- Flutter数据库概念(1)
- Flutter-数据库概念(1)
- 数据库中的时间概念
- 数据库中的时间概念(1)
- 基本数据库概念
- 分布式数据库的概念(1)
- 分布式数据库的概念
- 软件概念(1)
- 软件概念
- Flutter(1)
- Flutter
- flutter 卡(1)
- flutter 表(1)
- Flutter
- flutter 卡
- flutter 表
- Flutter – Widgets 中的 Key 概念
- Flutter – Widgets 中的 Key 概念(1)
- linux 的概念 - Shell-Bash (1)
- SQL 概念和查询(1)
- SQL概念和查询(1)
- SQL概念和查询
- SQL 概念和查询(1)
- SQL 概念和查询
- SQL 概念和查询
- R数据库(1)
- 数据库
- R-数据库(1)
- R-数据库
📅 最后修改于: 2020-12-08 04:49:23 🧑 作者: Mango
Flutter提供了许多高级软件包来处理数据库。最重要的软件包是-
-
sqflite-用于访问和操作SQLite数据库,以及
-
firebase_database-用于从Google访问和操纵云托管的NoSQL数据库。
在本章中,让我们详细讨论它们。
SQLite的
SQLite数据库是基于事实和标准SQL的嵌入式数据库引擎。它是小型且经过时间考验的数据库引擎。 sqflite软件包提供了许多功能,可以有效地与SQLite数据库一起使用。它提供了操作SQLite数据库引擎的标准方法。 sqflite软件包提供的核心功能如下:
-
创建/打开(openDatabase方法)SQLite数据库。
-
针对SQLite数据库执行SQL语句(执行方法)。
-
先进的查询方法(query method)简化为查询和从SQLite数据库获取信息所需的代码。
让我们创建一个产品应用程序,以使用sqflite包从标准SQLite数据库引擎存储和获取产品信息,并了解SQLite数据库和sqflite包背后的概念。
-
在Android Studio product_sqlite_app中创建一个新的Flutter应用程序。
-
用我们的product_rest_app代码替换默认的启动代码(main.dart)。
-
将资产文件夹从product_nav_app复制到product_rest_app,然后在* pubspec.yaml`文件中添加资产。
flutter:
assets:
- assets/appimages/floppy.png
- assets/appimages/iphone.png
- assets/appimages/laptop.png
- assets/appimages/pendrive.png
- assets/appimages/pixel.png
- assets/appimages/tablet.png
-
在pubspec.yaml文件中配置sqflite软件包,如下所示-
dependencies: sqflite: any
使用最新版本的sqflite代替任何其他版本
-
在pubspec.yaml文件中配置path_provider软件包,如下所示-
dependencies: path_provider: any
-
在这里,path_provider包用于获取系统的临时文件夹路径和应用程序的路径。使用最新版本的sqflite代替任何版本。
-
Android Studio将警告pubspec.yaml已更新。

-
单击获取依赖项选项。 Android studio将从Internet获得该程序包,并为应用程序正确配置它。
-
在数据库中,我们需要主键,id作为附加字段以及Product属性(例如名称,价格等),因此,请在Product类中添加id属性。另外,添加新方法toMap将产品对象转换为Map对象。 fromMap和toMap用于对Product对象进行序列化和反序列化,并在数据库操作方法中使用。
class Product {
final int id;
final String name;
final String description;
final int price;
final String image;
static final columns = ["id", "name", "description", "price", "image"];
Product(this.id, this.name, this.description, this.price, this.image);
factory Product.fromMap(Map data) {
return Product(
data['id'],
data['name'],
data['description'],
data['price'],
data['image'],
);
}
Map toMap() => {
"id": id,
"name": name,
"description": description,
"price": price,
"image": image
};
}
-
在lib文件夹中创建一个新文件Database.dart,以编写与SQLite相关的功能。
-
在Database.dart中导入必要的import语句。
import 'dart:async';
import 'dart:io';
import 'package:path/path.dart';
import 'package:path_provider/path_provider.dart';
import 'package:sqflite/sqflite.dart';
import 'Product.dart';
-
请注意以下几点-
-
异步用于编写异步方法。
-
io用于访问文件和目录。
-
path用于访问与文件路径相关的dart核心实用程序函数。
-
path_provider用于获取临时路径和应用程序路径。
-
sqflite用于操作SQLite数据库。
-
-
创建一个新的类SQLiteDbProvider
-
声明一个基于单例的静态SQLiteDbProvider对象,如下所示:
class SQLiteDbProvider {
SQLiteDbProvider._();
static final SQLiteDbProvider db = SQLiteDbProvider._();
static Database _database;
}
-
可以通过静态db变量访问SQLiteDBProvoider对象及其方法。
SQLiteDBProvoider.db.
-
创建一个方法来获取类型为Future
的数据库(Future选项)。创建产品表并在数据库本身创建期间加载初始数据。
Future get database async {
if (_database != null)
return _database;
_database = await initDB();
return _database;
}
initDB() async {
Directory documentsDirectory = await getApplicationDocumentsDirectory();
String path = join(documentsDirectory.path, "ProductDB.db");
return await openDatabase(
path,
version: 1,
onOpen: (db) {},
onCreate: (Database db, int version) async {
await db.execute(
"CREATE TABLE Product ("
"id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY,"
"name TEXT,"
"description TEXT,"
"price INTEGER,"
"image TEXT" ")"
);
await db.execute(
"INSERT INTO Product ('id', 'name', 'description', 'price', 'image')
values (?, ?, ?, ?, ?)",
[1, "iPhone", "iPhone is the stylist phone ever", 1000, "iphone.png"]
);
await db.execute(
"INSERT INTO Product ('id', 'name', 'description', 'price', 'image')
values (?, ?, ?, ?, ?)",
[2, "Pixel", "Pixel is the most feature phone ever", 800, "pixel.png"]
);
await db.execute(
"INSERT INTO Product ('id', 'name', 'description', 'price', 'image')
values (?, ?, ?, ?, ?)",
[3, "Laptop", "Laptop is most productive development tool", 2000, "laptop.png"]\
);
await db.execute(
"INSERT INTO Product ('id', 'name', 'description', 'price', 'image')
values (?, ?, ?, ?, ?)",
[4, "Tablet", "Laptop is most productive development tool", 1500, "tablet.png"]
);
await db.execute(
"INSERT INTO Product
('id', 'name', 'description', 'price', 'image')
values (?, ?, ?, ?, ?)",
[5, "Pendrive", "Pendrive is useful storage medium", 100, "pendrive.png"]
);
await db.execute(
"INSERT INTO Product
('id', 'name', 'description', 'price', 'image')
values (?, ?, ?, ?, ?)",
[6, "Floppy Drive", "Floppy drive is useful rescue storage medium", 20, "floppy.png"]
);
}
);
}
-
在这里,我们使用了以下方法-
-
getApplicationDocumentsDirectory-返回应用程序目录路径
-
join-用于创建系统特定的路径。我们已经使用它来创建数据库路径。
-
openDatabase-用于打开SQLite数据库
-
onOpen-用于在打开数据库时编写代码
-
onCreate-用于在首次创建数据库时编写代码
-
db.execute-用于执行SQL查询。它接受一个查询。如果查询具有占位符(?),则它将接受值作为第二个参数中的列表。
-
编写一种获取数据库中所有产品的方法-
Future> getAllProducts() async {
final db = await database;
List
-
在这里,我们完成了以下操作-
-
使用查询方法来获取所有产品信息。 query提供了查询表信息的快捷方式,而无需编写整个查询。查询方法将使用我们的输入(例如列,orderBy等)自行生成适当的查询,
-
使用Product的fromMap方法通过循环结果对象(包含表中的所有行)来获取产品详细信息。
-
编写获取特定于ID的产品的方法
Future getProductById(int id) async {
final db = await database;
var result = await db.query("Product", where: "id = ", whereArgs: [id]);
return result.isNotEmpty ? Product.fromMap(result.first) : Null;
}
-
在这里,我们使用where和whereArgs来应用过滤器。
-
创建三种方法-插入,更新和删除方法,以从数据库中插入,更新和删除产品。
insert(Product product) async {
final db = await database;
var maxIdResult = await db.rawQuery(
"SELECT MAX(id)+1 as last_inserted_id FROM Product");
var id = maxIdResult.first["last_inserted_id"];
var result = await db.rawInsert(
"INSERT Into Product (id, name, description, price, image)"
" VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?, ?)",
[id, product.name, product.description, product.price, product.image]
);
return result;
}
update(Product product) async {
final db = await database;
var result = await db.update("Product", product.toMap(),
where: "id = ?", whereArgs: [product.id]); return result;
}
delete(int id) async {
final db = await database;
db.delete("Product", where: "id = ?", whereArgs: [id]);
}
-
Database.dart的最终代码如下-
import 'dart:async';
import 'dart:io';
import 'package:path/path.dart';
import 'package:path_provider/path_provider.dart';
import 'package:sqflite/sqflite.dart';
import 'Product.dart';
class SQLiteDbProvider {
SQLiteDbProvider._();
static final SQLiteDbProvider db = SQLiteDbProvider._();
static Database _database;
Future get database async {
if (_database != null)
return _database;
_database = await initDB();
return _database;
}
initDB() async {
Directory documentsDirectory = await
getApplicationDocumentsDirectory();
String path = join(documentsDirectory.path, "ProductDB.db");
return await openDatabase(
path, version: 1,
onOpen: (db) {},
onCreate: (Database db, int version) async {
await db.execute(
"CREATE TABLE Product ("
"id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY,"
"name TEXT,"
"description TEXT,"
"price INTEGER,"
"image TEXT"")"
);
await db.execute(
"INSERT INTO Product ('id', 'name', 'description', 'price', 'image')
values (?, ?, ?, ?, ?)",
[1, "iPhone", "iPhone is the stylist phone ever", 1000, "iphone.png"]
);
await db.execute(
"INSERT INTO Product ('id', 'name', 'description', 'price', 'image')
values (?, ?, ?, ?, ?)",
[2, "Pixel", "Pixel is the most feature phone ever", 800, "pixel.png"]
);
await db.execute(
"INSERT INTO Product ('id', 'name', 'description', 'price', 'image')
values (?, ?, ?, ?, ?)",
[3, "Laptop", "Laptop is most productive development tool", 2000, "laptop.png"]
);
await db.execute(
"INSERT INTO Product ('id', 'name', 'description', 'price', 'image')
values (?, ?, ?, ?, ?)",
[4, "Tablet", "Laptop is most productive development tool", 1500, "tablet.png"]
);
await db.execute(
"INSERT INTO Product ('id', 'name', 'description', 'price', 'image')
values (?, ?, ?, ?, ?)",
[5, "Pendrive", "Pendrive is useful storage medium", 100, "pendrive.png"]
);
await db.execute(
"INSERT INTO Product ('id', 'name', 'description', 'price', 'image')
values (?, ?, ?, ?, ?)",
[6, "Floppy Drive", "Floppy drive is useful rescue storage medium", 20, "floppy.png"]
);
}
);
}
Future> getAllProducts() async {
final db = await database;
List
-
更改主要方法以获取产品信息。
void main() {
runApp(MyApp(products: SQLiteDbProvider.db.getAllProducts()));
}
-
在这里,我们使用了getAllProducts方法来从数据库中获取所有产品。
-
运行该应用程序并查看结果。它与先前的示例访问产品服务API相似,除了产品信息是从本地SQLite数据库存储和获取的。
Cloud Firestore
Firebase是BaaS应用开发平台。它提供了许多功能来加速移动应用程序的开发,例如身份验证服务,云存储等。Firebase的主要功能之一是Cloud Firestore,这是一种基于云的实时NoSQL数据库。
Flutter提供了一个特殊的包cloud_firestore与Cloud Firestore进行编程。让我们在Cloud Firestore中创建一个在线产品商店,并创建一个用于访问产品商店的应用程序。
-
在Android Studio product_firebase_app中创建一个新的Flutter应用程序。
-
用我们的product_rest_app代码替换默认的启动代码(main.dart)。
-
将product.dart文件从product_rest_app复制到lib文件夹中。
class Product {
final String name;
final String description;
final int price;
final String image;
Product(this.name, this.description, this.price, this.image);
factory Product.fromMap(Map json) {
return Product(
json['name'],
json['description'],
json['price'],
json['image'],
);
}
}
-
将资产文件夹从product_rest_app复制到product_firebase_app,然后在pubspec.yaml文件中添加资产。
flutter:
assets:
- assets/appimages/floppy.png
- assets/appimages/iphone.png
- assets/appimages/laptop.png
- assets/appimages/pendrive.png
- assets/appimages/pixel.png
- assets/appimages/tablet.png
-
在pubspec.yaml文件中配置cloud_firestore软件包,如下所示-
dependencies: cloud_firestore: ^0.9.13+1
-
在这里,使用最新版本的cloud_firestore软件包。
-
Android Studio将警告pubspec.yaml已更新,如下所示-

-
单击获取依赖项选项。 Android studio将从Internet获得该程序包,并为应用程序正确配置它。
-
使用以下步骤在Firebase中创建项目-
-
通过选择https://firebase.google.com/pricing/上的免费套餐来创建Firebase帐户。
-
创建Firebase帐户后,它将重定向到项目概述页面。它列出了所有基于Firebase的项目,并提供了创建新项目的选项。
-
单击添加项目,它将打开一个项目创建页面。
-
输入产品应用程序数据库作为项目名称,然后单击创建项目选项。
-
转到* Firebase控制台。
-
单击项目概述。它将打开项目概述页面。
-
点击android图标。它将打开特定于Android开发的项目设置。
-
输入Android软件包名称com.tutorialspoint.flutterapp.product_firebase_app。
-
点击注册应用。它会生成一个项目配置文件google_service.json。
-
下载google_service.json,然后将其移至项目的android / app目录。此文件是我们的应用程序和Firebase之间的连接。
-
打开android / app / build.gradle并包含以下代码-
apply plugin: 'com.google.gms.google-services'
-
打开android / build.gradle并包含以下配置-
buildscript {
repositories {
// ...
}
dependencies {
// ...
classpath 'com.google.gms:google-services:3.2.1' // new
}
}
-
打开android / app / build.gradle并包含以下代码。
在这里,插件和类路径用于读取google_service.json文件。
android {
defaultConfig {
...
multiDexEnabled true
}
...
}
dependencies {
...
compile 'com.android.support: multidex:1.0.3'
}
-
按照Firebase控制台中的其余步骤进行操作,或者直接跳过。
-
使用以下步骤在新创建的项目中创建产品商店-
-
转到Firebase控制台。
-
打开新创建的项目。
-
单击左侧菜单中的数据库选项。
-
单击创建数据库选项。
-
单击以测试模式启动,然后单击启用。
-
点击添加收藏集。输入产品作为集合名称,然后单击下一步。
-
输入示例产品信息,如此处的图像所示-
这种依赖性使android应用程序可以使用多种dex功能。
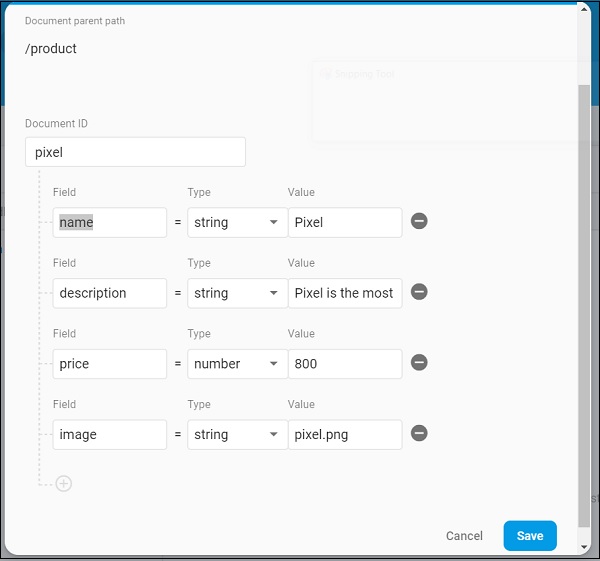
-
使用添加文档选项添加其他产品信息。
-
打开main.dart文件,然后导入Cloud Firestore插件文件并删除http包。
import 'package:cloud_firestore/cloud_firestore.dart';
-
删除parseProducts并更新fetchProducts以从Cloud Firestore而非产品服务API提取产品。
Stream fetchProducts() {
return Firestore.instance.collection('product').snapshots(); }
-
在这里,Firestore.instance.collection方法用于访问云存储中可用的产品集合。 Firestore.instance.collection提供了许多选项来过滤集合以获取必要的文档。但是,我们尚未应用任何过滤器来获取所有产品信息。
-
Cloud Firestore通过Dart Stream概念提供了集合,因此将MyApp和MyHomePage小部件中的产品类型从Future
- >修改为Stream
。 -
将MyHomePage小部件的生成方法更改为使用StreamBuilder而不是FutureBuilder。
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(title: Text("Product Navigation")),
body: Center(
child: StreamBuilder(
stream: products, builder: (context, snapshot) {
if (snapshot.hasError) print(snapshot.error);
if(snapshot.hasData) {
List
documents = snapshot.data.documents;
List
items = List();
for(var i = 0; i < documents.length; i++) {
DocumentSnapshot document = documents[i];
items.add(Product.fromMap(document.data));
}
return ProductBoxList(items: items);
} else {
return Center(child: CircularProgressIndicator());
}
},
),
)
);
}
-
在这里,我们以List
类型获取了产品信息。由于我们的小部件ProductBoxList与文档不兼容,因此我们将文档转换为List 类型,并进一步使用了它。 -
最后,运行应用程序并查看结果。由于我们使用了与SQLite应用程序相同的产品信息,并且仅更改了存储介质,因此生成的应用程序看上去与SQLite应用程序相同。