📌 相关文章
- 敏捷数据科学-数据可视化(1)
- 敏捷数据科学-数据可视化
- 敏捷数据科学-数据科学过程
- 敏捷数据科学-数据科学过程(1)
- 敏捷数据科学教程
- 敏捷数据科学教程(1)
- 敏捷数据科学-简介
- 敏捷数据科学-简介(1)
- 讨论敏捷数据科学
- 讨论敏捷数据科学(1)
- 敏捷数据科学-敏捷的实现
- 敏捷数据科学-敏捷的实现(1)
- 大数据与数据科学的区别
- 大数据与数据科学的区别(1)
- 大数据与数据科学的区别
- 敏捷数据科学-敏捷中的数据处理(1)
- 敏捷数据科学-敏捷中的数据处理
- 敏捷数据科学-有用的资源
- 敏捷数据科学-有用的资源(1)
- 数据科学用Python
- 数据科学用Python(1)
- 数据科学中的 R 与Python
- 数据科学中的 R 与Python(1)
- 数据科学用Python
- 敏捷数据科学-SQL与NoSQL
- 敏捷数据科学-SQL与NoSQL(1)
- 敏捷数据科学-处理报告(1)
- 敏捷数据科学-处理报告
- 什么是数据科学?(1)
📜 敏捷数据科学-数据丰富
📅 最后修改于: 2021-01-23 05:51:09 🧑 作者: Mango
数据充实是指用于增强,改进和改善原始数据的一系列过程。它指有用的数据转换(将原始数据转换为有用的信息)。数据丰富化过程着重于使数据成为现代企业或企业的宝贵数据资产。
最常见的数据丰富过程包括通过使用特定的决策算法来纠正数据库中的拼写错误或印刷错误。数据充实工具将有用的信息添加到简单的数据表中。
考虑以下代码对单词进行拼写纠正-
import re
from collections import Counter
def words(text): return re.findall(r'\w+', text.lower())
WORDS = Counter(words(open('big.txt').read()))
def P(word, N=sum(WORDS.values())):
"Probabilities of words"
return WORDS[word] / N
def correction(word):
"Spelling correction of word"
return max(candidates(word), key=P)
def candidates(word):
"Generate possible spelling corrections for word."
return (known([word]) or known(edits1(word)) or known(edits2(word)) or [word])
def known(words):
"The subset of `words` that appear in the dictionary of WORDS."
return set(w for w in words if w in WORDS)
def edits1(word):
"All edits that are one edit away from `word`."
letters = 'abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz'
splits = [(word[:i], word[i:]) for i in range(len(word) + 1)]
deletes = [L + R[1:] for L, R in splits if R]
transposes = [L + R[1] + R[0] + R[2:] for L, R in splits if len(R)>1]
replaces = [L + c + R[1:] for L, R in splits if R for c in letters]
inserts = [L + c + R for L, R in splits for c in letters]
return set(deletes + transposes + replaces + inserts)
def edits2(word):
"All edits that are two edits away from `word`."
return (e2 for e1 in edits1(word) for e2 in edits1(e1))
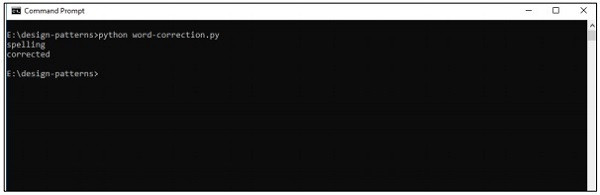
print(correction('speling'))
print(correction('korrectud'))
在此程序中,我们将与“ big.txt”匹配,其中包括更正的单词。单词与文本文件中包含的单词匹配,并相应地打印适当的结果。
输出
上面的代码将生成以下输出-