让我们考虑以下问题以了解二叉索引树。
我们有一个数组arr [0。 。 。 n-1]。我们想要
1计算前i个元素的总和。
2修改数组arr [i] = x的指定元素的值,其中0 <= i <= n-1。
一个简单的解决方案是运行一个从0到i-1的循环并计算元素的总和。要更新值,只需做arr [i] = x。第一次操作花费O(n)时间,第二次操作花费O(1)时间。另一个简单的解决方案是创建一个额外的数组,并将第i个元素的总和存储在此新数组中的第i个索引处。现在可以以O(1)的时间计算给定范围的总和,但是更新操作现在需要O(n)的时间。如果查询操作数量很多,但更新操作数量很少,则此方法效果很好。
我们可以在O(log n)时间内执行查询和更新操作吗?
一种有效的解决方案是使用在O(Logn)时间执行两项操作的细分树。
另一种解决方案是二进制索引树,它也为两个操作都实现了O(Logn)时间复杂度。与分段树相比,二进制索引树需要更少的空间,并且更易于实现。 。
表示
二进制索引树表示为数组。令数组为BITree []。二叉索引树的每个节点都存储输入数组中某些元素的总和。二进制索引树的大小等于输入数组的大小,表示为n。在下面的代码中,为了便于实现,我们使用n + 1的大小。
建造
我们将BITree []中的所有值初始化为0。然后我们为所有索引调用update(),下面将讨论update()操作。
运作方式
getSum(x): Returns the sum of the sub-array arr[0,…,x]
// Returns the sum of the sub-array arr[0,…,x] using BITree[0..n], which is constructed from arr[0..n-1]
1) Initialize the output sum as 0, the current index as x+1.
2) Do following while the current index is greater than 0.
…a) Add BITree[index] to sum
…b) Go to the parent of BITree[index]. The parent can be obtained by removing
the last set bit from the current index, i.e., index = index – (index & (-index))
3) Return sum.
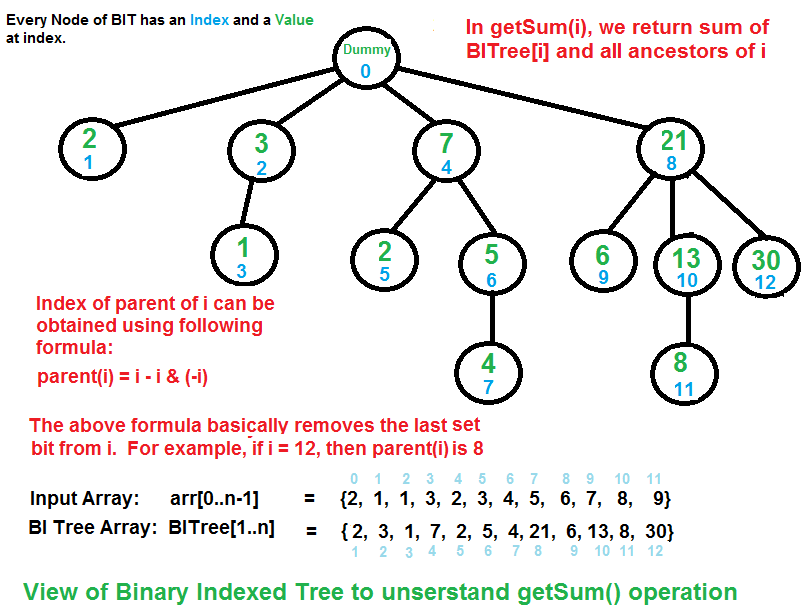
上图提供了有关getSum()如何工作的示例。这是一些重要的观察。
BITree [0]是一个虚拟节点。
BITree [y]是BITree [x]的父级,当且仅当y可以通过从x的二进制表示形式中删除最后一个设置位来获得y时,即y = x –(x&(-x))。
节点BITree [y]的子节点BITree [x]存储y(包括)和x(不包括)之间的元素之和:arr [y,…,x)。
update(x, val): Updates the Binary Indexed Tree (BIT) by performing arr[index] += val
// Note that the update(x, val) operation will not change arr[]. It only makes changes to BITree[]
1) Initialize the current index as x+1.
2) Do the following while the current index is smaller than or equal to n.
…a) Add the val to BITree[index]
…b) Go to parent of BITree[index]. The parent can be obtained by incrementing the last set bit of the current index, i.e., index = index + (index & (-index))
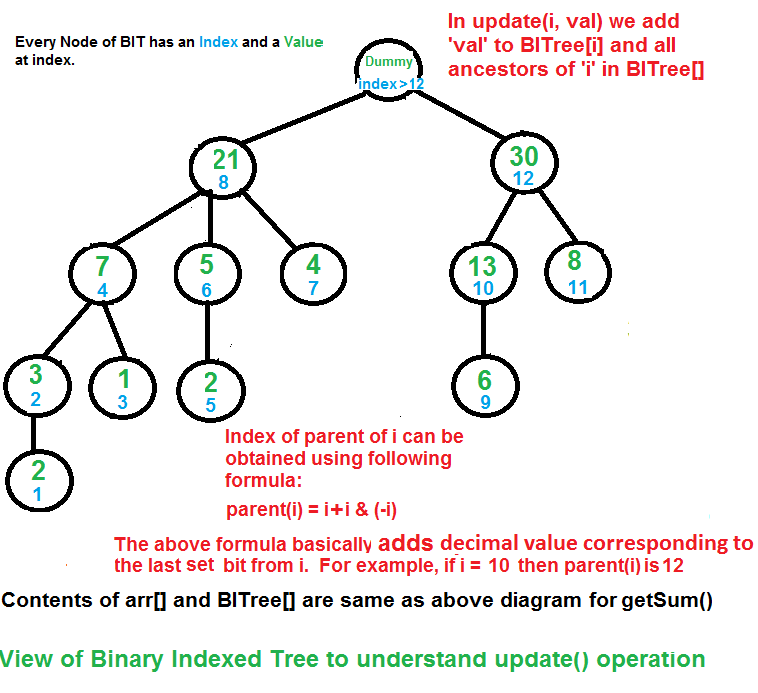
更新函数需要确保所有在其范围内包含arr [i]的BITree节点都被更新。通过重复添加与当前索引的最后一个设置位相对应的十进制数,我们遍历BITree中的此类节点。
二叉索引树如何工作?
该思想基于以下事实:所有正整数都可以表示为2的幂的和。例如19可以表示为16 + 2 +1。BITree的每个节点都存储n个元素的总和,其中n是a 2的幂。例如,在上面的第一个图表(getSum()的图表)中,前12个元素的总和可以通过后4个元素的总和(从9到12)加上8的总和来获得元素(从1到8)。数字n的二进制表示形式中的置位位数为O(Logn)。因此,我们遍历getSum()和update()操作中的最多O(Logn)节点。构造的时间复杂度为O(nLogn),因为它对所有n个元素都调用update()。
执行:
以下是二进制索引树的实现。
C++
// C++ code to demonstrate operations of Binary Index Tree
#include
using namespace std;
/* n --> No. of elements present in input array.
BITree[0..n] --> Array that represents Binary Indexed Tree.
arr[0..n-1] --> Input array for which prefix sum is evaluated. */
// Returns sum of arr[0..index]. This function assumes
// that the array is preprocessed and partial sums of
// array elements are stored in BITree[].
int getSum(int BITree[], int index)
{
int sum = 0; // Iniialize result
// index in BITree[] is 1 more than the index in arr[]
index = index + 1;
// Traverse ancestors of BITree[index]
while (index>0)
{
// Add current element of BITree to sum
sum += BITree[index];
// Move index to parent node in getSum View
index -= index & (-index);
}
return sum;
}
// Updates a node in Binary Index Tree (BITree) at given index
// in BITree. The given value 'val' is added to BITree[i] and
// all of its ancestors in tree.
void updateBIT(int BITree[], int n, int index, int val)
{
// index in BITree[] is 1 more than the index in arr[]
index = index + 1;
// Traverse all ancestors and add 'val'
while (index <= n)
{
// Add 'val' to current node of BI Tree
BITree[index] += val;
// Update index to that of parent in update View
index += index & (-index);
}
}
// Constructs and returns a Binary Indexed Tree for given
// array of size n.
int *constructBITree(int arr[], int n)
{
// Create and initialize BITree[] as 0
int *BITree = new int[n+1];
for (int i=1; i<=n; i++)
BITree[i] = 0;
// Store the actual values in BITree[] using update()
for (int i=0; i Java
// Java program to demonstrate lazy
// propagation in segment tree
import java.util.*;
import java.lang.*;
import java.io.*;
class BinaryIndexedTree
{
// Max tree size
final static int MAX = 1000;
static int BITree[] = new int[MAX];
/* n --> No. of elements present in input array.
BITree[0..n] --> Array that represents Binary
Indexed Tree.
arr[0..n-1] --> Input array for which prefix sum
is evaluated. */
// Returns sum of arr[0..index]. This function
// assumes that the array is preprocessed and
// partial sums of array elements are stored
// in BITree[].
int getSum(int index)
{
int sum = 0; // Iniialize result
// index in BITree[] is 1 more than
// the index in arr[]
index = index + 1;
// Traverse ancestors of BITree[index]
while(index>0)
{
// Add current element of BITree
// to sum
sum += BITree[index];
// Move index to parent node in
// getSum View
index -= index & (-index);
}
return sum;
}
// Updates a node in Binary Index Tree (BITree)
// at given index in BITree. The given value
// 'val' is added to BITree[i] and all of
// its ancestors in tree.
public static void updateBIT(int n, int index,
int val)
{
// index in BITree[] is 1 more than
// the index in arr[]
index = index + 1;
// Traverse all ancestors and add 'val'
while(index <= n)
{
// Add 'val' to current node of BIT Tree
BITree[index] += val;
// Update index to that of parent
// in update View
index += index & (-index);
}
}
/* Function to construct fenwick tree
from given array.*/
void constructBITree(int arr[], int n)
{
// Initialize BITree[] as 0
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++)
BITree[i] = 0;
// Store the actual values in BITree[]
// using update()
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
updateBIT(n, i, arr[i]);
}
// Main function
public static void main(String args[])
{
int freq[] = {2, 1, 1, 3, 2, 3,
4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9};
int n = freq.length;
BinaryIndexedTree tree = new BinaryIndexedTree();
// Build fenwick tree from given array
tree.constructBITree(freq, n);
System.out.println("Sum of elements in arr[0..5]"+
" is "+ tree.getSum(5));
// Let use test the update operation
freq[3] += 6;
// Update BIT for above change in arr[]
updateBIT(n, 3, 6);
// Find sum after the value is updated
System.out.println("Sum of elements in arr[0..5]"+
" after update is " + tree.getSum(5));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Ranjan BinwaniPython
# Python implementation of Binary Indexed Tree
# Returns sum of arr[0..index]. This function assumes
# that the array is preprocessed and partial sums of
# array elements are stored in BITree[].
def getsum(BITTree,i):
s = 0 #initialize result
# index in BITree[] is 1 more than the index in arr[]
i = i+1
# Traverse ancestors of BITree[index]
while i > 0:
# Add current element of BITree to sum
s += BITTree[i]
# Move index to parent node in getSum View
i -= i & (-i)
return s
# Updates a node in Binary Index Tree (BITree) at given index
# in BITree. The given value 'val' is added to BITree[i] and
# all of its ancestors in tree.
def updatebit(BITTree , n , i ,v):
# index in BITree[] is 1 more than the index in arr[]
i += 1
# Traverse all ancestors and add 'val'
while i <= n:
# Add 'val' to current node of BI Tree
BITTree[i] += v
# Update index to that of parent in update View
i += i & (-i)
# Constructs and returns a Binary Indexed Tree for given
# array of size n.
def construct(arr, n):
# Create and initialize BITree[] as 0
BITTree = [0]*(n+1)
# Store the actual values in BITree[] using update()
for i in range(n):
updatebit(BITTree, n, i, arr[i])
# Uncomment below lines to see contents of BITree[]
#for i in range(1,n+1):
# print BITTree[i],
return BITTree
# Driver code to test above methods
freq = [2, 1, 1, 3, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
BITTree = construct(freq,len(freq))
print("Sum of elements in arr[0..5] is " + str(getsum(BITTree,5)))
freq[3] += 6
updatebit(BITTree, len(freq), 3, 6)
print("Sum of elements in arr[0..5]"+
" after update is " + str(getsum(BITTree,5)))
# This code is contributed by Raju VarshneyC#
// C# program to demonstrate lazy
// propagation in segment tree
using System;
public class BinaryIndexedTree
{
// Max tree size
readonly static int MAX = 1000;
static int []BITree = new int[MAX];
/* n --> No. of elements present in input array.
BITree[0..n] --> Array that represents Binary
Indexed Tree.
arr[0..n-1] --> Input array for which prefix sum
is evaluated. */
// Returns sum of arr[0..index]. This function
// assumes that the array is preprocessed and
// partial sums of array elements are stored
// in BITree[].
int getSum(int index)
{
int sum = 0; // Iniialize result
// index in BITree[] is 1 more than
// the index in arr[]
index = index + 1;
// Traverse ancestors of BITree[index]
while(index>0)
{
// Add current element of BITree
// to sum
sum += BITree[index];
// Move index to parent node in
// getSum View
index -= index & (-index);
}
return sum;
}
// Updates a node in Binary Index Tree (BITree)
// at given index in BITree. The given value
// 'val' is added to BITree[i] and all of
// its ancestors in tree.
public static void updateBIT(int n, int index,
int val)
{
// index in BITree[] is 1 more than
// the index in arr[]
index = index + 1;
// Traverse all ancestors and add 'val'
while(index <= n)
{
// Add 'val' to current node of BIT Tree
BITree[index] += val;
// Update index to that of parent
// in update View
index += index & (-index);
}
}
/* Function to construct fenwick tree
from given array.*/
void constructBITree(int []arr, int n)
{
// Initialize BITree[] as 0
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
BITree[i] = 0;
// Store the actual values in BITree[]
// using update()
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
updateBIT(n, i, arr[i]);
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String []args)
{
int []freq = {2, 1, 1, 3, 2, 3,
4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9};
int n = freq.Length;
BinaryIndexedTree tree = new BinaryIndexedTree();
// Build fenwick tree from given array
tree.constructBITree(freq, n);
Console.WriteLine("Sum of elements in arr[0..5]"+
" is "+ tree.getSum(5));
// Let use test the update operation
freq[3] += 6;
// Update BIT for above change in arr[]
updateBIT(n, 3, 6);
// Find sum after the value is updated
Console.WriteLine("Sum of elements in arr[0..5]"+
" after update is " + tree.getSum(5));
}
}
// This code is contributed by PrinciRaj1992输出:
Sum of elements in arr[0..5] is 12
Sum of elements in arr[0..5] after update is 18
我们可以扩展二叉索引树来计算O(Logn)时间范围内的总和吗?
是的。 rangeSum(l,r)= getSum(r)– getSum(l-1)。
应用范围:
算术编码算法的实现。二叉索引树的发展主要是由它在这种情况下的应用推动的。有关更多详细信息,请参见此内容。
问题示例:
计算数组中的反转|第3组(使用BIT)
二维二元索引树或Fenwick树
使用BIT计算矩形空间中的三角形
参考:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fenwick_tree
http://community.topcoder.com/tc?module=Static&d1=tutorials&d2=binaryIndexedTrees