振动的幅度、时间周期和频率
声音是由振动物体产生的一种能量形式。它的传播需要使用媒介。结果,声音不能在真空中传播,因为没有材料可以传递声波。声音振动是导致发出声音的实体的来回运动。这通常被称为振荡运动。
什么是振荡?
振荡是通常的有节奏的来回运动。声音以波的形式从一个位置传播到另一个位置,这是由介质中物体的运动引起的。波是一种现象或破坏,其中能量在没有物理相互作用的情况下从一个点传输到另一个点。结果,声音被视为波。
每个振动或振荡都具有三个主要特征:幅度、时间周期和频率将在下一节中深入讨论:
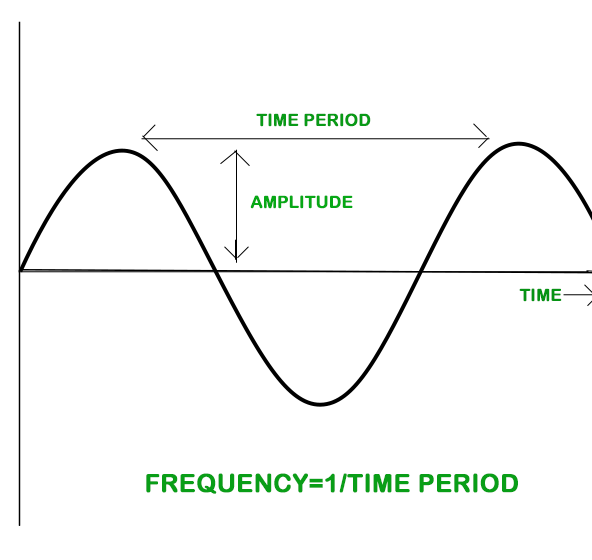
振幅
声波的幅度是波的高度的量度。声波的振幅称为响度或介质中振动粒子在发出声音时从它们的平均位置的最大位移。它是波峰或波谷与其平均位置之间的差异。
波的幅度是在平均值两侧的介质中粒子的最大破坏频率。
字母A常用来表示它。
它的 SI 单位是米 (m) 。
时间段
时间段可以描述为完成一项任务所花费的时间量。当一个事件定期发生时,它被称为是间歇性的。周期是季节性现象自我复制所需的时间。粒子完成一个振动循环所用的时间就是粒子的时间跨度。
在介质深处完成一次振动所需的时间称为声波的时间周期。
时间周期 (T) 和频率 (f) 之间的关系是,
T=1 / f
它由字母T表示。
它的 SI 单位是秒 (s) 。
频率
振荡频率定义为每秒的振荡次数。它的单位是赫兹,用符号Hz表示。一般来说,波的频率是指当波通过介质时,介质中的粒子振动的频率。
声波的频率定义为每单位时间的振动次数。
频率 (f) = 1 / 时间周期 (T)
它由字母 f 或 v 表示。
频率的 SI 单位是赫兹 (Hz) 。
示例问题
问题 1:为什么空的容器比装满的容器发出的声音更大?
解决方案:
An empty vessel produces a louder sound than a filled one because the air molecules in the filled vessel have greater amplitude and greater intensity than the liquid molecules in the filled vessel.
问题2:什么类型的波是声音?
解决方案:
Sound waves fall into three categories:
1.Longitudinal Sound Waves: A longitudinal wave is a wave in which the motion of the medium’s particles is parallel to the direction of the energy transport.
2. Mechanical Sound Waves: A mechanical wave is a wave that depends on the oscillation of matter, meaning that it transfers energy through a medium to propagate
3.Pressure Sound Waves: A pressure wave, or compression wave, has a regular pattern of high- and low-pressure regions. Because sound waves consist of compressions and rarefactions, their regions fluctuate between low and high-pressure patterns.
问题 3:一个人在距离声源 550 m 处聆听 600 Hz 的音调。从源头连续压缩之间的时间间隔是多少?
解决方案:
The time interval between two successive compressions is equal to the time period of the wave. This time period is reciprocal of the frequency of the wave and is given by the relation
T =1 / f
= 1 / 600 Hz
= 1.66 ms
问题 4:解释声纳的工作和应用。
解决方案:

An Ultrasonic sound wave is produced by the transducer of the SONAR, which propagates through any medium (seawater). The wave when hits a surface, is reflected and detected by the sonar detector. The distance of the surface can be calculated as:
2d = v × t
where d is distance, v is velocity of sound, t is time.
This method of measuring distance is also known as ‘echo-ranging’. The result is 2d because the wave covers d distance when outgoing and d distance again when coming back after reflection.
问题 5:描述如何在声源附近的空气中产生压缩和稀疏。
解决方案:
Compression is a region of high pressure where particles are close while rarefaction is a region where particle is far from each other. When a wave moves forward it is compressed because of pressure of the medium. Similarly, rarefactions are seen when the wave moves backward. As the wave in air hits many particles and moves back and forth, compression and rarefactions are produced.