Pytorch 中的向量运算
在本文中,我们将讨论 PyTorch 中的向量操作。向量是一维张量,用于操作数据。向量运算有不同的类型,例如数学运算、点积和线性空间。
PyTorch 是一个优化的张量库,主要用于使用 GPU 和 CPU 的深度学习应用程序。它是广泛使用的机器学习库之一,其他还有 TensorFlow 和 Keras。
我们可以使用torch.tensor()函数创建一个向量
句法:
torch.tensor([value1,value2,.value n])
其中 values 是将输入作为列表的输入值
例子:
Python3
# importing pytorch module
import torch
# create an vector
A = torch.tensor([7058, 7059, 7060, 7061, 7062])
# display
print(A)Python3
# importing pytorch module
import torch
# create an vector A
A = torch.tensor([58, 59, 60, 61, 62])
# create an vector B
B = torch.tensor([100, 120, 140, 160, 180])
# add two vectors
print("Addition of two vectors:", A+B)
# subtract two vectors
print("subtraction of two vectors:", A-B)
# multiply two vectors
print("multiplication of two vectors:", A*B)
# multiply two vectors
print("multiplication of two vectors:", A*B)
# divide two vectors
print("division of two vectors:", A/B)
# floor divide two vectors
print("floor division of two vectors:", A//B)
# modulous of two vectors
print("modulous operation of two vectors:", A % B)
# power of two vectors
print("power operation of two vectors:", A**B)Python3
# importing pytorch module
import torch
# create an vector A
A = torch.tensor([58, 59, 60, 61, 62])
# divide vector by 2
print(A/2)
# multiply vector by 2
print(A*2)
# subtract vector by 2
print(A-2)Python3
# importing pytorch module
import torch
# create an vector A
A = torch.tensor([58, 59, 60, 61, 62])
# create an vector B
B = torch.tensor([8, 9, 6, 1, 2])
# dot product of the two vectors
print(torch.dot(A, B))Python3
# importing pytorch module
import torch
# arrange the elements from 2 to 10
print(torch.linspace(2, 10))Python3
#import pytorch
import torch
#import numpy
import numpy as np
#import matplotlib
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# create lin space from 1 to 12
x = torch.linspace(1, 12)
# sin function
y = torch.sin(x)
# plot
plt.plot(x.numpy(), y.numpy())
# display
plt.show()Python3
#import pytorch
import torch
#import numpy
import numpy as np
#import matplotlib
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# create lin space from 1 to 12
x = torch.linspace(1, 12)
# cos function
y = torch.cos(x)
# plot
plt.plot(x.numpy(), y.numpy())
# display
plt.show()Python3
#import pytorch
import torch
#import numpy
import numpy as np
#import matplotlib
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# create lin space from 1 to 12
x = torch.linspace(1, 12)
# tan function
y = torch.tan(x)
# plot
plt.plot(x.numpy(), y.numpy())
# display
plt.show()输出:
tensor([7058, 7059, 7060, 7061, 7062])
现在让我们讨论张量支持的每个向量操作。
算术运算
该过程非常简单,只需创建两个向量并对它们执行操作,就像对两个常规变量执行它们一样。
例子:
蟒蛇3
# importing pytorch module
import torch
# create an vector A
A = torch.tensor([58, 59, 60, 61, 62])
# create an vector B
B = torch.tensor([100, 120, 140, 160, 180])
# add two vectors
print("Addition of two vectors:", A+B)
# subtract two vectors
print("subtraction of two vectors:", A-B)
# multiply two vectors
print("multiplication of two vectors:", A*B)
# multiply two vectors
print("multiplication of two vectors:", A*B)
# divide two vectors
print("division of two vectors:", A/B)
# floor divide two vectors
print("floor division of two vectors:", A//B)
# modulous of two vectors
print("modulous operation of two vectors:", A % B)
# power of two vectors
print("power operation of two vectors:", A**B)
输出:
Addition of two vectors: tensor([158, 179, 200, 221, 242])
subtraction of two vectors: tensor([ -42, -61, -80, -99, -118])
multiplication of two vectors: tensor([ 5800, 7080, 8400, 9760, 11160])
multiplication of two vectors: tensor([ 5800, 7080, 8400, 9760, 11160])
division of two vectors: tensor([0.5800, 0.4917, 0.4286, 0.3812, 0.3444])
floor division of two vectors: tensor([0, 0, 0, 0, 0])
modulous operation of two vectors: tensor([58, 59, 60, 61, 62])
power operation of two vectors: tensor([ 0, -4166911448072485343, 0,8747520307384418433, 0])
一元运算
它类似于算术运算,只是另一个向量部分被一个常数代替。
例子:
蟒蛇3
# importing pytorch module
import torch
# create an vector A
A = torch.tensor([58, 59, 60, 61, 62])
# divide vector by 2
print(A/2)
# multiply vector by 2
print(A*2)
# subtract vector by 2
print(A-2)
输出:
tensor([29.0000, 29.5000, 30.0000, 30.5000, 31.0000])
tensor([116, 118, 120, 122, 124])
tensor([56, 57, 58, 59, 60])
点积
dot() 用于获取点积。考虑中的向量只需要传递给它。
句法:
torch.dot(vector1,vector2)
例子:
蟒蛇3
# importing pytorch module
import torch
# create an vector A
A = torch.tensor([58, 59, 60, 61, 62])
# create an vector B
B = torch.tensor([8, 9, 6, 1, 2])
# dot product of the two vectors
print(torch.dot(A, B))
输出:
tensor(1540)
线性空间函数
linspace 用于在给定空间中线性排列数据。它在 torch 包中可用,使用带有 start 和 end 值的 linspace()函数就足够了。
语法:
torch.linspace(start,end)
其中 start 是起始值,end 是结束值。
例子
蟒蛇3
# importing pytorch module
import torch
# arrange the elements from 2 to 10
print(torch.linspace(2, 10))
输出:
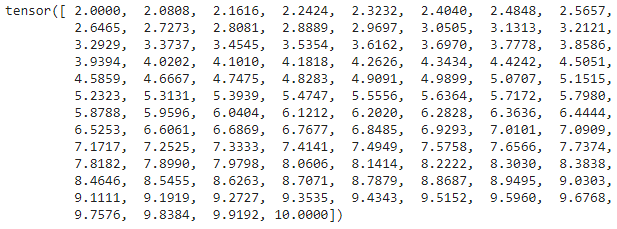
在二维坐标系上绘制函数
linspace函数用于在二维坐标系上绘制函数。对于 x 轴,我们以 2.5 的间隔创建一个从 0 到 10 的土地空间,Y 将是每个 x 值的函数。
示例 1: sin函数
蟒蛇3
#import pytorch
import torch
#import numpy
import numpy as np
#import matplotlib
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# create lin space from 1 to 12
x = torch.linspace(1, 12)
# sin function
y = torch.sin(x)
# plot
plt.plot(x.numpy(), y.numpy())
# display
plt.show()
输出:
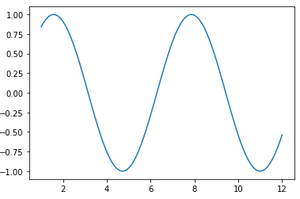
示例 2: cos函数
蟒蛇3
#import pytorch
import torch
#import numpy
import numpy as np
#import matplotlib
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# create lin space from 1 to 12
x = torch.linspace(1, 12)
# cos function
y = torch.cos(x)
# plot
plt.plot(x.numpy(), y.numpy())
# display
plt.show()
输出:

示例 3: tan()函数
蟒蛇3
#import pytorch
import torch
#import numpy
import numpy as np
#import matplotlib
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# create lin space from 1 to 12
x = torch.linspace(1, 12)
# tan function
y = torch.tan(x)
# plot
plt.plot(x.numpy(), y.numpy())
# display
plt.show()
输出:
