Java中的哈希表
Hashtable类实现了一个哈希表,它将键映射到值。任何非空对象都可以用作键或值。要成功地从哈希表中存储和检索对象,用作键的对象必须实现 hashCode 方法和 equals 方法。
哈希表的特点
- 它类似于 HashMap,但是是同步的。
- Hashtable 将键/值对存储在哈希表中。
- 在 Hashtable 中,我们指定一个用作键的对象,以及我们要与该键关联的值。然后对键进行哈希处理,生成的哈希码用作值存储在表中的索引。
- Hashtable 类的初始默认容量为 11,而 loadFactor 为 0.75。
- HashMap 不提供任何枚举,而 Hashtable 不提供快速失败的枚举。
宣言:
public class Hashtable extends Dictionary implements Map, Cloneable, Serializable 类型参数:
- K - 此映射维护的键的类型
- V – 映射值的类型
哈希表的层次结构
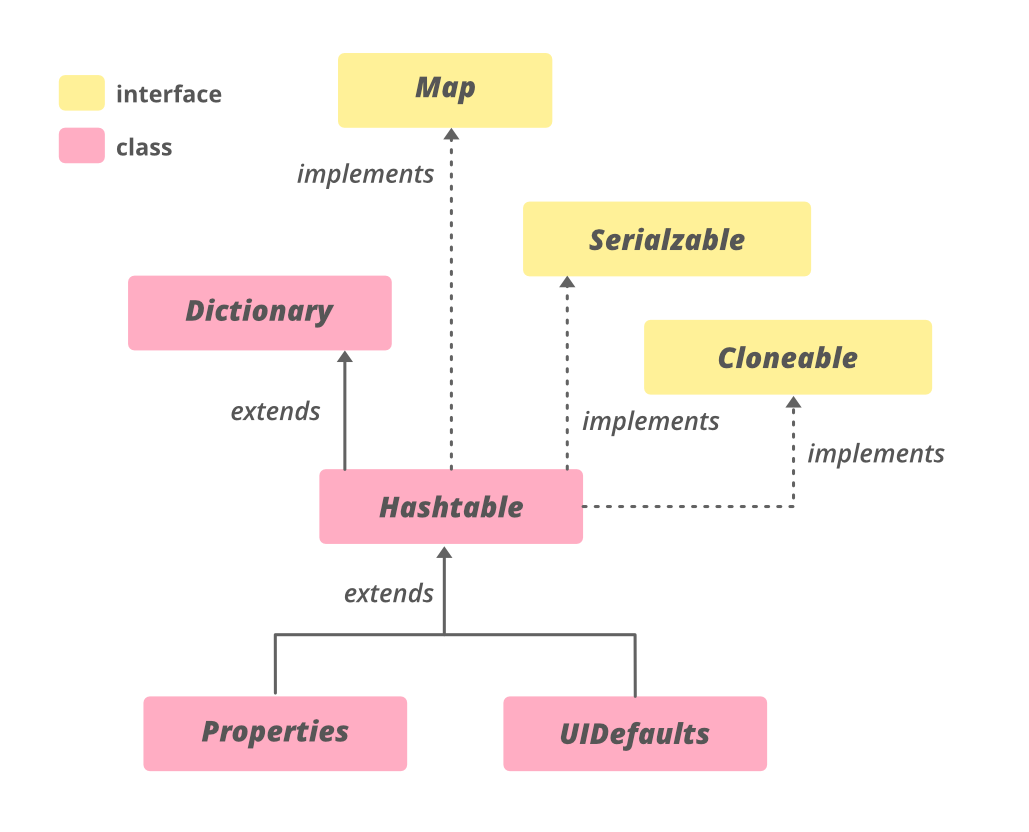
Hashtable 实现了 Serializable 、 Cloneable 、 Map
构造函数:
为了创建一个 Hashtable,我们需要从Java.util.Hashtable中导入它。我们可以通过多种方式创建 Hashtable。
1. Hashtable():这将创建一个空的哈希表,默认加载因子为 0.75,初始容量为 11。
Hashtable
Java
// Java program to demonstrate
// adding elements to Hashtable
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class AddElementsToHashtable {
public static void main(String args[])
{
// No need to mention the
// Generic type twice
Hashtable ht1 = new Hashtable<>();
// Initialization of a Hashtable
// using Generics
Hashtable ht2
= new Hashtable();
// Inserting the Elements
// using put() method
ht1.put(1, "one");
ht1.put(2, "two");
ht1.put(3, "three");
ht2.put(4, "four");
ht2.put(5, "five");
ht2.put(6, "six");
// Print mappings to the console
System.out.println("Mappings of ht1 : " + ht1);
System.out.println("Mappings of ht2 : " + ht2);
}
} Java
// Java program to demonstrate
// adding elements to Hashtable
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class AddElementsToHashtable {
public static void main(String args[])
{
// No need to mention the
// Generic type twice
Hashtable ht1 = new Hashtable<>(4);
// Initialization of a Hashtable
// using Generics
Hashtable ht2
= new Hashtable(2);
// Inserting the Elements
// using put() method
ht1.put(1, "one");
ht1.put(2, "two");
ht1.put(3, "three");
ht2.put(4, "four");
ht2.put(5, "five");
ht2.put(6, "six");
// Print mappings to the console
System.out.println("Mappings of ht1 : " + ht1);
System.out.println("Mappings of ht2 : " + ht2);
}
} Java
// Java program to demonstrate
// adding elements to Hashtable
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class AddElementsToHashtable {
public static void main(String args[])
{
// No need to mention the
// Generic type twice
Hashtable ht1
= new Hashtable<>(4, 0.75f);
// Initialization of a Hashtable
// using Generics
Hashtable ht2
= new Hashtable(3, 0.5f);
// Inserting the Elements
// using put() method
ht1.put(1, "one");
ht1.put(2, "two");
ht1.put(3, "three");
ht2.put(4, "four");
ht2.put(5, "five");
ht2.put(6, "six");
// Print mappings to the console
System.out.println("Mappings of ht1 : " + ht1);
System.out.println("Mappings of ht2 : " + ht2);
}
} Java
// Java program to demonstrate
// adding elements to Hashtable
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class AddElementsToHashtable {
public static void main(String args[])
{
// No need to mention the
// Generic type twice
Map hm = new HashMap<>();
// Inserting the Elements
// using put() method
hm.put(1, "one");
hm.put(2, "two");
hm.put(3, "three");
// Initialization of a Hashtable
// using Generics
Hashtable ht2
= new Hashtable(hm);
// Print mappings to the console
System.out.println("Mappings of ht2 : " + ht2);
}
} Java
// Java program to illustrate
// Java.util.Hashtable
import java.util.*;
public class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Create an empty Hashtable
Hashtable ht = new Hashtable<>();
// Add elements to the hashtable
ht.put("vishal", 10);
ht.put("sachin", 30);
ht.put("vaibhav", 20);
// Print size and content
System.out.println("Size of map is:- " + ht.size());
System.out.println(ht);
// Check if a key is present and if
// present, print value
if (ht.containsKey("vishal")) {
Integer a = ht.get("vishal");
System.out.println("value for key"
+ " \"vishal\" is:- " + a);
}
}
} Java
// Java program to demonstrate
// adding elements to Hashtable
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class AddElementsToHashtable {
public static void main(String args[])
{
// No need to mention the
// Generic type twice
Hashtable ht1 = new Hashtable<>();
// Initialization of a Hashtable
// using Generics
Hashtable ht2
= new Hashtable();
// Inserting the Elements
// using put() method
ht1.put(1, "Geeks");
ht1.put(2, "For");
ht1.put(3, "Geeks");
ht2.put(1, "Geeks");
ht2.put(2, "For");
ht2.put(3, "Geeks");
// Print mappings to the console
System.out.println("Mappings of ht1 : " + ht1);
System.out.println("Mappings of ht2 : " + ht2);
}
} Java
// Java program to demonstrate
// updating Hashtable
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class UpdatesOnHashtable {
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Initialization of a Hashtable
Hashtable ht
= new Hashtable();
// Inserting the Elements
// using put method
ht.put(1, "Geeks");
ht.put(2, "Geeks");
ht.put(3, "Geeks");
// print initial map to the console
System.out.println("Initial Map " + ht);
// Update the value at key 2
ht.put(2, "For");
// print the updated map
System.out.println("Updated Map " + ht);
}
} Java
// Java program to demonstrate
// the removing mappings from Hashtable
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class RemovingMappingsFromHashtable {
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Initialization of a Hashtable
Map ht
= new Hashtable();
// Inserting the Elements
// using put method
ht.put(1, "Geeks");
ht.put(2, "For");
ht.put(3, "Geeks");
ht.put(4, "For");
// Initial HashMap
System.out.println("Initial map : " + ht);
// Remove the map entry with key 4
ht.remove(4);
// Final Hashtable
System.out.println("Updated map : " + ht);
}
} Java
// Java program to illustrate
// traversal of Hashtable
import java.util.Hashtable;
import java.util.Map;
public class IteratingHashtable {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Create an instance of Hashtable
Hashtable ht = new Hashtable<>();
// Adding elements using put method
ht.put("vishal", 10);
ht.put("sachin", 30);
ht.put("vaibhav", 20);
// Iterating using enhanced for loop
for (Map.Entry e : ht.entrySet())
System.out.println(e.getKey() + " "
+ e.getValue());
}
} Mappings of ht1 : {3=three, 2=two, 1=one}
Mappings of ht2 : {6=six, 5=five, 4=four}2. Hashtable(int initialCapacity):这将创建一个哈希表,其初始大小由 initialCapacity 指定,默认加载因子为 0.75。
Hashtable
Java
// Java program to demonstrate
// adding elements to Hashtable
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class AddElementsToHashtable {
public static void main(String args[])
{
// No need to mention the
// Generic type twice
Hashtable ht1 = new Hashtable<>(4);
// Initialization of a Hashtable
// using Generics
Hashtable ht2
= new Hashtable(2);
// Inserting the Elements
// using put() method
ht1.put(1, "one");
ht1.put(2, "two");
ht1.put(3, "three");
ht2.put(4, "four");
ht2.put(5, "five");
ht2.put(6, "six");
// Print mappings to the console
System.out.println("Mappings of ht1 : " + ht1);
System.out.println("Mappings of ht2 : " + ht2);
}
}
Mappings of ht1 : {3=three, 2=two, 1=one}
Mappings of ht2 : {4=four, 6=six, 5=five}3. Hashtable(int size, float fillRatio):这个版本创建一个哈希表,其初始大小由size指定,填充率由fillRatio指定。填充率:基本上,它决定了哈希表在向上调整大小之前可以有多满,其值介于 0.0 到 1.0 之间。
Hashtable
Java
// Java program to demonstrate
// adding elements to Hashtable
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class AddElementsToHashtable {
public static void main(String args[])
{
// No need to mention the
// Generic type twice
Hashtable ht1
= new Hashtable<>(4, 0.75f);
// Initialization of a Hashtable
// using Generics
Hashtable ht2
= new Hashtable(3, 0.5f);
// Inserting the Elements
// using put() method
ht1.put(1, "one");
ht1.put(2, "two");
ht1.put(3, "three");
ht2.put(4, "four");
ht2.put(5, "five");
ht2.put(6, "six");
// Print mappings to the console
System.out.println("Mappings of ht1 : " + ht1);
System.out.println("Mappings of ht2 : " + ht2);
}
}
Mappings of ht1 : {3=three, 2=two, 1=one}
Mappings of ht2 : {6=six, 5=five, 4=four}4. Hashtable(Map m):这将创建一个用 m 中的元素初始化的哈希表。
Hashtable
Java
// Java program to demonstrate
// adding elements to Hashtable
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class AddElementsToHashtable {
public static void main(String args[])
{
// No need to mention the
// Generic type twice
Map hm = new HashMap<>();
// Inserting the Elements
// using put() method
hm.put(1, "one");
hm.put(2, "two");
hm.put(3, "three");
// Initialization of a Hashtable
// using Generics
Hashtable ht2
= new Hashtable(hm);
// Print mappings to the console
System.out.println("Mappings of ht2 : " + ht2);
}
}
Mappings of ht2 : {3=three, 2=two, 1=one}例子:
Java
// Java program to illustrate
// Java.util.Hashtable
import java.util.*;
public class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Create an empty Hashtable
Hashtable ht = new Hashtable<>();
// Add elements to the hashtable
ht.put("vishal", 10);
ht.put("sachin", 30);
ht.put("vaibhav", 20);
// Print size and content
System.out.println("Size of map is:- " + ht.size());
System.out.println(ht);
// Check if a key is present and if
// present, print value
if (ht.containsKey("vishal")) {
Integer a = ht.get("vishal");
System.out.println("value for key"
+ " \"vishal\" is:- " + a);
}
}
}
Size of map is:- 3
{vaibhav=20, vishal=10, sachin=30}
value for key "vishal" is:- 10对 Hashtable 执行各种操作
1. 添加元素:为了向哈希表中添加元素,我们可以使用 put() 方法。但是,插入顺序不会保留在哈希表中。在内部,对于每个元素,都会生成一个单独的散列,并根据该散列对元素进行索引,以提高效率。
Java
// Java program to demonstrate
// adding elements to Hashtable
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class AddElementsToHashtable {
public static void main(String args[])
{
// No need to mention the
// Generic type twice
Hashtable ht1 = new Hashtable<>();
// Initialization of a Hashtable
// using Generics
Hashtable ht2
= new Hashtable();
// Inserting the Elements
// using put() method
ht1.put(1, "Geeks");
ht1.put(2, "For");
ht1.put(3, "Geeks");
ht2.put(1, "Geeks");
ht2.put(2, "For");
ht2.put(3, "Geeks");
// Print mappings to the console
System.out.println("Mappings of ht1 : " + ht1);
System.out.println("Mappings of ht2 : " + ht2);
}
}
Mappings of ht1 : {3=Geeks, 2=For, 1=Geeks}
Mappings of ht2 : {3=Geeks, 2=For, 1=Geeks}2.更改元素:添加元素后,如果我们想更改元素,可以通过 put() 方法再次添加元素来完成。由于哈希表中的元素是使用键索引的,因此可以通过简单地插入我们希望更改的键的更新值来更改键的值。
Java
// Java program to demonstrate
// updating Hashtable
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class UpdatesOnHashtable {
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Initialization of a Hashtable
Hashtable ht
= new Hashtable();
// Inserting the Elements
// using put method
ht.put(1, "Geeks");
ht.put(2, "Geeks");
ht.put(3, "Geeks");
// print initial map to the console
System.out.println("Initial Map " + ht);
// Update the value at key 2
ht.put(2, "For");
// print the updated map
System.out.println("Updated Map " + ht);
}
}
Initial Map {3=Geeks, 2=Geeks, 1=Geeks}
Updated Map {3=Geeks, 2=For, 1=Geeks}3. 移除元素:为了从 Map 中移除元素,我们可以使用 remove() 方法。此方法获取键值并从该映射中删除该键的映射(如果它存在于映射中)。
Java
// Java program to demonstrate
// the removing mappings from Hashtable
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class RemovingMappingsFromHashtable {
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Initialization of a Hashtable
Map ht
= new Hashtable();
// Inserting the Elements
// using put method
ht.put(1, "Geeks");
ht.put(2, "For");
ht.put(3, "Geeks");
ht.put(4, "For");
// Initial HashMap
System.out.println("Initial map : " + ht);
// Remove the map entry with key 4
ht.remove(4);
// Final Hashtable
System.out.println("Updated map : " + ht);
}
}
Initial map : {4=For, 3=Geeks, 2=For, 1=Geeks}
Updated map : {3=Geeks, 2=For, 1=Geeks}4. Hashtable 的遍历:为了迭代表,我们可以使用高级的 for 循环。下面是迭代哈希表的示例。
Java
// Java program to illustrate
// traversal of Hashtable
import java.util.Hashtable;
import java.util.Map;
public class IteratingHashtable {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Create an instance of Hashtable
Hashtable ht = new Hashtable<>();
// Adding elements using put method
ht.put("vishal", 10);
ht.put("sachin", 30);
ht.put("vaibhav", 20);
// Iterating using enhanced for loop
for (Map.Entry e : ht.entrySet())
System.out.println(e.getKey() + " "
+ e.getValue());
}
}
vaibhav 20
vishal 10
sachin 30Hashtable的内部工作
Hashtable 数据结构是一个存储桶的数组,其中存储了键/值对。它使用hashCode() 方法来确定键/值对应该映射到哪个桶。
哈希函数有助于确定给定键在桶列表中的位置。通常,hashcode 是一个非负整数,它对于相等的对象是相等的,对于不相等的对象可能相等也可能不相等。为了确定两个对象是否相等,hashtable 使用了 equals() 方法。
两个不相等的对象可能具有相同的哈希码。这称为碰撞。为了解决冲突,哈希表使用列表数组。映射到单个桶(数组索引)的对存储在列表中,列表引用存储在数组索引中。
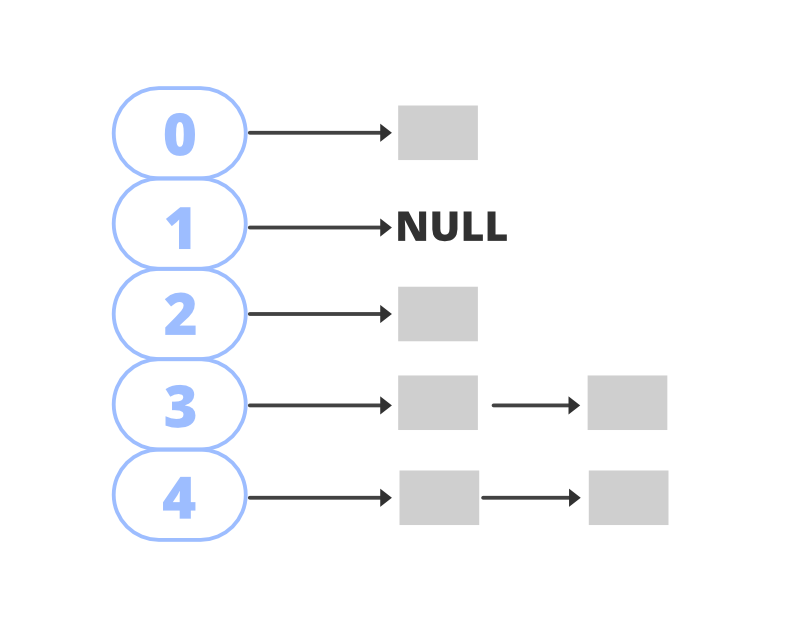
哈希表的方法
- K - 映射中键的类型。
- V – 映射中映射的值的类型。
METHOD | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| clear() | Clears this hashtable so that it contains no keys. |
| clone() | Creates a shallow copy of this hashtable. |
compute(K key, BiFunction K,? super V,? extends V> remappingFunction) | Attempts to compute a mapping for the specified key and its current mapped value (or null if there is no current mapping). |
computeIfAbsent(K key, Function extends V> mappingFunction) | If the specified key is not already associated with a value (or is mapped to null), attempts to compute its value using the given mapping function and enters it into this map unless null. |
| computeIfPresent(K key, BiFunction remappingFunction) | If the value for the specified key is present and non-null, attempts to compute a new mapping given the key and its current mapped value. |
| contains(Object value) | Tests if some key maps into the specified value in this hashtable. |
| containsKey(Object key) | Tests if the specified object is a key in this hashtable. |
| containsValue(Object value) | Returns true if this hashtable maps one or more keys to this value. |
| elements() | Returns an enumeration of the values in this hashtable. |
| entrySet() | Returns a Set view of the mappings contained in this map. |
| equals(Object o) | Compares the specified Object with this Map for equality, as per the definition in the Map interface. |
| get(Object key) | Returns the value to which the specified key is mapped, or null if this map contains no mapping for the key. |
| hashCode() | Returns the hash code value for this Map as per the definition in the Map interface. |
| isEmpty() | Tests if this hashtable maps no keys to values. |
| keys() | Returns an enumeration of the keys in this hashtable. |
| keySet() | Returns a Set view of the keys contained in this map. |
| merge(K key, V value, BiFunction remappingFunction) | If the specified key is not already associated with a value or is associated with null, associates it with the given non-null value. |
| put(K key, V value) | Maps the specified key to the specified value in this hashtable. |
| putAll(Map t) | Copies all of the mappings from the specified map to this hashtable. |
| rehash() | Increases the capacity of and internally reorganizes this hashtable, in order to accommodate and access its entries more efficiently. |
| remove(Object key) | Removes the key (and its corresponding value) from this hashtable. |
| size() | Returns the number of keys in this hashtable. |
| toString() | Returns a string representation of this Hashtable object in the form of a set of entries, enclosed in braces and separated by the ASCII characters “, ” (comma and space). |
| values() | Returns a Collection view of the values contained in this map. |
在接口Java.util.Map 中声明的方法
METHOD | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| forEach(BiConsumer action) | Performs the given action for each entry in this map until all entries have been processed or the action throws an exception. |
| getOrDefault(Object key, V defaultValue) | Returns the value to which the specified key is mapped, or defaultValue if this map contains no mapping for the key. |
| putIfAbsent(K key, V value) | If the specified key is not already associated with a value (or is mapped to null) associates it with the given value and returns null, else returns the current value. |
remove(Object key, Object value) | Removes the entry for the specified key only if it is currently mapped to the specified value. |
| replace(K key, V value) | Replaces the entry for the specified key only if it is currently mapped to some value. |
| replace(K key, V oldValue, V newValue) | Replaces the entry for the specified key only if currently mapped to the specified value. |
| replaceAll(BiFunction function) | Replaces each entry’s value with the result of invoking the given function on that entry until all entries have been processed or the function throws an exception. |
必读:
- Java中HashMap和HashTable的区别
参考: https://docs.oracle.com/en/ Java/javase/11/docs/api/ Java.base/ Java/util/Hashtable.html