📌 相关文章
- TensorFlow-形成图(1)
- TensorFlow-形成图
- TensorFlow 2.0(1)
- TensorFlow 2.0(1)
- TensorFlow 2.0
- TensorFlow 2.0
- tensorflow - Python (1)
- 形成从 i 到 j 的数组 javascript (1)
- 什么是Tensorflow | TensorFlow简介
- 什么是Tensorflow | TensorFlow简介(1)
- tensorflow - Python 代码示例
- 形成从 i 到 j 的数组 javascript 代码示例
- TensorFlow-安装
- TensorFlow-安装(1)
- tensorflow - Shell-Bash (1)
- TensorFlow 中的变量
- TensorFlow |克矩阵
- TensorFlow |克矩阵(1)
- TensorFlow API
- TensorFlow API(1)
- python中的tensorflow是什么(1)
- tensorflow - Shell-Bash 代码示例
- python 3.9 的 tensorflow - Python (1)
- TensorFlow教程(1)
- TensorFlow教程
- TensorFlow教程
- TensorFlow 简介
- TensorFlow-简介(1)
- TensorFlow 简介(1)
📜 TensorFlow形成图
📅 最后修改于: 2021-01-11 11:05:03 🧑 作者: Mango
TensorFlow形成图
偏微分方程(PDE)是微分方程的主要类型,它涉及具有多个独立变量的未知函数的偏导数。关于偏微分方程,我们专注于创建新图。
让我们假设有一个尺寸为500 * 500平方英寸的池塘-
N = 500
现在,我们将计算偏微分方程并使用它形成相应的图。生成下面给出的计算图形的步骤。
在TensorFlow代码中将v1升级到v2的操作如下:
import tensorflow.compat.v1 as tf
tf.disable_v2_behavior()
步骤1-首先,导入库进行仿真。
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
步骤2-包含用于将2D数组转换为卷积核的函数,并简化了成形图的2D卷积操作。
例:
def make_kernel(a):
a = np.asarray(a)
a = a.reshape (list(a.shape) + [1,1])
return tf.constant(a, dtype=1)
def simple_conv(x, j):
""2D convolutional operation is generated below"":
x = tf.expand_dims(tf.expand_dims(x, 0), -1)
y = tf.nn.depthwise_conv2d(x, j, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding = 'SAME')
return y[0, :, :, 0]
def laplace(x):
"""Computing 2D laplacian of the arrays""":
laplace_j = make_kernel ([[0.5, 1.0, 0.5], [1.0, -6., 1.0], [0.5, 1.0, 0.5]])
return simple_conv(x, laplace_j)
sess = tf.InteractiveSession()
We are going to step 3 now.
步骤3-包括迭代次数并计算图以相应地显示记录:-
N = 500
# Initial Conditions -- some raindrops hit the pond:
# Setting the zero here:
u_init = np.zeros([N, N], dtype = np.float32)
ut_init = np.zeros([N, N], dtype = np.float32)
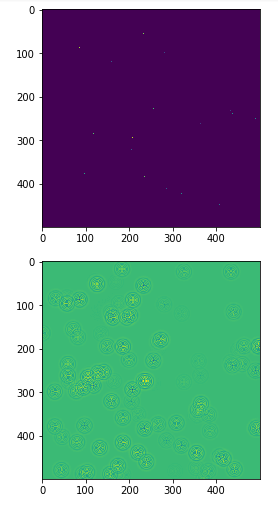
#Few rain drops hit a pond at random points:
for n in range(100):
a,b = np.random.randint(0, N, 2)
u_init[a,b] = np.random.uniform()
plt.imshow(u_init)
plt.show()
# Parameters of Graphs
# eps -- time resolution
# damping -- wave damping
eps = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape = ())
damping = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape = ())
# Creating variable for simulation state
U = tf.Variable(u_init)
Ut = tf.Variable(ut_init)
# Discretized PDE updated rule:
U_ = U + eps * Ut
Ut_ = Ut + eps*(laplace(U) - damping * Ut)
# Updating the state of rules:
step =tf.group(U.assign(U_), Ut.assign(Ut_))
# Initializing state to initial conditions
tf.initialize_all_variables().run()
# Running 1000 steps of PDE and forming graph
for i in range(1000):
# Step simulating:
step.run({eps: 0.03, damping: 0.04})
# Visualizing every 50 steps
if i % 500 == 0:
plt.imshow(U.eval())
plt.show()
输出: