📅 最后修改于: 2021-01-23 05:39:50 🧑 作者: Mango
自从计算机或机器发明以来,它们执行各种任务的能力呈指数增长。人们已经在计算机系统的各种工作领域,其不断提高的速度以及相对于时间的减小方面开发了强大的计算机系统。
计算机科学的一个分支,叫做人工智能,致力于创造像人类一样智能的计算机或机器。
什么是人工智能?
人工智能之父约翰·麦卡锡(John McCarthy)说,这是“制造智能机器,尤其是智能计算机程序的科学和工程学”。
人工智能是一种使计算机,计算机控制的机器人或软件进行智能思考的方式,类似于智能人类的思考方式。
通过研究人类大脑的思维方式,以及人类在尝试解决问题时的学习方式,决定方式和工作方式,然后将本研究的结果作为开发智能软件和系统的基础,可以实现人工智能。
人工智能哲学
在利用计算机系统的功能时,人类的好奇心使他想知道: “一台机器能像人类一样思考和行为吗?”
因此,人工智能的发展始于在我们发现并视为人类崇高的机器中创建类似智能的意图。
人工智能的目标
-
创建专家系统-表现出智能行为,学习,演示,解释和建议用户的系统。
-
在机器上实现人类智能-创建能够像人类一样理解,思考,学习和行为的系统。
对AI有何贡献?
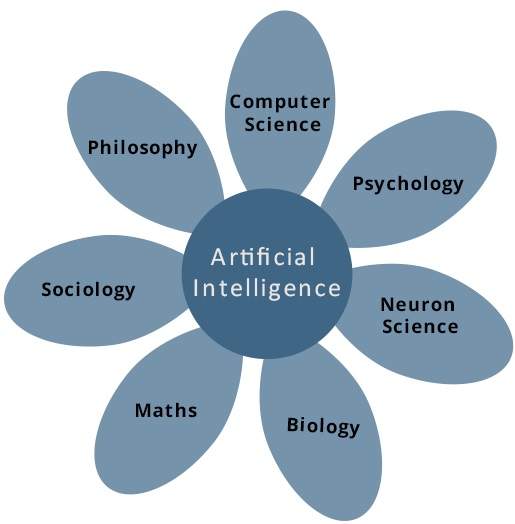
人工智能是基于诸如计算机科学,生物学,心理学,语言学,数学和工程学等学科的科学技术。 AI的主要目的是开发与人类智能相关的计算机功能,例如推理,学习和解决问题。
在以下区域中,一个或多个区域可以有助于构建智能系统。
不使用AI进行编程
不使用AI和使用AI的编程在以下方面有所不同-
| Programming Without AI | Programming With AI |
|---|---|
| A computer program without AI can answer the specific questions it is meant to solve. | A computer program with AI can answer the generic questions it is meant to solve. |
| Modification in the program leads to change in its structure. | AI programs can absorb new modifications by putting highly independent pieces of information together. Hence you can modify even a minute piece of information of program without affecting its structure. |
| Modification is not quick and easy. It may lead to affecting the program adversely. | Quick and Easy program modification. |
什么是AI技术?
在现实世界中,知识具有某些不受欢迎的属性-
- 它的体积巨大,几乎难以想象。
- 它的组织或格式不正确。
- 它不断变化。
AI技术是一种有效地组织和使用知识的方式,其方式是-
- 提供它的人员应该可以感知到它。
- 它应该很容易修改以纠正错误。
- 尽管它不完整或不准确,但在许多情况下应该很有用。
人工智能技术提高了其配备的复杂程序的执行速度。
人工智能的应用
人工智能在各个领域都占据主导地位,例如-
-
游戏-人工智能在战略游戏中起着至关重要的作用,例如国际象棋,扑克,井字游戏等,其中机器可以根据启发式知识来思考大量可能的位置。
-
自然语言处理-可以与理解人类所说自然语言的计算机进行交互。
-
专家系统-有些应用程序集成了机器,软件和特殊信息,以提供推理和建议。他们向用户提供解释和建议。
-
视觉系统-这些系统可以理解,解释和理解计算机上的视觉输入。例如,
-
间谍飞机拍摄照片,用于找出空间信息或区域地图。
-
医生使用临床专家系统来诊断患者。
-
警察使用计算机软件,该软件可以利用法医存储的肖像识别罪犯的脸。
-
-
语音识别-某些智能系统能够在人们与之交谈时,根据句子及其含义来听和理解该语言。它可以处理不同的口音,语,背景噪音,由于寒冷引起的人声变化等。
-
手写识别-手写识别软件可读取用笔写在纸上或手写笔在屏幕上的文字。它可以识别字母的形状并将其转换为可编辑的文本。
-
智能机器人-机器人能够执行人类给出的任务。它们具有传感器,可以检测来自现实世界的物理数据,例如光,热,温度,运动,声音,撞击和压力。它们具有高效的处理器,多个传感器和巨大的内存,以展现智能。此外,他们能够从错误中学习,并且能够适应新环境。
人工智能的历史
这是20世纪AI的历史-
| Year | Milestone / Innovation |
|---|---|
| 1923 |
Karel Čapek play named “Rossum’s Universal Robots” (RUR) opens in London, first use of the word “robot” in English. |
| 1943 |
Foundations for neural networks laid. |
| 1945 |
Isaac Asimov, a Columbia University alumni, coined the term Robotics. |
| 1950 |
Alan Turing introduced Turing Test for evaluation of intelligence and published Computing Machinery and Intelligence. Claude Shannon published Detailed Analysis of Chess Playing as a search. |
| 1956 |
John McCarthy coined the term Artificial Intelligence. Demonstration of the first running AI program at Carnegie Mellon University. |
| 1958 |
John McCarthy invents LISP programming language for AI. |
| 1964 |
Danny Bobrow’s dissertation at MIT showed that computers can understand natural language well enough to solve algebra word problems correctly. |
| 1965 |
Joseph Weizenbaum at MIT built ELIZA, an interactive problem that carries on a dialogue in English. |
| 1969 |
Scientists at Stanford Research Institute Developed Shakey, a robot, equipped with locomotion, perception, and problem solving. |
| 1973 |
The Assembly Robotics group at Edinburgh University built Freddy, the Famous Scottish Robot, capable of using vision to locate and assemble models. |
| 1979 |
The first computer-controlled autonomous vehicle, Stanford Cart, was built. |
| 1985 |
Harold Cohen created and demonstrated the drawing program, Aaron. |
| 1990 |
Major advances in all areas of AI −
|
| 1997 |
The Deep Blue Chess Program beats the then world chess champion, Garry Kasparov. |
| 2000 |
Interactive robot pets become commercially available. MIT displays Kismet, a robot with a face that expresses emotions. The robot Nomad explores remote regions of Antarctica and locates meteorites. |