用双哈希实现哈希表的Java程序
双散列是开放寻址方案中的一种技术。还有普通的哈希函数。在开放寻址方案中,实际散列函数在其空间不为空时取普通散列函数,然后执行另一个散列函数以获取一些空间插入。双哈希是开放寻址哈希表中的冲突解决技术。它使用了在发生冲突时将代码中提到的第二个哈希函数(myhash2) 应用于密钥的想法。
它是用于开放寻址的技术。在这里,我们将使用两个哈希函数。使用的第一个函数,类似于线性探测(线性探测是计算机编程中用于解决哈希表冲突的一种方案,用于维护键值对集合并查找与给定键关联的值的数据结构),表size 或“key-mod”,但如果发生冲突,则应用第二个哈希函数。
Note: It is used in open addressing, in which we used to hash function. The first function is used as same in linear probing (HASH_TABLE_SIZE or key-mod) but if the collision occur then the second hash function can be applied.
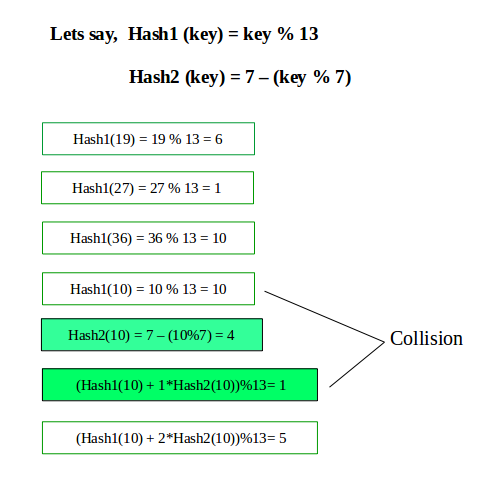
我们需要记住两个条件。
- 我们的第二个哈希函数永远不会计算为零。
- 它必须可到达单元格,即所有单元格必须首先探测。
算法:
h1(key) = key% hash_table_sizeh2(key) = PM-(key%PM)*PM
// where PM is prime number执行:
例子
Java
// Java Program to implement hashtable in
// double hashing
// Importing input output classes
import java.io.*;
// Class 1
// Helper Class
// LinkedHashEntry
class ValueEntry {
// Member variables of the class
String key;
int value;
// Constructor of this class
// Parameterized constructor
ValueEntry(String key, int value)
{
// This keyword refers to current object
// for assigning values to same object itself
this.key = key;
// this operator is pointer which contains location
// of that container that have key and value pairs
this.value = value;
}
}
// Class 2
// Helper Class
// HashTable
class HashTable {
// Member variable of this class
private int HASH_TABLE_SIZE;
private int size;
private ValueEntry[] table;
private int totalprimeSize;
// Constructor of this class
// Parameterized constructor
public HashTable(int ts)
{
// Initializing the member variables
size = 0;
HASH_TABLE_SIZE = ts;
table = new ValueEntry[HASH_TABLE_SIZE];
// Iterating using for loop over table
for (int i = 0; i < HASH_TABLE_SIZE; i++)
table[i] = null;
totalprimeSize = getPrime();
}
// Method 1
// To check for the prime number
public int getPrime()
{
// Iterating using for loop in reverse order
for (int i = HASH_TABLE_SIZE - 1; i >= 1; i--) {
// Initially assigning count to zero
int cnt = 0;
// Now, iterating from 2 upto the desired number
// to be checked by dividing it with all no
// in between [2 - no]
for (int j = 2; j * j <= i; j++)
// If number is divisible
// means not a prime number
if (i % j == 0)
// So simply move to next number
// to check for divisibility by
// incrementing the count variable
cnt++;
// By now number is not divisible
// hence count holds 0 till last
if (cnt == 0)
// It means it is a prime number so
// return the number as it is a prime number
return i;
}
// Returning a prime number
return 3;
}
// Method 2
// To get number of key-value pairs
public int getSize() { return size; }
public boolean isEmpty() { return size == 0; }
//
/* Function to clear hash table */
public void makeEmpty()
{
size = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < HASH_TABLE_SIZE; i++)
table[i] = null;
}
// Method 3
// To get value of a key
public int getkey(String key)
{
int hash1 = myhash1(key);
int hash2 = myhash2(key);
while (table[hash1] != null
&& !table[hash1].key.equals(key)) {
hash1 += hash2;
hash1 %= HASH_TABLE_SIZE;
}
return table[hash1].value;
}
// Method 4
// To insert a key value pair
public void insert(String key, int value)
{
// checking the size of table and
// comparing it with users input value
if (size == HASH_TABLE_SIZE) {
// Display message
System.out.println("Table is full");
return;
}
int hashing1 = myhash1(key);
int hashing2 = myhash2(key);
while (table[hashing1] != null) {
hashing1 += hashing2;
hashing1 %= HASH_TABLE_SIZE;
}
table[hashing1] = new ValueEntry(key, value);
size++;
}
// Method 5
// To remove a key
public void remove(String key)
{
int hash1 = myhash1(key);
int hash2 = myhash2(key);
while (table[hash1] != null
&& !table[hash1].key.equals(key)) {
hash1 += hash2;
hash1 %= HASH_TABLE_SIZE;
}
table[hash1] = null;
size--;
}
// Method 6
// Function gives a hash value for a given
// string basically it is linear probing
private int myhash1(String y)
{
int myhashVal1 = y.hashCode();
myhashVal1 %= HASH_TABLE_SIZE;
if (myhashVal1 < 0)
myhashVal1 += HASH_TABLE_SIZE;
return myhashVal1;
}
// Method 7
// Remember that the above function namely 'myhash'
// is used for double hashing
// Now after linear probing, quadratic probing
// is used in which two myhash functions are used
// as it is double chaining
private int myhash2(String y)
{
int myhashVal2 = y.hashCode();
myhashVal2 %= HASH_TABLE_SIZE;
if (myhashVal2 < 0)
myhashVal2 += HASH_TABLE_SIZE;
return totalprimeSize - myhashVal2 % totalprimeSize;
}
// Method 8
// To print the hash table
public void printHashTable()
{
// Display message
System.out.println("\nHash Table");
for (int i = 0; i < HASH_TABLE_SIZE; i++)
if (table[i] != null)
System.out.println(table[i].key + " "
+ table[i].value);
}
}
// Class 3
// Main class
// Class for DoubleHashingHashTableTest
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Display message
System.out.println("Hash Table Testing");
// Creating an object of HashTable
// in the main() method
// Custom hashtable of size 100
// means 100 key-value pairs the
// above hashtable can hold
HashTable ht = new HashTable(100);
// Inserting custom values to the hashtable
// that is key and value pairs
// Custom inputs
ht.insert("prime", 97);
ht.insert("even", 96);
ht.insert("odd", 95);
// Printing hash table after insertion of
// key value pairs and calling function
// which prints out the hashtable.
//
// Calling the function as usual
// with the help of objects
ht.printHashTable();
}
}Java
// Java Program to implement hashtable in
// double hashing
// Here performing additional task
// which is to remove the entered items
// Importing input output classes
import java.io.*;
// Importing all classes from java.util package
import java.util.*;
// Class 1
// Class LinkedHashEntry
class ValueEntry {
// Member variables of this class
String key;
int value;
// Constructor of this class
// Parameterized constructor
ValueEntry(String key, int value)
{
// 'This' keyword refers to the current object itself
// to assign the values
this.key = key;
// This keyword is pointer which contains location
// of that container that have key and value pairs
this.value = value;
}
}
// Class 2
// Helper class
// Class HashTable
class HashTable {
// Member variable of this class
private int HASH_TABLE_SIZE;
private int size;
private ValueEntry[] table;
private int totalprimeSize;
// Constructor of this class
// Parameterized constructor
public HashTable(int ts)
{
// Initially, initializing the parameters
// to some values
size = 0;
HASH_TABLE_SIZE = ts;
table = new ValueEntry[HASH_TABLE_SIZE];
// Iterating using for loop over table
for (int i = 0; i < HASH_TABLE_SIZE; i++)
// Initially table is empty
table[i] = null;
totalprimeSize = getPrime();
}
// Method 1
// To check for the prime number
public int getPrime()
{
// Iterating over hashtable using nested for loops
// in reverse order
for (int i = HASH_TABLE_SIZE - 1; i >= 1; i--) {
// Initially count is zero
int cnt = 0;
for (int j = 2; j * j <= i; j++)
if (i % j == 0)
cnt++;
if (cnt == 0)
return i;
}
// Returning a prime number
return 3;
}
// Method 2
// To get snumber of key-value pairs
public int getSize()
{ return size; }
public boolean isEmpty()
{ return size == 0; }
// Method 3
// To clear the hash table
public void makeEmpty()
{
// Initially size set to zero
size = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < HASH_TABLE_SIZE; i++)
table[i] = null;
}
// Method 3
// To get value of a key
public int getkey(String key)
{
int hash1 = myhash1(key);
int hash2 = myhash2(key);
while (table[hash1] != null
&& !table[hash1].key.equals(key)) {
hash1 += hash2;
hash1 %= HASH_TABLE_SIZE;
}
return table[hash1].value;
}
// Method 4
// To insert a key-value pair
public void insert(String key, int value)
{
// Checking the sie of table and
// comparing it with users input value
if (size == HASH_TABLE_SIZE) {
// Display message
System.out.println("Table is full");
return;
}
int hashing1 = myhash1(key);
int hashing2 = myhash2(key);
while (table[hashing1] != null) {
hashing1 += hashing2;
hashing1 %= HASH_TABLE_SIZE;
}
table[hashing1] = new ValueEntry(key, value);
size++;
}
// Method 4
// To remove a key from hashtable
public void remove(String key)
{
int hash1 = myhash1(key);
int hash2 = myhash2(key);
while (table[hash1] != null
&& !table[hash1].key.equals(key)) {
hash1 += hash2;
hash1 %= HASH_TABLE_SIZE;
}
table[hash1] = null;
size--;
}
// Method 5
// This method returns a hash value for a given
// string as it is linear probing
private int myhash1(String y)
{
int myhashVal1 = y.hashCode();
myhashVal1 %= HASH_TABLE_SIZE;
if (myhashVal1 < 0)
myhashVal1 += HASH_TABLE_SIZE;
return myhashVal1;
}
// Method 6
// In this function, 'myhash'function for double hashing
// after linear probing. A quadratic probing is used in
// which two 'myhash' functions are used
// as it is double chaining
private int myhash2(String y)
{
int myhashVal2 = y.hashCode();
myhashVal2 %= HASH_TABLE_SIZE;
if (myhashVal2 < 0)
myhashVal2 += HASH_TABLE_SIZE;
return totalprimeSize - myhashVal2 % totalprimeSize;
}
// Method 7
// To print hash table
public void printHashTable()
{
// Display message
System.out.println("\nHash Table");
// Iterating over the table
for (int i = 0; i < HASH_TABLE_SIZE; i++)
if (table[i] != null)
System.out.println(table[i].key + " "
+ table[i].value);
}
}
// Class 3
// Main class
// Class for DoubleHashingHashTableTest
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Display message
System.out.println("Hash Table Testing");
// Step 1: Creating an object of hashtable
// of custom size 100 which signifies
// table can hold 100 key-value pairs
HashTable ht = new HashTable(100);
// Step 2: Adding(appending) the values to
// the hashtable object
// Custom inputs of key-value pairs
ht.insert("prime", 97);
ht.insert("even", 96);
ht.insert("odd", 95);
// Step 3: Printing hash table after insertion
// of key-value pairs
// Calling print hash table function using object
// we call it with object.function_name
ht.printHashTable();
// Primarily goal of the program
// Step 4: Removing elements with using key values
// usong the remove() method
ht.remove("prime");
ht.printHashTable();
}
}Hash Table Testing
Hash Table
prime 97
even 96
odd 95示例 2
Java
// Java Program to implement hashtable in
// double hashing
// Here performing additional task
// which is to remove the entered items
// Importing input output classes
import java.io.*;
// Importing all classes from java.util package
import java.util.*;
// Class 1
// Class LinkedHashEntry
class ValueEntry {
// Member variables of this class
String key;
int value;
// Constructor of this class
// Parameterized constructor
ValueEntry(String key, int value)
{
// 'This' keyword refers to the current object itself
// to assign the values
this.key = key;
// This keyword is pointer which contains location
// of that container that have key and value pairs
this.value = value;
}
}
// Class 2
// Helper class
// Class HashTable
class HashTable {
// Member variable of this class
private int HASH_TABLE_SIZE;
private int size;
private ValueEntry[] table;
private int totalprimeSize;
// Constructor of this class
// Parameterized constructor
public HashTable(int ts)
{
// Initially, initializing the parameters
// to some values
size = 0;
HASH_TABLE_SIZE = ts;
table = new ValueEntry[HASH_TABLE_SIZE];
// Iterating using for loop over table
for (int i = 0; i < HASH_TABLE_SIZE; i++)
// Initially table is empty
table[i] = null;
totalprimeSize = getPrime();
}
// Method 1
// To check for the prime number
public int getPrime()
{
// Iterating over hashtable using nested for loops
// in reverse order
for (int i = HASH_TABLE_SIZE - 1; i >= 1; i--) {
// Initially count is zero
int cnt = 0;
for (int j = 2; j * j <= i; j++)
if (i % j == 0)
cnt++;
if (cnt == 0)
return i;
}
// Returning a prime number
return 3;
}
// Method 2
// To get snumber of key-value pairs
public int getSize()
{ return size; }
public boolean isEmpty()
{ return size == 0; }
// Method 3
// To clear the hash table
public void makeEmpty()
{
// Initially size set to zero
size = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < HASH_TABLE_SIZE; i++)
table[i] = null;
}
// Method 3
// To get value of a key
public int getkey(String key)
{
int hash1 = myhash1(key);
int hash2 = myhash2(key);
while (table[hash1] != null
&& !table[hash1].key.equals(key)) {
hash1 += hash2;
hash1 %= HASH_TABLE_SIZE;
}
return table[hash1].value;
}
// Method 4
// To insert a key-value pair
public void insert(String key, int value)
{
// Checking the sie of table and
// comparing it with users input value
if (size == HASH_TABLE_SIZE) {
// Display message
System.out.println("Table is full");
return;
}
int hashing1 = myhash1(key);
int hashing2 = myhash2(key);
while (table[hashing1] != null) {
hashing1 += hashing2;
hashing1 %= HASH_TABLE_SIZE;
}
table[hashing1] = new ValueEntry(key, value);
size++;
}
// Method 4
// To remove a key from hashtable
public void remove(String key)
{
int hash1 = myhash1(key);
int hash2 = myhash2(key);
while (table[hash1] != null
&& !table[hash1].key.equals(key)) {
hash1 += hash2;
hash1 %= HASH_TABLE_SIZE;
}
table[hash1] = null;
size--;
}
// Method 5
// This method returns a hash value for a given
// string as it is linear probing
private int myhash1(String y)
{
int myhashVal1 = y.hashCode();
myhashVal1 %= HASH_TABLE_SIZE;
if (myhashVal1 < 0)
myhashVal1 += HASH_TABLE_SIZE;
return myhashVal1;
}
// Method 6
// In this function, 'myhash'function for double hashing
// after linear probing. A quadratic probing is used in
// which two 'myhash' functions are used
// as it is double chaining
private int myhash2(String y)
{
int myhashVal2 = y.hashCode();
myhashVal2 %= HASH_TABLE_SIZE;
if (myhashVal2 < 0)
myhashVal2 += HASH_TABLE_SIZE;
return totalprimeSize - myhashVal2 % totalprimeSize;
}
// Method 7
// To print hash table
public void printHashTable()
{
// Display message
System.out.println("\nHash Table");
// Iterating over the table
for (int i = 0; i < HASH_TABLE_SIZE; i++)
if (table[i] != null)
System.out.println(table[i].key + " "
+ table[i].value);
}
}
// Class 3
// Main class
// Class for DoubleHashingHashTableTest
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Display message
System.out.println("Hash Table Testing");
// Step 1: Creating an object of hashtable
// of custom size 100 which signifies
// table can hold 100 key-value pairs
HashTable ht = new HashTable(100);
// Step 2: Adding(appending) the values to
// the hashtable object
// Custom inputs of key-value pairs
ht.insert("prime", 97);
ht.insert("even", 96);
ht.insert("odd", 95);
// Step 3: Printing hash table after insertion
// of key-value pairs
// Calling print hash table function using object
// we call it with object.function_name
ht.printHashTable();
// Primarily goal of the program
// Step 4: Removing elements with using key values
// usong the remove() method
ht.remove("prime");
ht.printHashTable();
}
}
Hash Table Testing
Hash Table
prime 97
even 96
odd 95
Hash Table
even 96
odd 95Similarly, we can get the size of hashed table, can clear the elements from hash table, can get our desired element in hash function. In order to get
- For size can use ht.getSize()
- For element can use ht.get(String)
Where ht is object name. In the same way, we can call our other functions in the above code.