- Flutter – 使用布局
- Flutter – 使用布局(1)
- Flutter – 使用布局(1)
- Flutter – 使用布局
- Flutter-布局简介
- Flutter-布局简介(1)
- Python| Kivy 中的布局(多个布局)中的布局
- Python| Kivy 中的布局(多个布局)中的布局(1)
- HTML 布局布局技术
- HTML 布局布局技术(1)
- HTML |布局
- HTML布局(1)
- HTML-布局(1)
- HTML |布局(1)
- HTML |布局
- HTML-布局
- HTML布局
- CSS-布局(1)
- CSS-布局
- Flutter:RenderBox 未布局 (1)
- Flutter(1)
- flutter 表(1)
- flutter 卡
- flutter 表
- Flutter
- Flutter
- flutter 卡(1)
- Flutter:RenderBox 未布局 - 无论代码示例
- C++ 中的矩阵布局(1)
📅 最后修改于: 2021-01-02 04:47:55 🧑 作者: Mango
颤振布局
布局机制的主要概念是小部件。我们知道,颤动将所有内容假定为小部件。因此,图像,图标,文本,甚至是应用程序的布局都是小部件。在这里,一些您在应用程序UI上看不到的东西(例如,排列,约束和对齐可见窗口小部件的行,列和网格)也是窗口小部件。
Flutter允许我们通过组合多个窗口小部件以构建更复杂的窗口小部件来创建布局。例如,我们可以看到下面的图像,其中显示了三个图标,每个图标下方都有一个标签。

在第二张图片中,我们可以看到上面图片的视觉布局。此图显示了三列的行,这些列包含一个图标和标签。
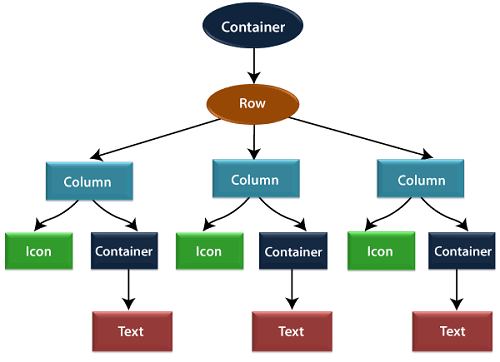
在上图中,容器是一个小部件类,允许我们自定义子小部件。它主要用于添加边框,填充,边距,背景色等等。在此,文本小部件位于用于添加边距的容器下方。整行也都放置在容器中,以增加行边距和填充。而且,UI的其余部分由颜色,text.style等属性控制。
布局小部件
让我们学习如何创建和显示简单的小部件。以下步骤显示了如何布局窗口小部件:
步骤1:首先,您需要选择Layout小部件。
步骤2:接下来,创建一个可见的小部件。
步骤3:然后,将可见窗口小部件添加到布局窗口小部件。
步骤4:最后,将布局小部件添加到要显示的页面。
布局小部件的类型
我们可以将布局小部件分为两种类型:
- 独生子女小工具
- 多个子小部件
独生子女小部件
单个子布局小部件是一种类型的小部件,其父布局小部件内只能有一个子小部件。这些小部件还可以包含特殊的布局功能。 Flutter为我们提供了许多单子小部件,以使应用程序UI更具吸引力。如果我们适当地使用这些小部件,则可以节省我们的时间并使应用程序代码更具可读性。单个子窗口小部件的不同类型的列表为:
容器:这是最流行的布局小部件,可为小部件的绘制,定位和大小提供可自定义的选项。
Center(
child: Container(
margin: const EdgeInsets.all(15.0),
color: Colors.blue,
width: 42.0,
height: 42.0,
),
)
填充:这是一个小部件,用于通过给定的填充来排列其子小部件。它包含EdgeInsets和EdgeInsets.fromLTRB,用于要在其中提供填充的所需侧面。
const Greetings(
child: Padding(
padding: EdgeInsets.all(14.0),
child: Text('Hello JavaTpoint!'),
),
)
居中:此小部件可让您将子小部件居中居中。
对齐:这是一个小部件,可将其子部件在其内部对齐并根据子部件的大小对其进行调整。它提供了更多控制权,可将子窗口小部件放置在所需的确切位置。
Center(
child: Container(
height: 110.0,
width: 110.0,
color: Colors.blue,
child: Align(
alignment: Alignment.topLeft,
child: FlutterLogo(
size: 50,
),
),
),
)
SizedBox:此小部件可让您在所有屏幕上为子小部件指定大小。
SizedBox(
width: 300.0,
height: 450.0,
child: const Card(child: Text('Hello JavaTpoint!')),
)
AspectRatio:此小部件可让您将子小部件的大小保持为指定的宽高比。
AspectRatio(
aspectRatio: 5/3,
child: Container(
color: Colors.bluel,
),
),
基线:此窗口小部件根据孩子的基线移动子窗口小部件。
child: Baseline(
baseline: 30.0,
baselineType: TextBaseline.alphabetic,
child: Container(
height: 60,
width: 50,
color: Colors.blue,
),
)
ConstrainedBox:这是一个小部件,可让您对其子级小部件施加附加约束。这意味着您可以强制子窗口小部件具有特定的约束,而无需更改子窗口小部件的属性。
ConstrainedBox(
constraints: new BoxConstraints(
minHeight: 150.0,
minWidth: 150.0,
maxHeight: 300.0,
maxWidth: 300.0,
),
child: new DecoratedBox(
decoration: new BoxDecoration(color: Colors.red),
),
),
CustomSingleChildLayout:这是一个小部件,从单个孩子的布局推迟到一个委托。委托决定放置子窗口小部件的位置,还用于确定父窗口小部件的大小。
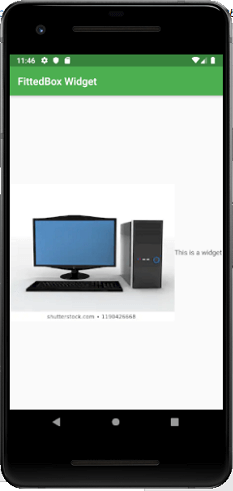
FittedBox:它根据指定的fit缩放和定位子窗口小部件。
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() => runApp(MyApp());
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
// It is the root widget of your application.
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
title: 'Multiple Layout Widget',
debugShowCheckedModeBanner: false,
theme: ThemeData(
// This is the theme of your application.
primarySwatch: Colors.green,
),
home: MyHomePage(),
);
}
}
class MyHomePage extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(title: Text("FittedBox Widget")),
body: Center(
child: FittedBox(child: Row(
children: [
Container(
child: Image.asset('assets/computer.png'),
),
Container(
child: Text("This is a widget"),
)
],
),
fit: BoxFit.contain,
)
),
);
}
}
输出量
FractionallySizedBox:这是一个小部件,允许根据可用空间的比例调整其子小部件的大小。
IntrinsicHeight和IntrinsicWidth:它们是一个小部件,允许我们将其子部件的大小调整为子部件的固有高度和宽度。
LimitedBox:此小部件允许我们仅在不受限制的情况下限制其大小。
台下:用于测量小部件的尺寸而不将其显示在屏幕上。
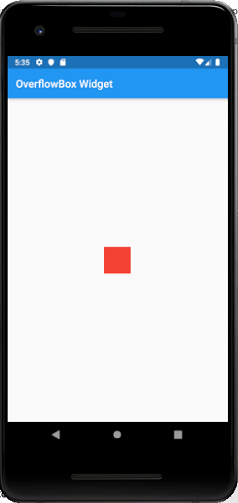
OverflowBox:这是一个小部件,允许对其子控件施加与从父控件获得的约束不同的约束。换句话说,它允许孩子溢出父窗口小部件。
例
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() => runApp(MyApp());
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
// It is the root widget of your application.
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
title: 'Single Layout Widget',
debugShowCheckedModeBanner: false,
theme: ThemeData(
// This is the theme of your application.
primarySwatch: Colors.blue,
),
home: MyHomePage(),
);
}
}
class MyHomePage extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text("OverflowBox Widget"),
),
body: Center(
child: Container(
height: 50.0,
width: 50.0,
color: Colors.red,
child: OverflowBox(
minHeight: 70.0,
minWidth: 70.0,
child: Container(
height: 50.0,
width: 50.0,
color: Colors.blue,
),
),
),
),
);
}
}
输出量
多个子小部件
多个子窗口小部件是一种窗口小部件,其中包含多个子窗口小部件,并且这些窗口小部件的布局是唯一的。例如,“行”窗口小部件在水平方向上从其子窗口小部件布置,而“列”窗口小部件在垂直方向上从其子窗口小部件布置。如果我们将行和列小部件组合在一起,则它可以构建任何级别的复杂小部件。
在这里,我们将学习不同类型的多个子窗口小部件:
行:允许沿水平方向排列其子窗口小部件。
例
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() => runApp(MyApp());
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
// It is the root widget of your application.
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
title: 'Multiple Layout Widget',
debugShowCheckedModeBanner: false,
theme: ThemeData(
// This is the theme of your application.
primarySwatch: Colors.blue,
),
home: MyHomePage(),
);
}
}
class MyHomePage extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Center(
child: Container(
alignment: Alignment.center,
color: Colors.white,
child: Row(
children: [
Expanded(
child: Text('Peter', textAlign: TextAlign.center),
),
Expanded(
child: Text('John', textAlign: TextAlign.center ),
),
Expanded(
child: FittedBox(
fit: BoxFit.contain, // otherwise the logo will be tiny
child: const FlutterLogo(),
),
),
],
),
),
);
}
}
输出量

列:它允许沿垂直方向排列其子窗口小部件。
ListView:这是最流行的滚动小部件,它使我们可以在滚动方向上一个接一个地排列其子小部件。
GridView:它允许我们将其子窗口小部件排列为可滚动的2D窗口小部件阵列。它由以水平和垂直布局排列的单元的重复图案组成。
扩展:允许使“行和列”小部件的子级占据最大可能面积。
表格:它是一个小部件,可让我们在基于表格的小部件中安排其子级。
流:它允许我们实现基于流的小部件。
堆栈:这是必不可少的小部件,主要用于重叠多个子小部件。它允许您将多层放置到屏幕上。以下示例有助于理解它。
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() => runApp(MyApp());
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
// It is the root widget of your application.
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
title: 'Multiple Layout Widget',
debugShowCheckedModeBanner: false,
theme: ThemeData(
// This is the theme of your application.
primarySwatch: Colors.blue,
),
home: MyHomePage(),
);
}
}
class MyHomePage extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Center(
child: Container(
alignment: Alignment.center,
color: Colors.white,
child: Stack(
children: [
// Max Size
Container(
color: Colors.blue,
),
Container(
color: Colors.pink,
height: 400.0,
width: 300.0,
),
Container(
color: Colors.yellow,
height: 220.0,
width: 200.0,
)
],
),
),
);
}
}
输出量

建筑群布局
在本节中,我们将学习如何使用单个和多个子布局小部件创建复杂的用户界面。布局框架允许您通过在行和列内嵌套行和列来创建复杂的用户界面布局。
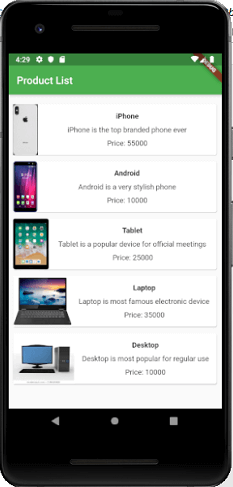
让我们通过创建产品列表来查看复杂用户界面的示例。为此,您需要首先用以下代码片段替换main.dart文件的代码。
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() => runApp(MyApp());
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
// It is the root widget of your application.
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
title: 'Flutter Demo Application', theme: ThemeData(
primarySwatch: Colors.green,),
home: MyHomePage(title: 'Complex layout example'),
);
}
}
class MyHomePage extends StatelessWidget {
MyHomePage({Key key, this.title}) : super(key: key);
final String title;
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(title: Text("Product List")),
body: ListView(
padding: const EdgeInsets.fromLTRB(3.0, 12.0, 3.0, 12.0),
children: [
ProductBox(
name: "iPhone",
description: "iPhone is the top branded phone ever",
price: 55000,
image: "iphone.png"
),
ProductBox(
name: "Android",
description: "Android is a very stylish phone",
price: 10000,
image: "android.png"
),
ProductBox(
name: "Tablet",
description: "Tablet is a popular device for official meetings",
price: 25000,
image: "tablet.png"
),
ProductBox(
name: "Laptop",
description: "Laptop is most famous electronic device",
price: 35000,
image: "laptop.png"
),
ProductBox(
name: "Desktop",
description: "Desktop is most popular for regular use",
price: 10000,
image: "computer.png"
),
],
)
);
}
}
class ProductBox extends StatelessWidget {
ProductBox({Key key, this.name, this.description, this.price, this.image}) :
super(key: key);
final String name;
final String description;
final int price;
final String image;
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.all(2),
height: 110,
child: Card(
child: Row(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.spaceEvenly,
children: [
Image.asset("assets/" + image),
Expanded(
child: Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.all(5),
child: Column(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.spaceEvenly,
children: [
Text(
this.name, style: TextStyle(
fontWeight: FontWeight.bold
)
),
Text(this.description), Text(
"Price: " + this.price.toString()
),
],
)
)
)
]
)
)
);
}
}
在上面的代码中,我们创建了窗口小部件ProductBox ,其中包含产品的详细信息,例如图像,名称,价格和描述。在ProductBox小部件中,我们使用以下子小部件:容器,行,列,扩展,卡片,文本,图像等。此小部件包含以下布局:
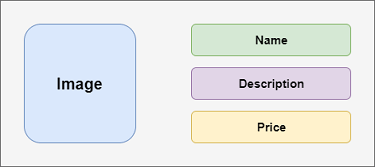
输出量
现在,当我们在android仿真器中运行dart文件时,它将提供以下输出。