先决条件:段树和深度优先搜索。
在本文中,讨论了一种将N元根树(具有2个以上子级的树)转换为段树的方法,该树用于执行范围更新查询。
为什么我们已经有了n元根树,为什么需要一个段树?
很多时候,会出现必须在多个节点及其子树上多次执行相同操作以及相同操作的情况。
假设我们必须在不同的子树上执行N次更新。每个操作都需要花费O(N)的时间,因为它是一棵N元树,因此总体复杂度为O(N ^ 2),这太慢了,无法处理超过10 ^ 3个更新查询。因此,我们必须走另一条路,我们将为此构建一个分段树。
方法:执行深度优先搜索以遍历所有节点,并使用两个数组tin和tout (这是进行更新和查询的范围)来跟踪转换后的数组中每个节点的子树的索引。 DFS将执行欧拉行走。这个想法是创建一个数组,并按照访问转换后的数组的顺序向其中添加节点。
让我们看看tin和tout数组如何帮助确定转换后的数组中的范围。
令N元根树为:
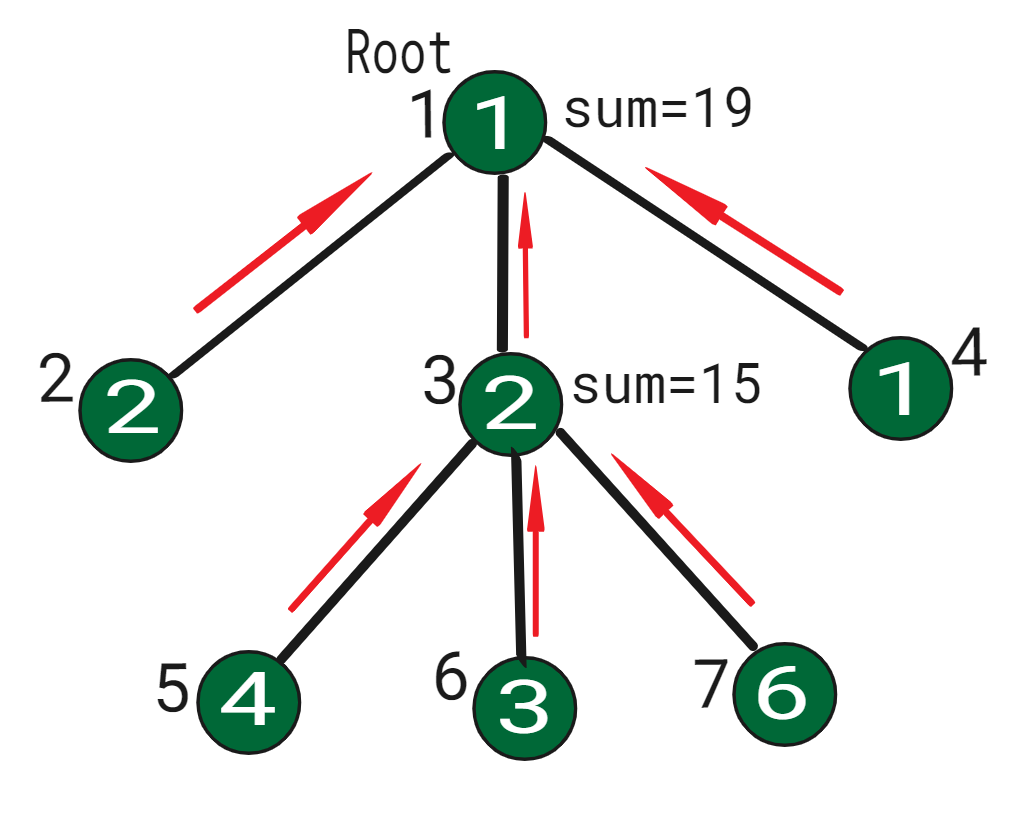
real values on nodes: 1 2 2 1 4 3 6
converted arr(indexes): 1 2 3 5 6 7 4
Node 3 has three children 5, 6, 7.
Therefore, the range of node 3 is index 3-6.
NODE: RANGE(tin-tout)
NODE 1: 1 - 7
NODE 2: 2 - 2
NODE 3: 3 - 6
NODE 5: 4 - 4
NODE 6: 5 - 5
NODE 7: 6 - 6
NODE 4: 7 - 7此处,节点1的范围为1-7(所有节点),因此将在所有节点上执行更新和查询。像2这样没有子节点的叶子节点只会更新范围2-2(仅自身),这证明我们的范围数组tin和tout是正确的。类似地,所有节点的tin和tout确定了查询范围并在段树中进行了更新。
以下是该方法的实现:
C++
// C++ implementation of the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
#define pb push_back
#define N 100005
// Keeping the values array indexed by 1.
int arr[8] = { 0, 1, 2, 2, 1, 4, 3, 6 };
vector tree[N];
int idx, tin[N], tout[N], converted[N];
// Function to perform DFS in the tree
void dfs(ll node, ll parent)
{
++idx;
converted[idx] = node;
// To store starting range of a node
tin[node] = idx;
for (auto i : tree[node]) {
if (i != parent)
dfs(i, node);
}
// To store ending range of a node
tout[node] = idx;
}
// Segment tree
ll t[N * 4];
// Build using the converted array indexes.
// Here a simple n-ary tree is converted
// into a segment tree.
// Now O(NlogN) range updates and queries
// can be performed.
void build(ll node, ll start, ll end)
{
if (start == end)
t[node] = arr[converted[start]];
else {
ll mid = (start + end) >> 1;
build(2 * node, start, mid);
build(2 * node + 1, mid + 1, end);
t[node] = t[2 * node] + t[2 * node + 1];
}
}
// Function to perform update operation
// on the tree
void update(ll node, ll start, ll end,
ll lf, ll rg, ll c)
{
if (start > end or start > rg or end < lf)
return;
if (start == end) {
t[node] = c;
}
else {
ll mid = (start + end) >> 1;
update(2 * node, start, mid, lf, rg, c);
update(2 * node + 1, mid + 1, end, lf, rg, c);
t[node] = t[2 * node] + t[2 * node + 1];
}
}
// Function to find the sum at every node
ll query(ll node, ll start, ll end, ll lf, ll rg)
{
if (start > rg or end < lf)
return 0;
if (lf <= start and end <= rg) {
return t[node];
}
else {
ll ans = 0;
ll mid = (start + end) >> 1;
ans += query(2 * node, start, mid, lf, rg);
ans += query(2 * node + 1, mid + 1,
end, lf, rg);
return ans;
}
}
// Function to print the tree
void printTree(int q, int node, int n)
{
while (q--) {
// Calculating range of node in segment tree
ll lf = tin[node];
ll rg = tout[node];
ll res = query(1, 1, n, lf, rg);
cout << "sum at node " << node
<< ": " << res << endl;
node++;
}
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int n = 7;
int q = 7;
// Creating the tree.
tree[1].pb(2);
tree[1].pb(3);
tree[1].pb(4);
tree[3].pb(5);
tree[3].pb(6);
tree[3].pb(7);
// DFS to get converted array.
idx = 0;
dfs(1, -1);
// Build segment tree with converted array.
build(1, 1, n);
printTree(7, 1, 7);
// Updating the value at node 3
int node = 3;
ll lf = tin[node];
ll rg = tout[node];
ll value = 4;
update(1, 1, n, lf, rg, value);
cout << "After Update" << endl;
printTree(7, 1, 7);
return 0;
} Java
// Java implementation of the above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
static final int N = 100005;
// Keeping the values array indexed by 1.
static int arr[] = { 0, 1, 2, 2, 1, 4, 3, 6 };
static Vector []tree = new Vector[N];
static int idx;
static int []tin = new int[N];
static int []tout = new int[N];
static int []converted = new int[N];
// Function to perform DFS in the tree
static void dfs(int node, int parent)
{
++idx;
converted[idx] = node;
// To store starting range of a node
tin[node] = idx;
for (int i : tree[node])
{
if (i != parent)
dfs(i, node);
}
// To store ending range of a node
tout[node] = idx;
}
// Segment tree
static int []t = new int[N * 4];
// Build using the converted array indexes.
// Here a simple n-ary tree is converted
// into a segment tree.
// Now O(NlogN) range updates and queries
// can be performed.
static void build(int node, int start, int end)
{
if (start == end)
t[node] = arr[converted[start]];
else
{
int mid = (start + end) >> 1;
build(2 * node, start, mid);
build(2 * node + 1, mid + 1, end);
t[node] = t[2 * node] + t[2 * node + 1];
}
}
// Function to perform update operation
// on the tree
static void update(int node, int start, int end,
int lf, int rg, int c)
{
if (start > end || start > rg || end < lf)
return;
if (start == end)
{
t[node] = c;
}
else
{
int mid = (start + end) >> 1;
update(2 * node, start, mid, lf, rg, c);
update(2 * node + 1, mid + 1, end, lf, rg, c);
t[node] = t[2 * node] + t[2 * node + 1];
}
}
// Function to find the sum at every node
static int query(int node, int start, int end,
int lf, int rg)
{
if (start > rg || end < lf)
return 0;
if (lf <= start && end <= rg)
{
return t[node];
}
else
{
int ans = 0;
int mid = (start + end) >> 1;
ans += query(2 * node, start, mid, lf, rg);
ans += query(2 * node + 1, mid + 1,
end, lf, rg);
return ans;
}
}
// Function to print the tree
static void printTree(int q, int node, int n)
{
while (q-- > 0)
{
// Calculating range of node in segment tree
int lf = tin[node];
int rg = tout[node];
int res = query(1, 1, n, lf, rg);
System.out.print("sum at node " + node
+ ": " + res +"\n");
node++;
}
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int n = 7;
int q = 7;
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++)
tree[i] = new Vector();
// Creating the tree.
tree[1].add(2);
tree[1].add(3);
tree[1].add(4);
tree[3].add(5);
tree[3].add(6);
tree[3].add(7);
// DFS to get converted array.
idx = 0;
dfs(1, -1);
// Build segment tree with converted array.
build(1, 1, n);
printTree(7, 1, 7);
// Updating the value at node 3
int node = 3;
int lf = tin[node];
int rg = tout[node];
int value = 4;
update(1, 1, n, lf, rg, value);
System.out.print("After Update" + "\n");
printTree(7, 1, 7);
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar Python3
# Python3 implementation of the above approach
N = 100005
# Keeping the values array indexed by 1.
arr = [0, 1, 2, 2, 1, 4, 3, 6]
tree = [[] for i in range(N)]
idx = 0
tin = [0]*N
tout = [0]*N
converted = [0]*N
# Function to perform DFS in the tree
def dfs(node, parent):
global idx
idx += 1
converted[idx] = node
# To store starting range of a node
tin[node] = idx
for i in tree[node]:
if (i != parent):
dfs(i, node)
# To store ending range of a node
tout[node] = idx
# Segment tree
t = [0]*(N * 4)
# Build using the converted array indexes.
# Here a simple n-ary tree is converted
# into a segment tree.
# Now O(NlogN) range updates and queries
# can be performed.
def build(node, start, end):
if (start == end):
t[node] = arr[converted[start]]
else:
mid = (start + end) >> 1
build(2 * node, start, mid)
build(2 * node + 1, mid + 1, end)
t[node] = t[2 * node] + t[2 * node + 1]
# Function to perform update operation
# on the tree
def update(node, start, end,lf, rg, c):
if (start > end or start > rg or end < lf):
return
if (start == end):
t[node] = c
else:
mid = (start + end) >> 1
update(2 * node, start, mid, lf, rg, c)
update(2 * node + 1, mid + 1, end, lf, rg, c)
t[node] = t[2 * node] + t[2 * node + 1]
# Function to find the sum at every node
def query(node, start, end, lf, rg):
if (start > rg or end < lf):
return 0
if (lf <= start and end <= rg):
return t[node]
else:
ans = 0
mid = (start + end) >> 1
ans += query(2 * node, start, mid, lf, rg)
ans += query(2 * node + 1, mid + 1,
end, lf, rg)
return ans
# Function to prthe tree
def printTree(q, node, n):
while (q > 0):
# Calculating range of node in segment tree
lf = tin[node]
rg = tout[node]
res = query(1, 1, n, lf, rg)
print("sum at node",node,":",res)
node += 1
q -= 1
# Driver code
if __name__ == '__main__':
n = 7
q = 7
# Creating the tree.
tree[1].append(2)
tree[1].append(3)
tree[1].append(4)
tree[3].append(5)
tree[3].append(6)
tree[3].append(7)
# DFS to get converted array.
idx = 0
dfs(1, -1)
# Build segment tree with converted array.
build(1, 1, n)
printTree(7, 1, 7)
# Updating the value at node 3
node = 3
lf = tin[node]
rg = tout[node]
value = 4
update(1, 1, n, lf, rg, value)
print("After Update")
printTree(7, 1, 7)
# This code is contributed by mohit kumar 29C#
// C# implementation of the above approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG
{
static readonly int N = 100005;
// Keeping the values array indexed by 1.
static int []arr = { 0, 1, 2, 2, 1, 4, 3, 6 };
static List []tree = new List[N];
static int idx;
static int []tin = new int[N];
static int []tout = new int[N];
static int []converted = new int[N];
// Function to perform DFS in the tree
static void dfs(int node, int parent)
{
++idx;
converted[idx] = node;
// To store starting range of a node
tin[node] = idx;
foreach (int i in tree[node])
{
if (i != parent)
dfs(i, node);
}
// To store ending range of a node
tout[node] = idx;
}
// Segment tree
static int []t = new int[N * 4];
// Build using the converted array indexes.
// Here a simple n-ary tree is converted
// into a segment tree.
// Now O(NlogN) range updates and queries
// can be performed.
static void build(int node, int start, int end)
{
if (start == end)
t[node] = arr[converted[start]];
else
{
int mid = (start + end) >> 1;
build(2 * node, start, mid);
build(2 * node + 1, mid + 1, end);
t[node] = t[2 * node] + t[2 * node + 1];
}
}
// Function to perform update operation
// on the tree
static void update(int node, int start, int end,
int lf, int rg, int c)
{
if (start > end || start > rg || end < lf)
return;
if (start == end)
{
t[node] = c;
}
else
{
int mid = (start + end) >> 1;
update(2 * node, start, mid, lf, rg, c);
update(2 * node + 1, mid + 1, end, lf, rg, c);
t[node] = t[2 * node] + t[2 * node + 1];
}
}
// Function to find the sum at every node
static int query(int node, int start, int end,
int lf, int rg)
{
if (start > rg || end < lf)
return 0;
if (lf <= start && end <= rg)
{
return t[node];
}
else
{
int ans = 0;
int mid = (start + end) >> 1;
ans += query(2 * node, start, mid, lf, rg);
ans += query(2 * node + 1, mid + 1,
end, lf, rg);
return ans;
}
}
// Function to print the tree
static void printTree(int q, int node, int n)
{
while (q-- > 0)
{
// Calculating range of node in segment tree
int lf = tin[node];
int rg = tout[node];
int res = query(1, 1, n, lf, rg);
Console.Write("sum at node " + node
+ ": " + res +"\n");
node++;
}
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int n = 7;
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++)
tree[i] = new List();
// Creating the tree.
tree[1].Add(2);
tree[1].Add(3);
tree[1].Add(4);
tree[3].Add(5);
tree[3].Add(6);
tree[3].Add(7);
// DFS to get converted array.
idx = 0;
dfs(1, -1);
// Build segment tree with converted array.
build(1, 1, n);
printTree(7, 1, 7);
// Updating the value at node 3
int node = 3;
int lf = tin[node];
int rg = tout[node];
int value = 4;
update(1, 1, n, lf, rg, value);
Console.Write("After Update" + "\n");
printTree(7, 1, 7);
}
}
// This code is contributed by PrinciRaj1992 输出:
sum at node 1: 19
sum at node 2: 2
sum at node 3: 15
sum at node 4: 1
sum at node 5: 4
sum at node 6: 3
sum at node 7: 6
After Update
sum at node 1: 20
sum at node 2: 2
sum at node 3: 16
sum at node 4: 1
sum at node 5: 4
sum at node 6: 4
sum at node 7: 4