给定一棵二叉树和3个节点a,b和c,任务是在树中找到一个节点,以便在除去连接到该节点的所有边缘之后,a,b和c位于三个不同的树中。
下面给出的是一棵输入节点为c,j和o的树。 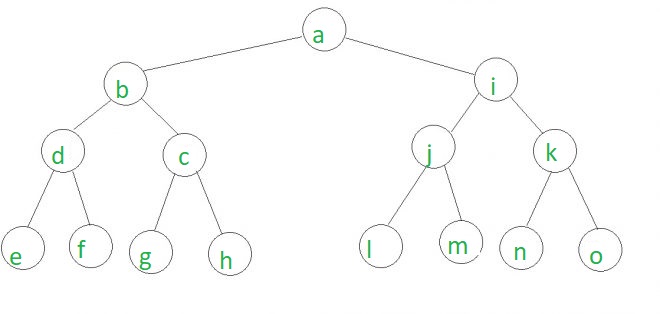
在上面的树中,如果节点i与树断开连接,则给定的节点c,j和o将位于三棵不同的树中,如下所示。
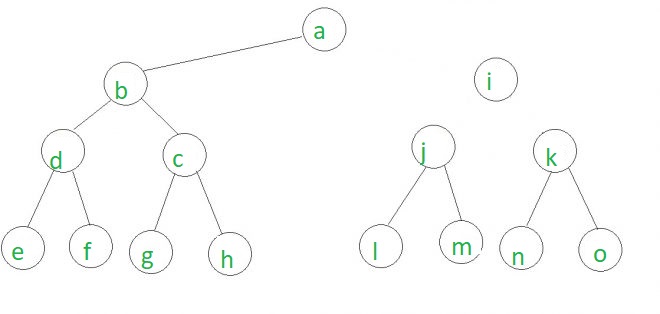
一种简单的方法是查找给定所有可能的节点对的LCA。
让,
- (a,b)的lca = x
- (b,c)= y的lca
- (c,a)的lca = z
在任何情况下,(x,y),(y,z),(z,x)或(x,y,z)中的任何一个都将始终相同。在前三种情况下,返回不相同的节点。在最后一种情况下,返回x,y或z的任何节点都将给出答案。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program for disconnecting a
// node to result in three different tree
#include
using namespace std;
// node class
struct Node {
int key;
struct Node *left, *right;
};
Node* newNode(int key)
{
Node* temp = new Node;
temp->key = key;
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
return (temp);
}
// LCA function taken from the above link mentioned
// This function returns a pointer to LCA of two given
// values n1 and n2. This function assumes that n1 and n2
// are present in Binary Tree
struct Node* findLCA(struct Node* root, int n1, int n2)
{
// Base case
if (root == NULL)
return NULL;
// If either n1 or n2 matches with root's key, report
// the presence by returning root (Note that if a key is
// ancestor of other, then the ancestor key becomes LCA
if (root->key == n1 || root->key == n2)
return root;
// Look for keys in left and right subtrees
Node* left_lca = findLCA(root->left, n1, n2);
Node* right_lca = findLCA(root->right, n1, n2);
// If both of the above calls return Non-NULL, then one key
// is present in once subtree and other is present in other,
// So this node is the LCA
if (left_lca && right_lca)
return root;
// Otherwise check if left subtree or right subtree is LCA
return (left_lca != NULL) ? left_lca : right_lca;
}
// the function assumes a, b, c are present in the tree
// and returns a node disconnecting which
// results in all three nodes in different trees
Node* findNode(Node* root, int a, int b, int c)
{
// lca of a, b
Node* x = findLCA(root, a, b);
// lca of b, c
Node* y = findLCA(root, b, c);
// lca of c, a
Node* z = findLCA(root, c, a);
if (x->key == y->key)
return z;
else if (x->key == z->key)
return y;
else
return x;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Declare tree
// Insert elements in the tree
Node* root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right = newNode(5);
root->left->left->left = newNode(8);
root->left->left->right = newNode(9);
root->left->right->left = newNode(10);
root->left->right->right = newNode(11);
root->right->left = newNode(6);
root->right->right = newNode(7);
root->right->left->left = newNode(12);
root->right->left->right = newNode(13);
root->right->right->left = newNode(14);
root->right->right->right = newNode(15);
/*
1
/ \
2 3
/ \ / \
4 5 6 7
/\ / \ / \ / \
8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
*/
// update all the suitable_children
// keys of all the nodes in O( N )
cout << "Disconnect node "
<< findNode(root, 5, 6, 15)->key
<< " from the tree";
return 0;
} Java
// Java program for disconnecting a
// node to result in three different tree
public class RemoveEdge {
// LCA function taken from the above link mentioned
// This function returns a pointer to LCA of two given
// values n1 and n2. This function assumes that n1 and n2
// are present in Binary Tree
static Node findLCA(Node root, int n1, int n2)
{
// Base case
if (root == null)
return root;
// If either n1 or n2 matches with root's key, report
// the presence by returning root (Note that if a key is
// ancestor of other, then the ancestor key becomes LCA
if (root.key == n1 || root.key == n2)
return root;
// Look for keys in left and right subtrees
Node left_lca = findLCA(root.left, n1, n2);
Node right_lca = findLCA(root.right, n1, n2);
// If both of the above calls return Non-NULL, then one key
// is present in once subtree and other is present in other,
// So this node is the LCA
if (left_lca!=null && right_lca!=null)
return root;
// Otherwise check if left subtree or right subtree is LCA
return (left_lca != null) ? left_lca : right_lca;
}
// the function assumes a, b, c are present in the tree
// and returns a node disconnecting which
// results in all three nodes in different trees
static Node findNode(Node root, int a, int b, int c)
{
// lca of a, b
Node x = findLCA(root, a, b);
// lca of b, c
Node y = findLCA(root, b, c);
// lca of c, a
Node z = findLCA(root, c, a);
if (x.key == y.key)
return z;
else if (x.key == z.key)
return y;
else
return x;
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
Node root = new Node(1);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(3);
root.left.left = new Node(4);
root.left.right = new Node(5);
root.left.left.left = new Node(8);
root.left.left.right = new Node(9);
root.left.right.left = new Node(10);
root.left.right.right = new Node(11);
root.right.left = new Node(6);
root.right.right = new Node(7);
root.right.left.left = new Node(12);
root.right.left.right = new Node(13);
root.right.right.left = new Node(14);
root.right.right.right = new Node(15);
System.out.print("Disconnect node "+findNode(root, 5, 6, 15).key+" from the tree");
}
}
// Node class
class Node {
int key;
Node left, right;
Node (int data)
{
this.key=data;
}
};
//This code is contributed by Gaurav TiwariC#
// C# program for disconnecting a
// node to result in three different tree
using System;
public class RemoveEdge
{
// LCA function taken from the
// above link mentioned This function
// returns a pointer to LCA of two given
// values n1 and n2. This function
// assumes that n1 and n2
// are present in Binary Tree
static Node findLCA(Node root, int n1, int n2)
{
// Base case
if (root == null)
return root;
// If either n1 or n2 matches
// with root's key, report
// the presence by returning
// root (Note that if a key is
// ancestor of other, then the
// ancestor key becomes LCA
if (root.key == n1 || root.key == n2)
return root;
// Look for keys in left and right subtrees
Node left_lca = findLCA(root.left, n1, n2);
Node right_lca = findLCA(root.right, n1, n2);
// If both of the above calls
// return Non-NULL, then one key
// is present in once subtree and
// other is present in other,
// So this node is the LCA
if (left_lca!=null && right_lca!=null)
return root;
// Otherwise check if left
// subtree or right subtree is LCA
return (left_lca != null) ? left_lca : right_lca;
}
// the function assumes a, b, c
// are present in the tree and returns
// a node disconnecting which results
// in all three nodes in different trees
static Node findNode(Node root, int a, int b, int c)
{
// lca of a, b
Node x = findLCA(root, a, b);
// lca of b, c
Node y = findLCA(root, b, c);
// lca of c, a
Node z = findLCA(root, c, a);
if (x.key == y.key)
return z;
else if (x.key == z.key)
return y;
else
return x;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String []args)
{
Node root = new Node(1);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(3);
root.left.left = new Node(4);
root.left.right = new Node(5);
root.left.left.left = new Node(8);
root.left.left.right = new Node(9);
root.left.right.left = new Node(10);
root.left.right.right = new Node(11);
root.right.left = new Node(6);
root.right.right = new Node(7);
root.right.left.left = new Node(12);
root.right.left.right = new Node(13);
root.right.right.left = new Node(14);
root.right.right.right = new Node(15);
Console.Write("Disconnect node "+
findNode(root, 5, 6, 15).key+
" from the tree");
}
}
// Node class
public class Node
{
public int key;
public Node left, right;
public Node (int data)
{
this.key=data;
}
};
// This code contributed by Rajput-Ji输出:
Disconnect node 3 from the tree