度升高,能量等于或大于(>= E a )的分子的比例增加。结果,反应速率会增加。对于两个不同的温度 T 1和 T 2绘制具有特定动能的部分分子与动能的关系图说明了这一点。
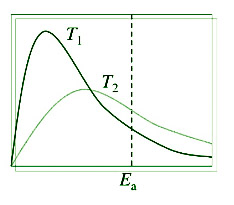
具有这些动能水平的分子数量与曲线下面积成正比。在 T 1和 T 2处,整个区域是相同的。在T 1和T 2处动能大于E a的分子分数由区域(a)和(b)表示。这意味着当温度升高时,能量大于 Ea 的分子的百分比会升高。结果,反应速度加快。
催化剂的作用
催化剂是一种提高反应速率而不发生任何持久化学变化的材料。中间配合物理念:根据该理论,催化剂与反应物发生瞬时键合以产生中间配合物。这种复合物随时间分解,释放产物和催化剂。
催化剂通过降低活化能来降低势能势垒。结果,催化剂提供了替代反应途径。用最少的催化剂催化大量的反应物。吉布斯的能量不会被催化剂改变。催化剂只能催化自发反应,不能催化非自发反应。此外,催化剂不会改变平衡常数;相反,它有助于更快地达到平衡。
示例问题
问题1:在化学品中,反应速率是多少?
回答:
The frequency with which a chemical reaction occurs is referred to as reaction rate in chemistry. It can also be described in terms of the concentration of a material generated in a time unit (amount per unit volume) or the concentration of a reactant absorbed in a time unit.
问题 2:酶如何加速反应?
回答:
Enzymes are enzymes that act as biochemical catalysts. Catalysts reduce the amount of energy required to initiate reactions. The activation energy of a reaction decreases as the rate of the reaction increases. Enzymes also accelerate processes by lowering the activation energy.
问题 3:解释反应速率的温度依赖性。
回答:
The rate constant approximately doubles for a chemical process when the temperature rises by ten degrees.
Temperature coefficient = Rate constant at T + 10° / Rate constant at T°
Explanation:
If fractions of molecules are plotted against corresponding kinetic energies at a specific temperature, a graph similar to the one depicted is created. The most probable kinetic energy is represented by the peak of the curve, which indicates the kinetic energy possessed by the largest fraction of molecules.
With increase in temperature:
The maximum of the curve shifts to a higher energy value, indicating that the most likely kinetic energy increases. The curve shifts to the right, indicating that there are more molecules with very high energies.
Since total probability must always be one, the area under the curve remains constant. At (t +10), the region depicting the fraction of molecules with energy equal to or greater than activation energy doubles, resulting in a reaction rate doubled.
问题 4:定义温度的影响。
回答:
Temperature is one of the variables that has a significant impact on the rate of a chemical reaction. Milk has frequently been spotted boiling on a gas stove. The rate at which a certain amount of milk boils is determined by the stove’s flame. The milk boils faster if the flame height is set to maximum, while it takes longer if the flame height is set to minimum. The height of the flame here corresponds to the temperature.
When the temperature is high, the milk boils faster, and when the temperature is low, the milk takes longer to boil. Temperature has an impact on many reactions, including the boiling of milk. The reaction rate of the majority of chemical reactions changes as the temperature changes.
For every 10° Celsius increase in temperature, the rate constant for a chemical reaction doubles. There was no definite means to physically measure the temperature dependency of a chemical reaction’s pace until 1889. Svante Arrhenius improved J.H van’t Hoff’s work in 1889 by proposing an equation that quantitatively connected temperature and the rate constant for a process. Arrhenius Equation was the name given to the proposed equation.
问题 5:pH 在反应速率中起什么作用?
回答:
Chemical reactions can be speed up or slowed down by changing the pH, temperature, or concentration of the substratum. The enzyme complex to which it interacts is referred to as the substrate. The enzyme’s reaction rate increases at appropriate pH, but decreases at less than optimal pH. It is eventually harmed when an enzyme is denatured.
问题 6:简要解释催化剂的作用。
回答:
A catalyst is a material that enhances the rate of a reaction while not undergoing any lasting chemical changes. Intermediate Complex Idea: A catalyst makes transient bonds with reactants to produce an intermediate complex, according to this theory. This complex decomposes over time, releasing products and the catalyst.
A catalyst decreases the potential energy barrier by lowering the activation energy. As a result, the catalyst gives an alternative reaction pathway. Catalyze a large number of reactants with a minimal amount of catalyst. Gibbs energy is not changed by a catalyst. A catalyst can only catalyze spontaneous reactions and not non-spontaneous reactions. Furthermore, a catalyst does not alter the equilibrium constant; rather, it aids in the speedier attainment of equilibrium.
问题 7:写出 Arrhenius 方程并解释其中涉及的项。
回答 :
k = Ae-Ea/RT
Where,
k = rate constant of the reaction
A = Arrhenius Constant
Ea = Activation Energy for the reaction (in Joules mol-1)
R = Universal Gas Constant
T = Temperature in absolute scale (in kelvins)