在 Julia 中使用 DataFrame
数据框是类似于表的二维数据结构,其中列代表变量,行包含这些变量的值。它是可变的,可以保存各种数据类型。
Julia 是一种高性能的动态编程语言,具有高级语法。 Julia 中的 DataFrame 包提供了创建和使用数据框来操作数据以用于数据科学和机器学习目的的能力。为此,您必须对 Julia 中的数据帧有足够的了解。
要了解有关 Data Frame 包的更多信息,请访问官方文档。
创建数据框
必须安装 Julia 的数据框包才能使用数据框。在 Julia 命令提示符中键入以下命令,然后单击 Enter 以安装数据框包:
using Pkg
Pkg.add("DataFrames") 安装过程的结束应如下图所示:
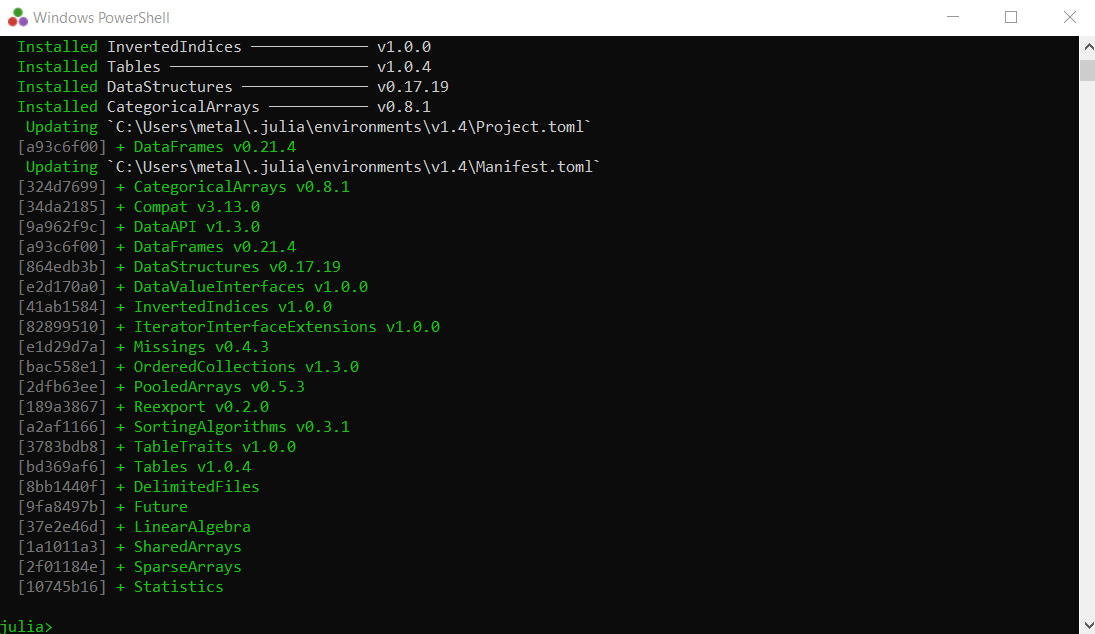
现在您已经安装了数据框包,您可以通过各种方式创建数据框。
您可以使用DataFrame()函数简单地创建一个数据框。您可以在 DataFrame()函数的括号中提及列及其值作为参数,然后按如下所示运行它。在此之前,您必须告诉 Julia 您将使用命令“ using DataFrames ”来使用数据帧。
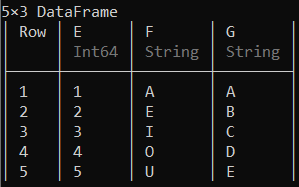
示例 1:
python3
# Creating a data frame
using DataFrames
df = DataFrame(A = 1:5, B = ["A", "E", "I", "O", "U"],
C = ["A", "B", "C", "D", "E"])python3
# Creating a data frame by adding columns separately
df = Dataframe()
df.C = 1:5
df.D = ["A", "E", "I", "O", "U"]
dfpython3
# Creating a data frame by adding rows separately
df = Dataframe(E = Int[], F = String[])
push!(df, (1, "A"))
push!(df, (2, "E"))
push!(df, (3, "I"))
push!(df, (4, "O"))
push!(df, (5, "U"))
dfpython3
# Selecting the first two rows of the data frame
first(df, 2)python3
# Selecting the last two rows of the data frame
last(df, 2)python3
# Selecting the 3rd row of the data frame
df[:3, :]python3
# Selecting column 'B' of the data frame
df[:, [:B]]python3
# Creating a subset with column 'B' and
# first 3 rows of the data frame
first(select(df, :B ), 3)python3
# Creating a subset with first 4 rows and
# excluding column 'B' of the data frame
first(select(df, Not(:B)), 4)python3
# Creating a subset with 2nd, 3rd and 4th rows
# and 'B', 'C' columns of the data frame
df[2:4, [:B, :C]]python3
# Replacing the number 4 with 7 in the column 'A'
replace !(df.A, 4 => 7)
dfpython3
# Replacing the character 'E' with 'None'
# in the columns 'B' and 'C'
df[:, [:B, :C]] .= ifelse.(df[!, [:B, :C]] .== "E", "None", df[!, [:B, :C]])
dfpython3
# Replacing the character 'A' with 'E' in the data frame
df .= ifelse.(df .== "A", "E", df)python3
# Adding a new column to the end of the data frame
push !(df, [6 "None" "F"])python3
# Adding a new column to the 3rd position
# of the data frame
insert !(df, 3, ["Q", "W", "E", "R", "T", "Y"], :D)python3
# Adding a new column in the
# last position of the data frame
arr = [2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13]
df[:E] = arr
dfpython3
# Deleting the 4th row of the data frame
deleterows !(df, 4)python3
# Deleting the 3rd column of the data frame
deletecols !(df, 3)python3
# Creating new data frames
df2 = DataFrame(F =["A", "E", "I", "O", "U"],
G =["G", "E", "E", "K", "S"])
df4 = DataFrame(H =["G", "R", "E", "A", "T"])python3
# Merging the created data frames horizontally
hcat(df, df2, df4)python3
# Creating new data frames
df3 = DataFrame(A = 7, B ="O", C ="G", E = 17)
df5 = DataFrame(A = 8, B ="None", C ="H", E = 19)
# Merging the created dataframes vertically
vcat(df, df3, df5)输出:
您还可以创建一个空的数据框并分别填写各列,如下所示。
示例 2:
蟒蛇3
# Creating a data frame by adding columns separately
df = Dataframe()
df.C = 1:5
df.D = ["A", "E", "I", "O", "U"]
df
输出:

另一种创建数据框的方法是使用push!()函数将行逐个添加到空数据框中。在插入行之前,您必须声明列的类型。
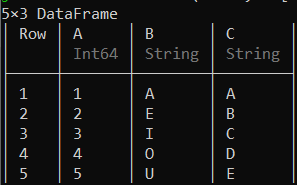
示例 3:
蟒蛇3
# Creating a data frame by adding rows separately
df = Dataframe(E = Int[], F = String[])
push!(df, (1, "A"))
push!(df, (2, "E"))
push!(df, (3, "I"))
push!(df, (4, "O"))
push!(df, (5, "U"))
df
输出:
访问行和列
现在您已经创建了数据框,可以对其进行探索。我们将使用首先创建的包含“A”、“B”和“C”列的数据框。要访问第一行或最后几行,您可以分别使用 first(DataFrame, rows) 或 last(DataFrame, rows) 函数,其中“rows”表示您要访问的行数。
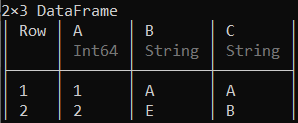
示例 1:
蟒蛇3
# Selecting the first two rows of the data frame
first(df, 2)
输出:
示例 2:
蟒蛇3
# Selecting the last two rows of the data frame
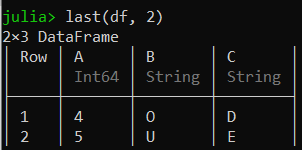
last(df, 2)
输出:
要选择特定的行数或列数,您可以在 'df[:, :]' 中分别提及要访问的行或列的索引号或变量,如下所示。
示例 3:
蟒蛇3
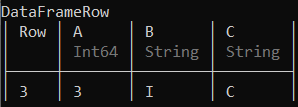
# Selecting the 3rd row of the data frame
df[:3, :]
输出:
示例 4:
蟒蛇3
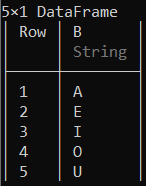
# Selecting column 'B' of the data frame
df[:, [:B]]
输出:
创建数据框的子集
要创建具有特定列和行数的数据框子集,您可以使用select()函数,如下所示:
示例 1:
蟒蛇3
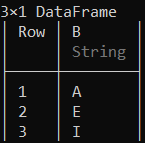
# Creating a subset with column 'B' and
# first 3 rows of the data frame
first(select(df, :B ), 3)
输出:
您还可以使用 select() 创建不包括特定列的子集,如下所示。
示例 2:
蟒蛇3
# Creating a subset with first 4 rows and
# excluding column 'B' of the data frame
first(select(df, Not(:B)), 4)
输出:
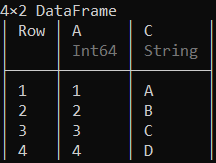
也可以使用特定的行和列轻松创建数据框的子集,如下所示。
示例 3:
蟒蛇3
# Creating a subset with 2nd, 3rd and 4th rows
# and 'B', 'C' columns of the data frame
df[2:4, [:B, :C]]
输出:

修改数据框的内容
可以使用各种功能将数据替换为数据框中的一些其他数据。 要在数据框中执行替换操作,您可以简单地使用replace!()函数。
示例 1:
蟒蛇3
# Replacing the number 4 with 7 in the column 'A'
replace !(df.A, 4 => 7)
df
输出:
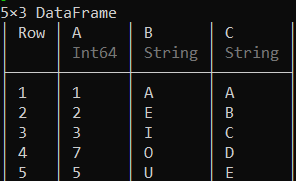
可以使用创建子集的广播语法对多个列执行替换操作,如下所示。
示例 2:
蟒蛇3
# Replacing the character 'E' with 'None'
# in the columns 'B' and 'C'
df[:, [:B, :C]] .= ifelse.(df[!, [:B, :C]] .== "E", "None", df[!, [:B, :C]])
df
输出:
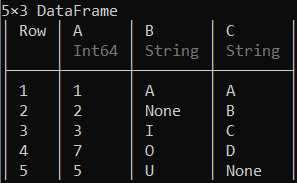
完整数据帧的替换操作可以执行如下所示。
示例 3:
蟒蛇3
# Replacing the character 'A' with 'E' in the data frame
df .= ifelse.(df .== "A", "E", df)
输出:

这里每个“A”都替换为“E”。
向数据框中添加额外的行和列
可以使用push!()函数将新行添加到数据框的末尾。
示例 1:
蟒蛇3
# Adding a new column to the end of the data frame
push !(df, [6 "None" "F"])
输出:
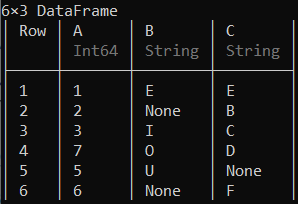
可以使用insert!()函数将列添加到数据框中的特定位置。
示例 2:
蟒蛇3
# Adding a new column to the 3rd position
# of the data frame
insert !(df, 3, ["Q", "W", "E", "R", "T", "Y"], :D)
输出:
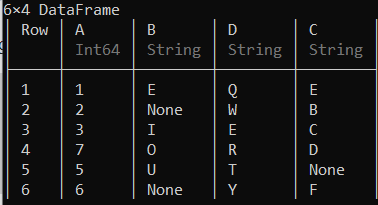
您还可以通过在列中创建所需的元素数组来添加列,并将其添加到数据框的末尾,如下所示。
示例 3:
蟒蛇3
# Adding a new column in the
# last position of the data frame
arr = [2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13]
df[:E] = arr
df
输出:

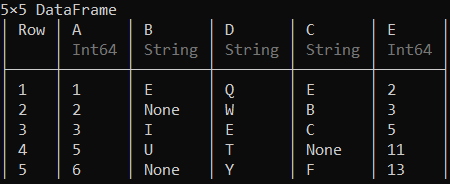
删除数据框中的行和列
可以使用deleterows!()函数删除数据框中的特定行。
示例 1:
蟒蛇3
# Deleting the 4th row of the data frame
deleterows !(df, 4)
输出:
可以使用deletecols!()函数删除列。
示例 2:
蟒蛇3
# Deleting the 3rd column of the data frame
deletecols !(df, 3)
输出:
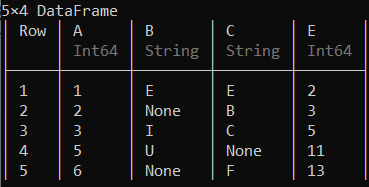
这里第 3 列的“D”列已被删除。
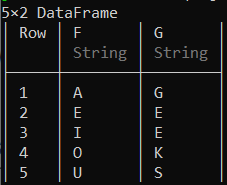
合并数据框
这里创建了多个数据框来表示合并操作的实现。
示例 1:
蟒蛇3
# Creating new data frames
df2 = DataFrame(F =["A", "E", "I", "O", "U"],
G =["G", "E", "E", "K", "S"])
df4 = DataFrame(H =["G", "R", "E", "A", "T"])
输出:

您可以使用连接函数hcat() 将这两个新数据帧与第一个数据帧合并。此函数水平合并数据帧,注意所有数据帧在水平合并时应包含相同的行数。
示例 2:
蟒蛇3
# Merging the created data frames horizontally
hcat(df, df2, df4)
输出:
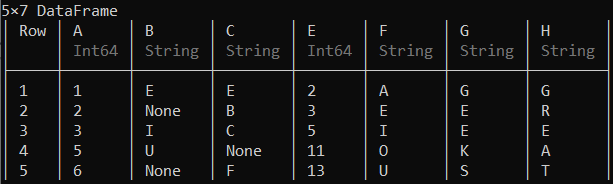
vcat()连接函数可用于垂直合并数据帧,从而表示创建的数据帧与第一个数据帧具有相同的列数和名称。
示例 3:
蟒蛇3
# Creating new data frames
df3 = DataFrame(A = 7, B ="O", C ="G", E = 17)
df5 = DataFrame(A = 8, B ="None", C ="H", E = 19)
# Merging the created dataframes vertically
vcat(df, df3, df5)
输出:

这里使用了带有手动输入数据的基本数据框。对于包含大量分析数据的 CSV 文件,可以使用许多功能完成更多操作。