📌 相关文章
- 决策树归纳
- R-决策树
- R-决策树(1)
- 决策树(1)
- 决策树
- 决策树 - Python (1)
- 数学归纳
- 数学归纳(1)
- 决策树 - Python 代码示例
- 决策树 - 任何代码示例
- 数据挖掘 | 2套
- 数据挖掘
- 数据挖掘(1)
- 数据挖掘 | 2套(1)
- 数据挖掘
- 归纳学习算法
- 归纳学习算法(1)
- R 编程中的决策树(1)
- R 编程中的决策树
- 决策树 - R 编程语言代码示例
- 递归与归纳之间的区别
- 递归与归纳之间的区别(1)
- 决策树算法 - Python (1)
- 决策树算法 - Python 代码示例
- 软件工程中的决策树(1)
- 软件工程中的决策树
- 决策树介绍与示例
- 决策树介绍与示例(1)
- 决策树介绍与示例
📜 数据挖掘-决策树归纳
📅 最后修改于: 2021-01-11 06:30:03 🧑 作者: Mango
决策树是包括根节点,分支和叶节点的结构。每个内部节点表示对属性的测试,每个分支表示测试的结果,并且每个叶节点均具有类标签。树中最顶层的节点是根节点。
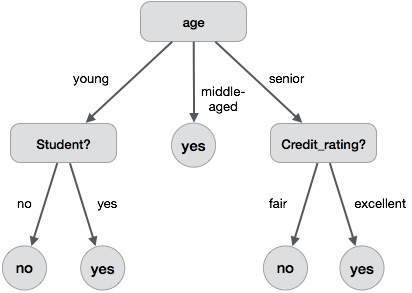
以下决策树用于概念buy_computer,该概念指示公司的客户是否可能购买计算机。每个内部节点代表一个对属性的测试。每个叶节点代表一个类。
拥有决策树的好处如下-
- 它不需要任何领域知识。
- 很容易理解。
- 决策树的学习和分类步骤既简单又快速。
决策树归纳算法
一位名为J. Ross Quinlan的机器研究人员于1980年开发了一种决策树算法,称为ID3(迭代二分器)。后来,他提出了C4.5,它是ID3的后继产品。 ID3和C4.5采用贪婪的方法。在这种算法中,没有回溯。这些树以自顶向下的递归分而治之的方式构造。
Generating a decision tree form training tuples of data partition D
Algorithm : Generate_decision_tree
Input:
Data partition, D, which is a set of training tuples
and their associated class labels.
attribute_list, the set of candidate attributes.
Attribute selection method, a procedure to determine the
splitting criterion that best partitions that the data
tuples into individual classes. This criterion includes a
splitting_attribute and either a splitting point or splitting subset.
Output:
A Decision Tree
Method
create a node N;
if tuples in D are all of the same class, C then
return N as leaf node labeled with class C;
if attribute_list is empty then
return N as leaf node with labeled
with majority class in D;|| majority voting
apply attribute_selection_method(D, attribute_list)
to find the best splitting_criterion;
label node N with splitting_criterion;
if splitting_attribute is discrete-valued and
multiway splits allowed then // no restricted to binary trees
attribute_list = splitting attribute; // remove splitting attribute
for each outcome j of splitting criterion
// partition the tuples and grow subtrees for each partition
let Dj be the set of data tuples in D satisfying outcome j; // a partition
if Dj is empty then
attach a leaf labeled with the majority
class in D to node N;
else
attach the node returned by Generate
decision tree(Dj, attribute list) to node N;
end for
return N;
修剪树木
进行树修剪是为了消除由于噪声或离群值而导致的训练数据异常。修剪后的树木较小且较不复杂。
修剪树木的方法
修剪树有两种方法-
-
预修剪-通过尽早停止构建来修剪树。
-
后修剪-此方法从完全生长的树中删除子树。
成本复杂度
成本复杂度由以下两个参数衡量-
- 树上的叶子数,以及
- 树的错误率。