📌 相关文章
- TensorFlow 2.0(1)
- TensorFlow 2.0
- TensorFlow 2.0(1)
- TensorFlow 2.0
- tensorflow 矩阵乘法 - Python (1)
- tensorflow 矩阵乘法 - Python 代码示例
- tensorflow - Python (1)
- R矩阵
- c# 矩阵 - C# (1)
- R中矩阵的逆(1)
- 矩阵求幂
- R中矩阵的逆
- 矩阵求幂
- R-矩阵
- R – 矩阵(1)
- 矩阵求幂(1)
- R-矩阵(1)
- R矩阵(1)
- 矩阵求幂
- R – 矩阵
- 矩阵求幂(1)
- 矩阵(1)
- 矩阵求幂(1)
- 矩阵
- 什么是Tensorflow | TensorFlow简介(1)
- 什么是Tensorflow | TensorFlow简介
- tensorflow - Python 代码示例
- TensorFlow-安装
- TensorFlow-安装(1)
📜 TensorFlow |克矩阵
📅 最后修改于: 2021-01-11 10:53:24 🧑 作者: Mango
克矩阵
克矩阵来自有限维空间中的一个函数。则Gram矩阵项就是有限维子空间基本服务的内积。我们必须计算样式损失。但是我们还没有看到“为什么使用Gram矩阵计算样式损失”。 Gram矩阵捕获给定层中一组要素图的“要素分布”。
注意:我们认为上述问题并未得到令人满意的回答。例如,让我们拍摄更直观的说明。假设我们具有以下特征图。为简单起见,我们仅考虑三个特征图,其中两个是完全被动的。我们有一个特征图集,其中第一个特征图看起来像一幅自然图片,而在第二个特征图中,第一个特征图看起来像一团乌云。然后,如果我们尝试手动计算内容和样式损失,我们将获得这些值。
这意味着我们没有丢失两个要素图集之间的样式信息。但是,内容不同。
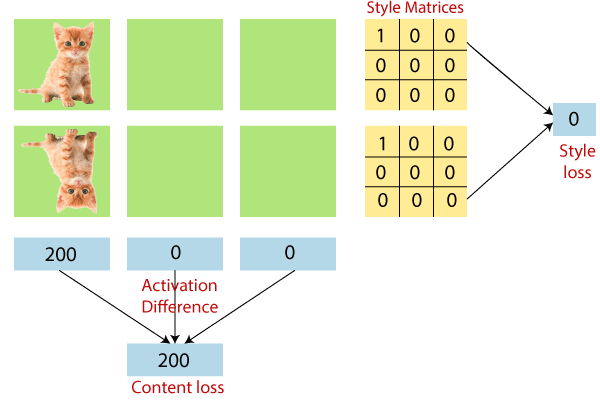
了解样式丢失
最终损失
定义为

其中α和β是用户定义的超参数。在此, β吸收了先前定义的M ^ 1归一化因子。通过控制α和β ,我们可以控制注入到生成图像中的内容和样式的数量。我们还可以在本文中看到不同α和β值的不同影响的优美可视化效果。
定义优化器
接下来,我们使用Adam优化器来优化网络损耗。
定义输入管道
在这里,我们描述了完整的输入管道。 tf.data提供了一个非常易于使用和直观的界面来实现输入管道。对于大多数图像处理任务,我们使用tf。图像API仍然使tf.image动态调整图像大小的能力很小。
例如,如果我们要动态裁剪和调整图像大小,最好以生成器的形式进行,如下所示。
我们定义了两个输入管道;一种是风格,另一种是内容。内容输入管道仅查找以单词content_开头的jpg图像,而样式管道则查找以style_开头的模型。
def image_gen_function(data_dir, file_match_str, do_shuffle=True):
"""
" The function returns a produced image, and the color channel is like values.
This is a generator function that is used by the service of tf.data api.
"""" # Load the filenames
files = [f for f in os.listdir(data_dir) if f.startswith(file_match_str)]
if do_shuffle:
shuffle(files)
mean = np.array([[vgg_mean]])
# For each file preprocess the image
for f in file:
img = Image.open(os.path.join(data_dir, f))
width, height = img.size
#Here, we crop the image to a square by cropping on the longer axis
if width < height:
left,right = 0, width
top, bottom = (height-width)/2, ((height-width)/2) + width
elif width > height:
top, bottom = 0, height
left, right = (width - height)/2, ((width-height)/2) + height
else:
arr = np.array(img.resize((image_size,image_size))).astype(np.float32)
yield (arr, mean)
arr = np.array(img.crop((left, top, right, bottom)).resize((image_size,image_size))).astype(np.float32)
yield (arr, mean)
def load_images_iterator(gen_func, zero_mean=False):
"""This function returns a dataset iterator of tf.data API.
"""
image_dataset = tf.data.Dataset.from_generator(
gen_func,
output_types=(tf.float32, tf.float32),
output_shapes=(tf.TensorShape(input_shape[1:]), tf.TensorShape([1, 1, 3]))
)
# If true, the mean will be subtracted
定义计算图
我们将代表完整的计算图。
- 定义提供输入的迭代器
- 定义输入和CNN变量
- 定义内容,样式和总损失
- 定义优化操作
config = tf.ConfigProto(allow_soft_placement=True)
# 1. Define the input pipeline in this step
part_style_gen_func = partial(image_gen_func, 'data', "style_")
part_content_gen_func = partial(image_gen_func, 'data', "content_")
style_iter = load_images_iterator(part_style_gen_func, zero_mean=True)
content_iter = load_images_iterator(part_content_gen_func, zero_mean=True)
# 2. Defining the inputs and weights
inputs = define_inputs(input_shape)
define_tf_weights()
layer_ids = list(vgg_layers.keys())
## gen_ph is used for initializing the generated image with the pixel value
##trying initializing with white noise
.
## The init_generate gives the initialization operation.
gen_ph = tf.placeholder(shape=input_shape, dtype=tf.float32)
init_generated = tf.assign(inputs["generated"], gen_ph)
# 3. Loss
# 3.1 Content loss in tf
c_loss = define_content_loss(
inputs=inputs,
layer_ids=layer_ids, pool_inds=pool_inds, c_weight=alpha
)
# 3.2 Style loss
layer_weights_ph = tf.placeholder(shape=[len(layer_ids)], dtype=tf.float32, name='layer_weights')
s_loss = define_style_loss(
inputs=inputs,
layer_ids=layer_ids, pool_inds=pool_inds, s_weight=beta, layer_weights=None
)