Java中的哈希集
HashSet类实现了 Set 接口,由一个哈希表支持,该哈希表实际上是一个 HashMap 实例。不保证集合的迭代顺序,这意味着该类不保证元素随时间的恒定顺序。此类允许空元素。该类还为添加、删除、包含和大小等基本操作提供恒定的时间性能,假设哈希函数将元素正确地分散在桶中,我们将在本文中进一步了解。
HashSet 的几个重要特性是:
- 实现设置接口。
- HashSet 的底层数据结构是 Hashtable。
- 由于它实现了 Set 接口,因此不允许重复值。
- 您在 HashSet 中插入的对象不保证以相同的顺序插入。对象根据其哈希码插入。
- HashSet 中允许使用 NULL 元素。
- HashSet 还实现了 Serializable和Cloneable接口。
HashSet的层次结构如下:
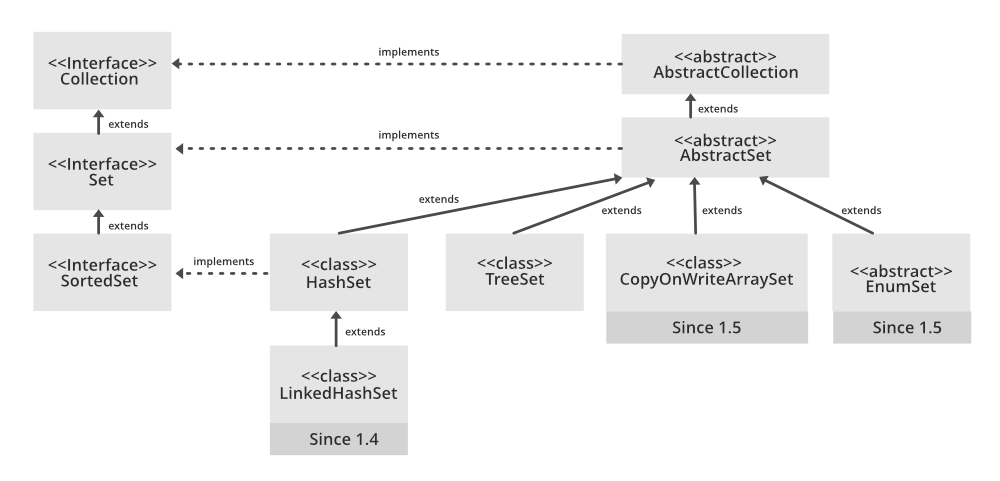
HashSet 扩展了 Abstract Set
现在为了保持恒定的时间性能,迭代 HashSet 需要的时间与 HashSet 实例的大小(元素数)加上支持 HashMap 实例的“容量”(桶数)的总和成正比。因此,如果迭代性能很重要,则不要将初始容量设置得太高(或负载因子太低),这一点非常重要。
- 初始容量:初始容量是指创建hashtable(HashSet内部使用hashtable数据结构)时的桶数。如果当前大小已满,桶的数量将自动增加。
- 负载因子:负载因子是 HashSet 在其容量自动增加之前允许达到的程度的度量。当哈希表中的条目数超过负载因子和当前容量的乘积时,对哈希表进行重新哈希(即重建内部数据结构),使哈希表的桶数大约增加一倍。
Number of stored elements in the table
Load Factor = -----------------------------------------
Size of the hash table Example: If internal capacity is 16 and the load factor is 0.75 then the number of buckets will automatically get increased when the table has 12 elements in it.
对性能的影响:负载因子和初始容量是影响 HashSet 操作性能的两个主要因素。 0.75 的负载因子在时间和空间复杂度方面提供了非常有效的性能。如果我们增加负载因子值超过这个值,那么内存开销将会减少(因为它会减少内部重建操作)但是,它会影响哈希表中的添加和搜索操作。为了减少重新散列操作,我们应该明智地选择初始容量。如果初始容量大于最大条目数除以负载因子,则不会发生重新哈希操作。
Note: The implementation in a HashSet is not synchronized, in the sense that if multiple threads access a hash set concurrently, and at least one of the threads modifies the set, it must be synchronized externally. This is typically accomplished by synchronizing on some object that naturally encapsulates the set. If no such object exists, the set should be “wrapped” using the Collections.synchronizedSet method. This is best done at creation time, to prevent accidental unsynchronized access to the set as shown below:
Set s = Collections.synchronizedSet(new HashSet(...));语法: HashSet 声明
public class HashSet extends AbstractSet implements Set, Cloneable, Serializable 其中E是存储在 HashSet 中的元素的类型。
HashSet 的内部工作: Set 接口的所有类都由 Map 内部备份。 HashSet 使用 HashMap 在内部存储其对象。您一定想知道,要在 HashMap 中输入一个值,我们需要一个键值对,但在 HashSet 中,我们只传递一个值。
HashMap 中的存储:实际上,我们在 HashSet 中插入的值作为映射对象的键,对于它的值, Java使用一个常量变量。所以在键值对中,所有的值都是一样的。
Java文档中HashSet的实现
private transient HashMap map;
// Constructor - 1
// All the constructors are internally creating HashMap Object.
public HashSet()
{
// Creating internally backing HashMap object
map = new HashMap();
}
// Constructor - 2
public HashSet(int initialCapacity)
{
// Creating internally backing HashMap object
map = new HashMap(initialCapacity);
}
// Dummy value to associate with an Object in Map
private static final Object PRESENT = new Object();如果我们看一下 HashSet 类的add()方法:
public boolean add(E e)
{
return map.put(e, PRESENT) == null;
}我们可以注意到,HashSet 类的 add() 方法在内部调用支持 HashMap 对象的put()方法,方法是将您指定为键的元素和常量“PRESENT”作为其值传递。 remove()方法也以相同的方式工作。它在内部调用 Map 接口的 remove 方法。
public boolean remove(Object o)
{
return map.remove(o) == PRESENT;
} HashSet 不仅存储了唯一的对象,还存储了唯一的对象集合 像 ArrayList
执行:
Java
// Java program to illustrate the concept
// of Collection objects storage in a HashSet
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class CollectionObjectStorage {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Instantiate an object of HashSet
HashSet set = new HashSet<>();
// create ArrayList list1
ArrayList list1 = new ArrayList<>();
// create ArrayList list2
ArrayList list2 = new ArrayList<>();
// Add elements using add method
list1.add(1);
list1.add(2);
list2.add(1);
list2.add(2);
set.add(list1);
set.add(list2);
// print the set size to understand the
// internal storage of ArrayList in Set
System.out.println(set.size());
}
} Java
// Java program to Demonstrate Working of HashSet Class
// Importing required classes
import java.util.*;
// Main class
// HashSetDemo
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating an empty HashSet
HashSet h = new HashSet();
// Adding elements into HashSet
// using add() method
h.add("India");
h.add("Australia");
h.add("South Africa");
// Adding duplicate elements
h.add("India");
// Displaying the HashSet
System.out.println(h);
System.out.println("List contains India or not:"
+ h.contains("India"));
// Removing items from HashSet
// using remove() method
h.remove("Australia");
System.out.println("List after removing Australia:"
+ h);
// Display message
System.out.println("Iterating over list:");
// Iterating over hashSet items
Iterator i = h.iterator();
// Holds true till there is single element remaining
while (i.hasNext())
// Iterating over elements
// using next() method
System.out.println(i.next());
}
} Java
// Java program to Adding Elements to HashSet
// Importing required classes
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
// Main class
// AddingElementsToHashSet
class GFG {
// Method 1
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating an empty HashSet of string entities
HashSet hs = new HashSet();
// Adding elements using add() method
hs.add("Geek");
hs.add("For");
hs.add("Geeks");
// Printing all string el=ntries inside the Set
System.out.println("HashSet elements : " + hs);
}
} Java
// Java program Illustrating Removal Of Elements of HashSet
// Importing required classes
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
// Main class
// RemoveElementsOfHashSet
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating an
HashSet hs = new HashSet();
// Adding elements to above Set
// using add() method
hs.add("Geek");
hs.add("For");
hs.add("Geeks");
hs.add("A");
hs.add("B");
hs.add("Z");
// Printing the elements of HashSet elements
System.out.println("Initial HashSet " + hs);
// Removing the element B
hs.remove("B");
// Printing the updated HashSet elements
System.out.println("After removing element " + hs);
// Returns false if the element is not present
System.out.println("Element AC exists in the Set : "
+ hs.remove("AC"));
}
} Java
// Java Program to Illustrate Iteration Over HashSet
// Importing required classes
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
// Main class
// IterateTheHashSet
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating an empty HashSet of string entries
HashSet hs = new HashSet();
// Adding elements to above Set
// using add() method
hs.add("Geek");
hs.add("For");
hs.add("Geeks");
hs.add("A");
hs.add("B");
hs.add("Z");
// Iterating though the HashSet using iterators
Iterator itr = hs.iterator();
// Holds true till there is single element
// remaining in Set
while (itr.hasNext())
// Traversing elements and printing them
System.out.print(itr.next() + ", ");
System.out.println();
// Using enhanced for loop for traversal
for (String s : hs)
// Traversing elements and printing them
System.out.print(s + ", ");
System.out.println();
}
} 1在存储 Object 之前,HashSet 使用 hashCode() 和 equals() 方法检查是否存在现有条目。在上面的示例中,如果两个列表具有相同顺序的相同元素,则认为它们相等。当您在两个列表上调用 hashCode() 方法时,它们都会给出相同的哈希值,因为它们是相等的。
HashSet 不存储重复项,如果你给两个相等的对象,那么它只存储第一个,这里是 list1。
HashSet 类的构造函数
为了创建一个 HashSet,我们需要创建一个 HashSet 类的对象。 HashSet 类由允许创建 HashSet 的各种构造函数组成。以下是此类中可用的构造函数。
1. HashSet() :该构造函数用于构建一个空的HashSet对象,其中默认初始容量为16,默认加载因子为0.75。如果我们希望创建一个名为 hs 的空 HashSet,则可以将其创建为:
HashSet hs = new HashSet(); 2. HashSet(int initialCapacity):该构造函数用于构建一个空的HashSet对象,在对象创建时指定initialCapacity。这里,默认的 loadFactor 保持为 0.75。
HashSet hs = new HashSet(int initialCapacity); 3. HashSet(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor):该构造函数用于构建一个空的HashSet对象,在创建对象时指定initialCapacity和loadFactor。
HashSet hs = new HashSet(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor); 4. HashSet(Collection):此构造函数用于构建包含给定集合中所有元素的 HashSet 对象。简而言之,当需要从任何 Collection 对象到 HashSet 对象的任何转换时,都会使用此构造函数。如果我们希望创建一个名为 hs 的 HashSet,它可以创建为:
HashSet hs = new HashSet(Collection C); 执行:
Java
// Java program to Demonstrate Working of HashSet Class
// Importing required classes
import java.util.*;
// Main class
// HashSetDemo
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating an empty HashSet
HashSet h = new HashSet();
// Adding elements into HashSet
// using add() method
h.add("India");
h.add("Australia");
h.add("South Africa");
// Adding duplicate elements
h.add("India");
// Displaying the HashSet
System.out.println(h);
System.out.println("List contains India or not:"
+ h.contains("India"));
// Removing items from HashSet
// using remove() method
h.remove("Australia");
System.out.println("List after removing Australia:"
+ h);
// Display message
System.out.println("Iterating over list:");
// Iterating over hashSet items
Iterator i = h.iterator();
// Holds true till there is single element remaining
while (i.hasNext())
// Iterating over elements
// using next() method
System.out.println(i.next());
}
}
[South Africa, Australia, India]
List contains India or not:true
List after removing Australia:[South Africa, India]
Iterating over list:
South Africa
India对 HashSet 执行各种操作
让我们看看如何对 HashSet 进行一些常用的操作。
操作 1:添加元素
为了向 HashSet 添加元素,我们可以使用 add() 方法。但是,插入顺序不会保留在 HashSet 中。我们需要注意,不允许重复元素,所有重复元素都将被忽略。
例子
Java
// Java program to Adding Elements to HashSet
// Importing required classes
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
// Main class
// AddingElementsToHashSet
class GFG {
// Method 1
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating an empty HashSet of string entities
HashSet hs = new HashSet();
// Adding elements using add() method
hs.add("Geek");
hs.add("For");
hs.add("Geeks");
// Printing all string el=ntries inside the Set
System.out.println("HashSet elements : " + hs);
}
}
HashSet elements : [Geek, For, Geeks]操作 2:移除元素
可以使用 remove() 方法从 HashSet 中删除这些值。
例子
Java
// Java program Illustrating Removal Of Elements of HashSet
// Importing required classes
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
// Main class
// RemoveElementsOfHashSet
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating an
HashSet hs = new HashSet();
// Adding elements to above Set
// using add() method
hs.add("Geek");
hs.add("For");
hs.add("Geeks");
hs.add("A");
hs.add("B");
hs.add("Z");
// Printing the elements of HashSet elements
System.out.println("Initial HashSet " + hs);
// Removing the element B
hs.remove("B");
// Printing the updated HashSet elements
System.out.println("After removing element " + hs);
// Returns false if the element is not present
System.out.println("Element AC exists in the Set : "
+ hs.remove("AC"));
}
}
Initial HashSet [A, B, Geek, For, Geeks, Z]
After removing element [A, Geek, For, Geeks, Z]
Element AC exists in the Set : false操作3:遍历HashSet
使用 iterator() 方法遍历 HashSet 的元素。此外,最著名的一种是使用增强的 for 循环。
例子
Java
// Java Program to Illustrate Iteration Over HashSet
// Importing required classes
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
// Main class
// IterateTheHashSet
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating an empty HashSet of string entries
HashSet hs = new HashSet();
// Adding elements to above Set
// using add() method
hs.add("Geek");
hs.add("For");
hs.add("Geeks");
hs.add("A");
hs.add("B");
hs.add("Z");
// Iterating though the HashSet using iterators
Iterator itr = hs.iterator();
// Holds true till there is single element
// remaining in Set
while (itr.hasNext())
// Traversing elements and printing them
System.out.print(itr.next() + ", ");
System.out.println();
// Using enhanced for loop for traversal
for (String s : hs)
// Traversing elements and printing them
System.out.print(s + ", ");
System.out.println();
}
}
A, B, Geek, For, Geeks, Z,
A, B, Geek, For, Geeks, Z, Time Complexity of HashSet Operations: The underlying data structure for HashSet is hashtable. So amortize (average or usual case) time complexity for add, remove and look-up (contains method) operation of HashSet takes O(1) time.
HashSet 中的方法
METHOD | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| add(E e) | Used to add the specified element if it is not present, if it is present then return false. |
| clear() | Used to remove all the elements from set. |
| contains(Object o) | Used to return true if an element is present in set. |
| remove(Object o) | Used to remove the element if it is present in set. |
| iterator() | Used to return an iterator over the element in the set. |
| isEmpty() | Used to check whether the set is empty or not. Returns true for empty and false for a non-empty condition for set. |
| size() | Used to return the size of the set. |
| clone() | Used to create a shallow copy of the set. |
从类Java.util.AbstractSet 继承的方法
METHOD | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| equals() | Used to verify the equality of an Object with a HashSet and compare them. The list returns true only if both HashSet contains same elements, irrespective of order. |
| hashcode() | Returns the hash code value for this set. |
| removeAll(collection) | This method is used to remove all the elements from the collection which are present in the set. This method returns true if this set changed as a result of the call. |
从类Java.util.AbstractCollection 继承的方法
METHOD | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| addAll(collection) | This method is used to append all of the elements from the mentioned collection to the existing set. The elements are added randomly without following any specific order. |
| containsAll(collection) | This method is used to check whether the set contains all the elements present in the given collection or not. This method returns true if the set contains all the elements and returns false if any of the elements are missing. |
| retainAll(collection) | This method is used to retain all the elements from the set which are mentioned in the given collection. This method returns true if this set changed as a result of the call. |
| toArray() | This method is used to form an array of the same elements as that of the Set. |
| toString() | The toString() method of Java HashSet is used to return a string representation of the elements of the HashSet Collection. |
在接口Java.util.Collection 中声明的方法
METHOD | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| parallelStream() | Returns a possibly parallel Stream with this collection as its source. |
| removeIf(Predicate filter) | Removes all of the elements of this collection that satisfy the given predicate. |
| stream() | Returns a sequential Stream with this collection as its source. |
| toArray(IntFunction | Returns an array containing all of the elements in this collection, using the provided generator function to allocate the returned array. |
在接口Java.lang.Iterable 中声明的方法
METHOD | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| forEach(Consumer action) | Performs the given action for each element of the Iterable until all elements have been processed or the action throws an exception. |
在接口Java.util.Set 中声明的方法
METHOD | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| addAll(Collection c) | Adds all of the elements in the specified collection to this set if they’re not already present (optional operation). |
| containsAll(Collection c) | Returns true if this set contains all of the elements of the specified collection. |
| equals(Object o) | Compares the specified object with this set for equality. |
| hashCode() | Returns the hash code value for this set. |
| removeAll(Collection c) | Removes from this set all of its elements that are contained in the specified collection (optional operation). |
| retainAll(Collection c) | Retains only the elements in this set that are contained in the specified collection (optional operation). |
| toArray() | Returns an array containing all of the elements in this set. |
| toArray(T[] a) | Returns an array containing all of the elements in this set; the runtime type of the returned array is that of the specified array. |
HashSet 与 HashMap
BASIS | HashSet | HashMap |
|---|---|---|
| Implementation | HashSet implements Set interface. | HashMap implements Map interface. |
| Duplicates | HashSet doesn’t allow duplicate values. | HashMap store key, value pairs and it does not allow duplicate keys. If key is duplicate then the old key is replaced with the new value. |
| Number of objects during storing objects | HashSet requires only one object add(Object o). | HashMap requires two objects put(K key, V Value) to add an element to the HashMap object. |
| Dummy value | HashSet internally uses HashMap to add elements. In HashSet, the argument passed in add(Object) method serves as key K. Java internally associates dummy value for each value passed in add(Object) method. | HashMap does not have any concept of dummy value. |
| Storing or Adding mechanism | HashSet internally uses the HashMap object to store or add the objects. | HashMap internally uses hashing to store or add objects |
| Faster | HashSet is slower than HashMap. | HashMap is faster than HashSet. |
| Insertion | HashSet uses the add() method for add or storing data. | HashMap uses the put() method for storing data. |
| Example | HashSet is a set, e.g. {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7}. | HashMap is a key -> value pair(key to value) map, e.g. {a -> 1, b -> 2, c -> 2, d -> 1}. |
HashSet 与 TreeSet
BASIS | HashSet | TreeSet |
|---|---|---|
| Speed and internal implementation | For operations like search, insert and delete. It takes constant time for these operations on average. HashSet is faster than TreeSet. HashSet is Implemented using a hash table. | TreeSet takes O(Log n) for search, insert and delete which is higher than HashSet. But TreeSet keeps sorted data. Also, it supports operations like higher() (Returns least higher element), floor(), ceiling(), etc. These operations are also O(Log n) in TreeSet and not supported in HashSet. TreeSet is implemented using a Self Balancing Binary Search Tree (Red-Black Tree). TreeSet is backed by TreeMap in Java. |
| Ordering | Elements in HashSet are not ordered. | TreeSet maintains objects in Sorted order defined by either Comparable or Comparator method in Java. TreeSet elements are sorted in ascending order by default. It offers several methods to deal with the ordered set like first(), last(), headSet(), tailSet(), etc. |
| Null Object | HashSet allows the null object. | TreeSet doesn’t allow null Object and throw NullPointerException, Why, because TreeSet uses compareTo() method to compare keys and compareTo() will throw java.lang.NullPointerException. |
| Comparison | HashSet uses equals() method to compare two objects in Set and for detecting duplicates. | TreeSet uses compareTo() method for same purpose. If equals() and compareTo() are not consistent, i.e. for two equal object equals should return true while compareTo() should return zero, then it will break the contract of the Set interface and will allow duplicates in Set implementations like TreeSet |