给定具有除根节点0(从1到N的编号)之外的N个节点的二叉索引树,请找到其直径。
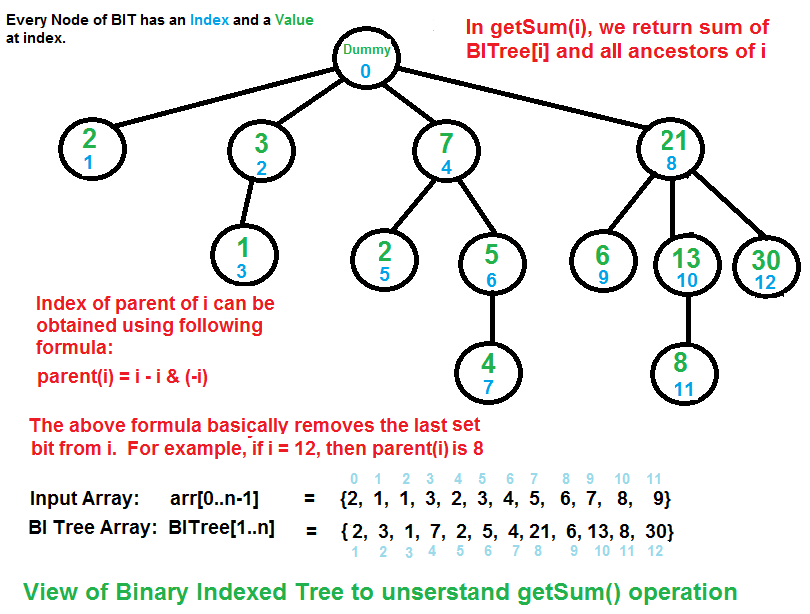
二进制索引树是其中节点编号X = X –(X&(X – 1))的父节点,即X中未设置最后一位的树。树的直径是任意两片叶子之间最长的简单路径。
例子:
Input: N = 12
Output: 6
Explanation: Path from node 7 to node 11.
Input : n = 15
Output : 7
方法:
- 在BIT中,根始终是节点0。在第一级,所有节点的幂都是2。 (1、2、4、8,…。)
- 考虑第一级(1、2、4、8)中的任何节点,其子树将包括具有与根相同位数的所有节点。
- 根为1的子树将没有子树。
- 根为2的子树将有3个子树。
- 根为4的子树将有5、6、7作为子级。
- 根为8的子树将有9、10、11、12、13、14、15作为孩子。 (是前一个子树的大小的两倍)
- 因此,具有根K的子树将具有包括根在内的K个节点。并且每个子树的高度将相等:
- 用于根为1的子树
- 用于根为2的子树
- 用于根为4的子树
- 现在,我们需要找到N所在的子树。假设N所在的子树之前的子树的高度为H,大小为L。因此,以下情况是可能的:
- 情况1:当N> = L * 2-1 – 1时,在这种情况下,N位于其子树的最后一级。因此,直径将为2 * H +1。(从先前子树的最低层叶子到N的路径)。
- 情况2:当N> = L + L / 2 – 1时,在这种情况下,N在其子树中处于级别H。因此,直径将为2 * H。
- 情况3:否则,最好考虑两个子树的叶子节点之间的最大路径长度,恰好在N所在的子树之前,即直径为2 * H – 1。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
#include
using namespace std;
// Function to find diameter
// of BIT with N + 1 nodes
int diameter(int n)
{
// L is size of subtree just before subtree
// in which N lies
int L, H, templen;
L = 1;
// H is the height of subtree just before
// subtree in which N lies
H = 0;
// Base Cases
if (n == 1) {
return 1;
}
if (n == 2) {
return 2;
}
if (n == 3) {
return 3;
}
// Size of subtree are power of 2
while (L * 2 <= n) {
L *= 2;
H++;
}
// 3 Cases as explained in Approach
if (n >= L * 2 - 1)
return 2 * H + 1;
else if (n >= L + (L / 2) - 1)
return 2 * H;
return 2 * H - 1;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int n = 15;
cout << diameter(n) << endl;
} Java
// Java implementation of the approach
class GFG
{
// Function to find diameter
// of BIT with N + 1 nodes
static int diameter(int n)
{
// L is size of subtree just before subtree
// in which N lies
int L, H, templen;
L = 1;
// H is the height of subtree just before
// subtree in which N lies
H = 0;
// Base Cases
if (n == 1) {
return 1;
}
if (n == 2) {
return 2;
}
if (n == 3) {
return 3;
}
// Size of subtree are power of 2
while (L * 2 <= n) {
L *= 2;
H++;
}
// 3 Cases as explained in Approach
if (n >= L * 2 - 1)
return 2 * H + 1;
else if (n >= L + (L / 2) - 1)
return 2 * H;
return 2 * H - 1;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String []args)
{
int n = 15;
System.out.println(diameter(n));
}
}
// This code contributed by PrinciRaj1992Python3
# Python3 implementation of the approach
# Function to find diameter
# of BIT with N + 1 nodes
def diameter(n):
# L is size of subtree just before
# subtree in which N lies
L, H, templen = 0, 0, 0;
L = 1;
# H is the height of subtree just before
# subtree in which N lies
H = 0;
# Base Cases
if (n == 1):
return 1;
if (n == 2):
return 2;
if (n == 3):
return 3;
# Size of subtree are power of 2
while (L * 2 <= n):
L *= 2;
H += 1;
# 3 Cases as explained in Approach
if (n >= L * 2 - 1):
return 2 * H + 1;
elif (n >= L + (L / 2) - 1):
return 2 * H;
return 2 * H - 1;
# Driver Code
n = 15;
print(diameter(n));
# This code is contributed by Rajput-JiC#
// C# implementation of the approach
using System;
class GFG
{
// Function to find diameter
// of BIT with N + 1 nodes
static int diameter(int n)
{
// L is size of subtree just before subtree
// in which N lies
int L, H;
L = 1;
// H is the height of subtree just before
// subtree in which N lies
H = 0;
// Base Cases
if (n == 1)
{
return 1;
}
if (n == 2)
{
return 2;
}
if (n == 3)
{
return 3;
}
// Size of subtree are power of 2
while (L * 2 <= n)
{
L *= 2;
H++;
}
// 3 Cases as explained in Approach
if (n >= L * 2 - 1)
return 2 * H + 1;
else if (n >= L + (L / 2) - 1)
return 2 * H;
return 2 * H - 1;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String []args)
{
int n = 15;
Console.WriteLine(diameter(n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar输出:
7